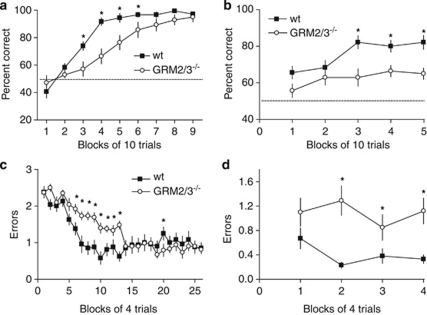
Figure 1.
GRM2/3−/− mice were impaired in appetitive SRM (left panels, a and c) and SWM tasks (right panels, b and d). (a) GRM2/3−/− mice (n=14) displayed slower acquisition of a Y-maze SRM task than wild-type (wt; n=18) mice and (b) GRM2/3−/− mice (n=14) were persistently impaired in an appetitive T-maze rewarded alternation SWM task compared with wild-types (wt; n=18). Data shown are percent correct responses (mean±SEM) for each block of 10 trials. Chance performance is indicated by the dashed line. (c) GRM2/3−/− mice (n=13) displayed slower acquisition of the SRM component of an appetitive six-arm radial maze task than wt (n=13) and (d) GRM2/3−/− mice subsequently made significantly more SWM errors than wt. Data shown are mean errors (±SEM) per trial in each block of four trials. Asterisks indicate statistical significance at p<0.05.