Abstract
Parathymosin has been isolated from rat thymus and from rat liver. Its primary structure is reported as follows: (Sequence; see text). The blocking group at the NH2 terminus was identified by mass spectrometry as acetyl. Regions homologous to amino acid sequences in prothymosin alpha were found to be located between residues 14-20, 23-25, 33-39, 41-43, and 83-87 of parathymosin.
Full text
PDF
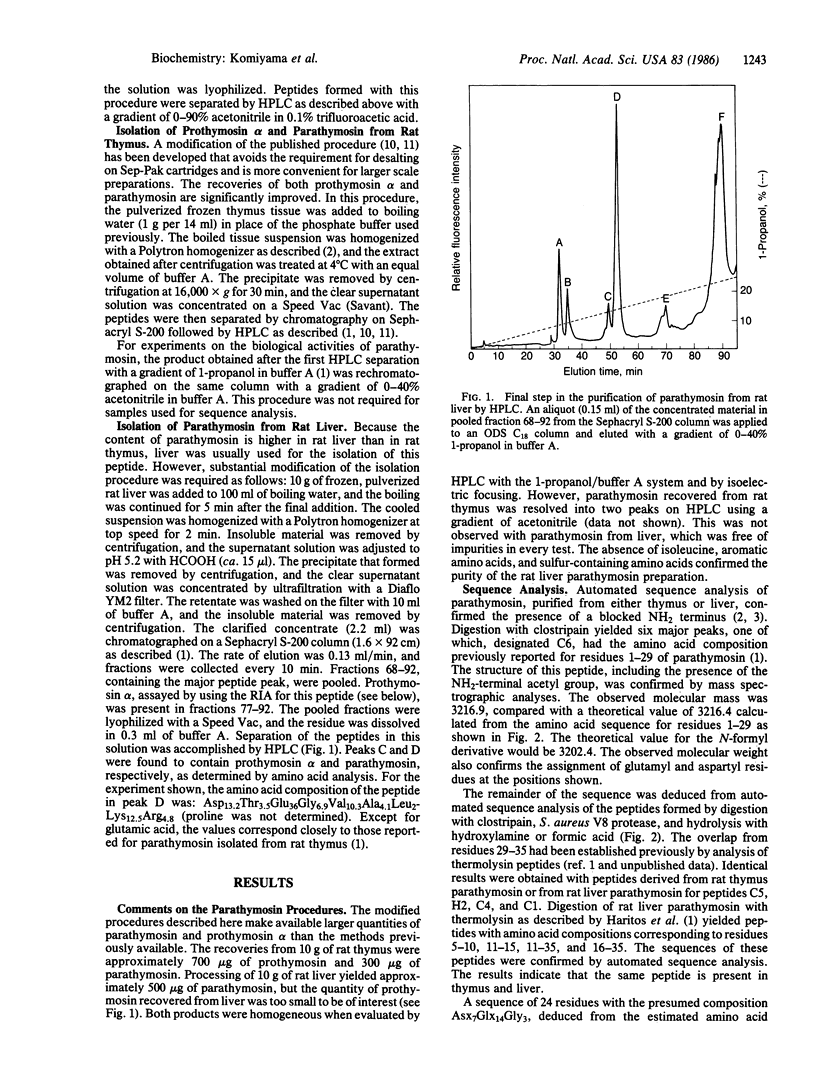


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bornstein P., Balian G. Cleavage at Asn-Gly bonds with hydroxylamine. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:132–145. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47016-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haritos A. A., Blacher R., Stein S., Caldarella J., Horecker B. L. Primary structure of rat thymus prothymosin alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):343–346. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haritos A. A., Caldarella J., Horecker B. L. Simultaneous isolation and determination of prothymosin alpha, parathymosin alpha, thymosin beta 4, and thymosin beta 10. Anal Biochem. 1985 Feb 1;144(2):436–440. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(85)90138-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haritos A. A., Goodall G. J., Horecker B. L. Prothymosin alpha and alpha 1-like peptides. Methods Enzymol. 1985;116:255–265. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)16019-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haritos A. A., Goodall G. J., Horecker B. L. Prothymosin alpha: isolation and properties of the major immunoreactive form of thymosin alpha 1 in rat thymus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1008–1011. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1008. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haritos A. A., Horecker B. L. A radioimmunoassay for thymosin alpha 1 that detects the native polypeptide, prothymosin alpha. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Aug 2;81(2):199–205. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90204-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haritos A. A., Salvin S. B., Blacher R., Stein S., Horecker B. L. Parathymosin alpha: a peptide from rat tissues with structural homology to prothymosin alpha. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1050–1053. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishitsuka H., Umeda Y., Nakamura J., Yagi Y. Protective activity of thymosin against opportunistic infections in animal models. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 1983;14(3):145–150. doi: 10.1007/BF00205352. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lai C. Y. Detection of peptides by fluorescence methods. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:236–243. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47028-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landon Cleavage at aspartyl-prolyl bonds. Methods Enzymol. 1977;47:145–149. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(77)47017-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


