Abstract
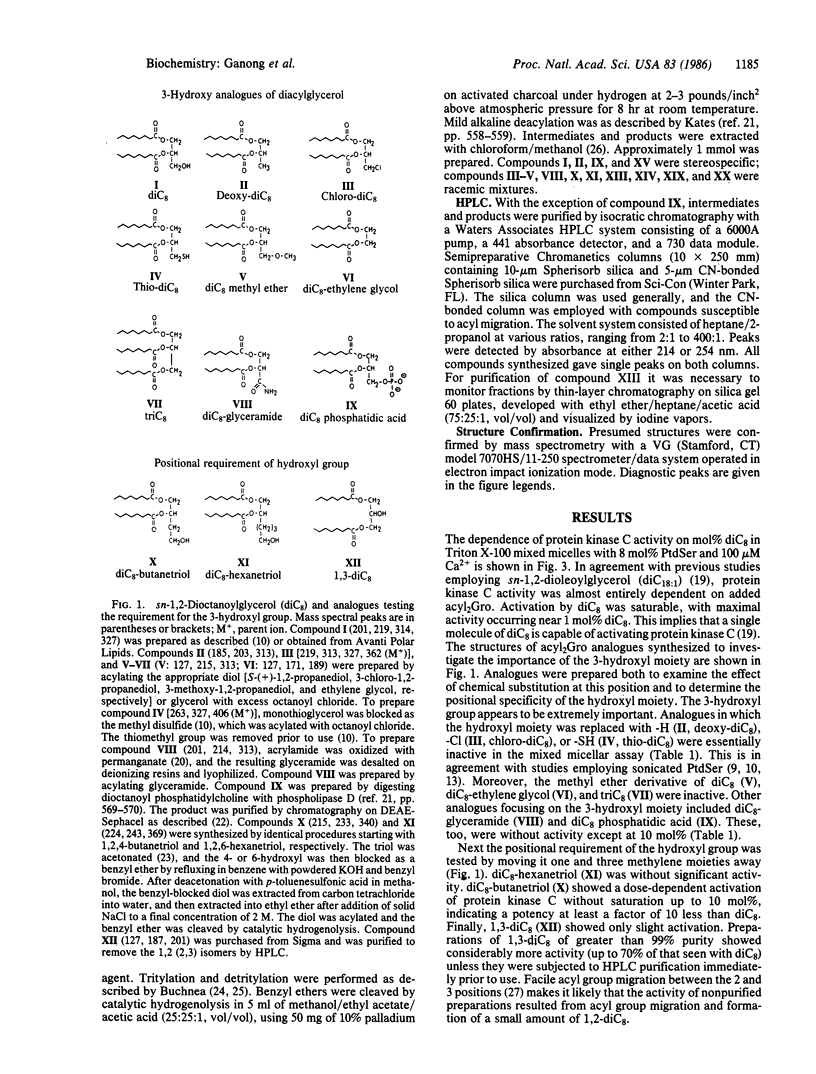
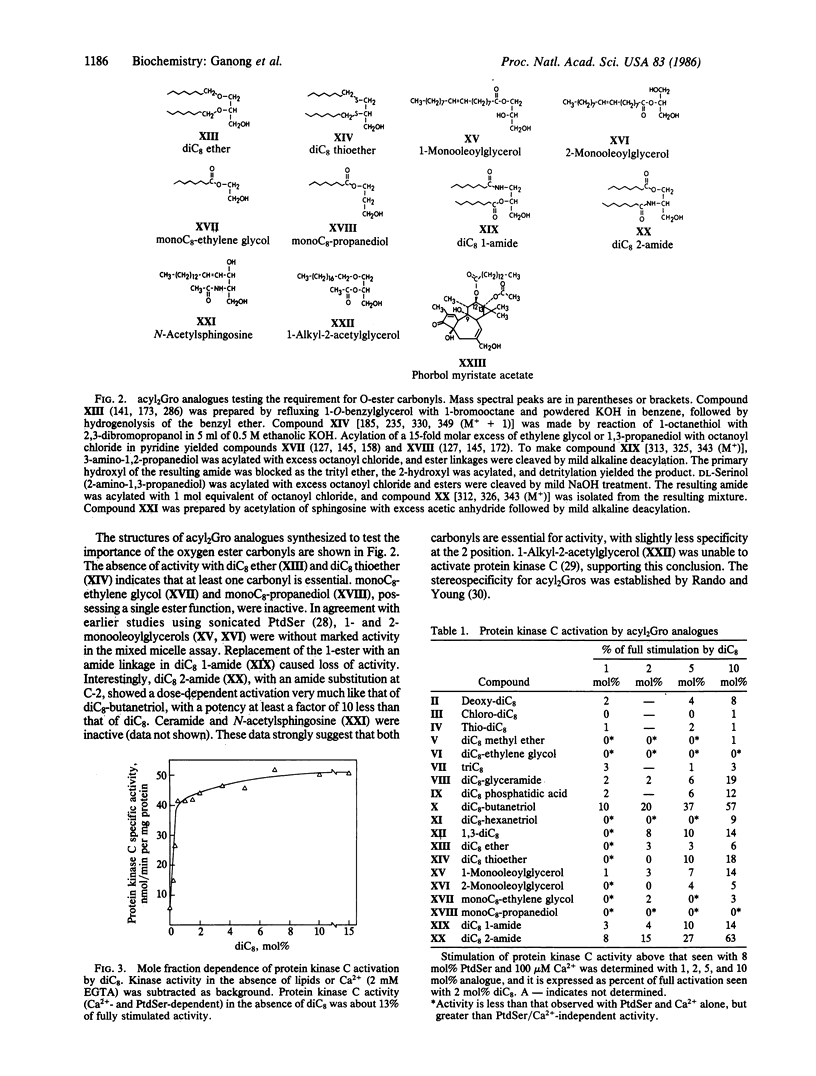
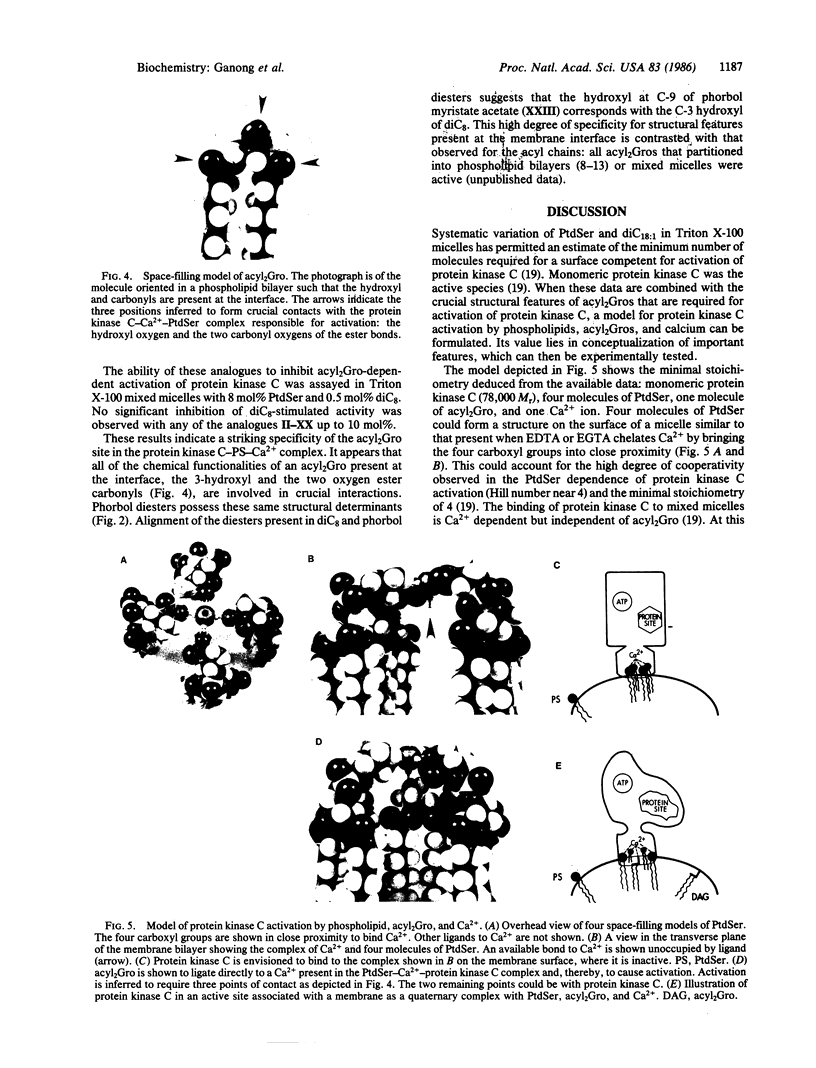
The specificity of protein kinase C activation by sn-1,2-diacylglycerols and analogues was investigated by using a Triton X-100 mixed micellar assay [Hannun, Y. A., Loomis, C. R. & Bell, R. M. (1985) J. Biol. Chem. 260, 10039-10043]. Analogues containing acyl or alkyl chains eight carbons in length were synthesized because sn-1,2-dioctanoylglycerol is an effective cell-permeant activator of protein kinase C. These analogues were tested as activators and antagonists of rat brain protein kinase C to determine the exact structural features important for activity. The analogues established that activation of protein kinase C by diacylglycerols is highly specific. Several analogues established that both carbonyl moieties of the oxygen esters are required for maximal activity and that the 3-hydroxyl moiety is also required. None of the analogues were antagonists. These data, combined with previous investigations, permitted formulation of a model of protein kinase C activation. A three-point attachment of sn-1,2-diacylglycerol to the surface-bound protein kinase C-phosphatidylserine-Ca2+ complex is envisioned to cause activation. Direct ligation of diacylglycerol to Ca2+ is proposed to be an essential step in the mechanism of activation of protein kinase C.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabot M. C., Jaken S. Structural and chemical specificity of diacylglycerols for protein kinase C activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 30;125(1):163–169. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn P. M., Ganong B. R., Ebeling J., Staley D., Neidel J. E., Bell R. M. Diacylglycerols release LH: structure-activity relations reveal a role for protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Jan 16;126(1):532–539. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90638-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M., Czech M. P. Structural requirements for diacylglycerols to mimic tumor-promoting phobol diester action on the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5315–5322. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis R. J., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M., Czech M. P. sn-1,2-Dioctanoylglycerol. A cell-permeable diacylglycerol that mimics phorbol diester action on the epidermal growth factor receptor and mitogenesis. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1562–1566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Delclos K. B., Yeh E., Blumberg P. M. Specific labeling of mouse brain membrane phospholipids with [20-3H]phorbol 12-p-azidobenzoate 13-benzoate, a photolabile phorbol ester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3054–3058. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3054. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling J. G., Vandenbark G. R., Kuhn L. J., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M., Niedel J. E. Diacylglycerols mimic phorbol diester induction of leukemic cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):815–819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ganong B. R., Bell R. M. Transmembrane movement of phosphatidylglycerol and diacylglycerol sulfhydryl analogues. Biochemistry. 1984 Oct 9;23(21):4977–4983. doi: 10.1021/bi00316a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hannun Y. A., Loomis C. R., Bell R. M. Activation of protein kinase C by Triton X-100 mixed micelles containing diacylglycerol and phosphatidylserine. J Biol Chem. 1985 Aug 25;260(18):10039–10043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Ganong B. R., Vandenbark G. R., Shirley J. E., Bell R. M. Role of protein kinase C in diacylglycerol-mediated induction of ornithine decarboxylase and reduction of epidermal growth factor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1941–1945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Takai Y., Sawamura M., Hoshijima M., Fujikura T., Nishizuka Y. Synergistic functions of protein phosphorylation and calcium mobilization in platelet activation. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jun 10;258(11):6701–6704. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Minakuchi R., Inohara S., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase from rat brain. Subcellular distribution, purification, and properties. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 25;257(22):13341–13348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Tanaka Y., Miyake R., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C as a possible receptor protein of tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11442–11445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Kajikawa N., Shiota M., Nishizuka Y. Proteolytic activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by calcium-dependent neutral protease. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 25;258(2):1156–1164. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kishimoto A., Takai Y., Mori T., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Activation of calcium and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by diacylglycerol, its possible relation to phosphatidylinositol turnover. J Biol Chem. 1980 Mar 25;255(6):2273–2276. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kretsinger R. H. Calcium-binding proteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:239–266. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001323. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Reep B., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M. Exogenous sn-1,2-diacylglycerols containing saturated fatty acids function as bioregulators of protein kinase C in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1358–1361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori T., Takai Y., Yu B., Takahashi J., Nishizuka Y., Fujikura T. Specificity of the fatty acyl moieties of diacylglycerol for the activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biochem. 1982 Feb;91(2):427–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Calcium, phospholipid turnover and transmembrane signalling. Philos Trans R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1983 Jul 5;302(1108):101–112. doi: 10.1098/rstb.1983.0043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rand R. P., Kachar B., Reese T. S. Dynamic morphology of calcium-induced interactions between phosphatidylserine vesicles. Biophys J. 1985 Apr;47(4):483–489. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(85)83941-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rando R. R., Young N. The stereospecific activation of protein kinase C. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):818–823. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80107-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sano K., Takai Y., Yamanishi J., Nishizuka Y. A role of calcium-activated phospholipid-dependent protein kinase in human platelet activation. Comparison of thrombin and collagen actions. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 10;258(3):2010–2013. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Iwasa Y., Kawahara Y., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Calcium-dependent activation of a multifunctional protein kinase by membrane phospholipids. J Biol Chem. 1979 May 25;254(10):3692–3695. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]