Abstract
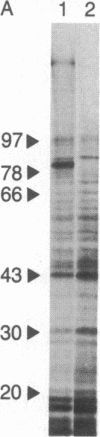
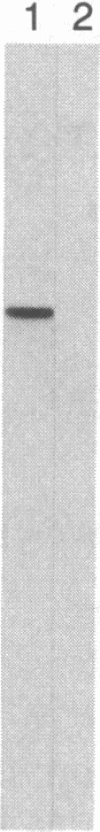
p97 is a cell-surface glycoprotein that is present in most human melanomas but only in trace amounts in normal adult tissues. To determine the structure of this tumor-associated antigen and to identify its functional domains, we have purified and cloned p97 mRNA and determined its nucleotide sequence. The mRNA encodes a 738-residue precursor, which contains the previously determined N-terminal amino acid sequence of p97. After removal of a 19-residue signal peptide, the mature p97 molecule comprises extracellular domains of 342 and 352 residues and a C-terminal 25-residue stretch of predominantly uncharged and hydrophobic amino acids, which we believe acts as a membrane anchor. Each extracellular domain contains 14 cysteine residues, which form seven intradomain disulfide bridges, and one or two potential N-glycosylation sites. Protease digestion studies show that the three major antigenic determinants of p97 are present on the N-terminal domain. The domains are strikingly homologous to each other (46% amino acid sequence homology) and to the corresponding domains of human serum transferrin (39% homology). Conservation of disulfide bridges and of amino acids thought to compose the iron binding pockets suggests that p97 is also related to transferrin in tertiary structure and function. We propose that p97 be renamed melanotransferrin to denote its original identification in melanoma cells and its evolutionary relationship to serotransferrin and lactotransferrin, the other members of the transferrin superfamily.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Benoist C., O'Hare K., Breathnach R., Chambon P. The ovalbumin gene-sequence of putative control regions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Jan 11;8(1):127–142. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. P., Hewick R. M., Hellström I., Hellström K. E., Doolittle R. F., Dreyer W. J. Human melanoma-associated antigen p97 is structurally and functionally related to transferrin. Nature. 1982 Mar 11;296(5853):171–173. doi: 10.1038/296171a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. P., Nishiyama K., Hellström I., Hellström K. E. Structural characterization of human melanoma-associated antigen p97 with monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1981 Aug;127(2):539–546. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. P., Woodbury R. G., Hart C. E., Hellström I., Hellström K. E. Quantitative analysis of melanoma-associated antigen p97 in normal and neoplastic tissues. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jan;78(1):539–543. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.1.539. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brown J. P., Wright P. W., Hart C. E., Woodbury R. G., Hellström K. E., Hellström I. Protein antigens of normal and malignant human cells identified by immunoprecipitation with monoclonal antibodies. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jun 10;255(11):4980–4983. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carey T. E., Takahashi T., Resnick L. A., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Cell surface antigens of human malignant melanoma: mixed hemadsorption assays for humoral immunity to cultured autologous melanoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Sep;73(9):3278–3282. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.9.3278. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davis N. G., Boeke J. D., Model P. Fine structure of a membrane anchor domain. J Mol Biol. 1985 Jan 5;181(1):111–121. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(85)90329-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Schwartz R. M., Chen H. R., Hunt L. T., Barker W. C., Orcutt B. C. Data bank. Nature. 1981 Mar 5;290(5801):8–8. doi: 10.1038/290008a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dente L., Cesareni G., Cortese R. pEMBL: a new family of single stranded plasmids. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Mar 25;11(6):1645–1655. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.6.1645. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dippold W. G., Lloyd K. O., Li L. T., Ikeda H., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Cell surface antigens of human malignant melanoma: definition of six antigenic systems with mouse monoclonal antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Oct;77(10):6114–6118. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.10.6114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrigues H. J., Tilgen W., Hellstróm I., Franke W., Hellström K. E. Detection of a human melanoma-associated antigen, p97, in histological sections of primary human melanomas. Int J Cancer. 1982 May 15;29(5):511–515. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910290505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman M., Moore G. W., Matsuda G. Darwinian evolution in the genealogy of haemoglobin. Nature. 1975 Feb 20;253(5493):603–608. doi: 10.1038/253603a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorinsky B., Horsburgh C., Lindley P. F., Moss D. S., Parkar M., Watson J. L. Evidence for the bilobal nature of diferric rabbit plasma transferrin. Nature. 1979 Sep 13;281(5727):157–158. doi: 10.1038/281157a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosveld F. G., Dahl H. H., de Boer E., Flavell R. A. Isolation of beta-globin-related genes from a human cosmid library. Gene. 1981 Apr;13(3):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90028-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henikoff S. Unidirectional digestion with exonuclease III creates targeted breakpoints for DNA sequencing. Gene. 1984 Jun;28(3):351–359. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(84)90153-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hong G. F. A systemic DNA sequencing strategy. J Mol Biol. 1982 Jul 5;158(3):539–549. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(82)90213-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jeltsch J. M., Chambon P. The complete nucleotide sequence of the chicken ovotransferrin mRNA. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Feb;122(2):291–295. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05879.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Khosravi M. J., Dent P. B., Liao S. K. Structural characterization and biosynthesis of gp87, a melanoma-associated oncofetal antigen defined by monoclonal antibody 140.240. Int J Cancer. 1985 Jan 15;35(1):73–80. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350112. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Korman A. J., Knudsen P. J., Kaufman J. F., Strominger J. L. cDNA clones for the heavy chain of HLA-DR antigens obtained after immunopurification of polysomes by monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Mar;79(6):1844–1848. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.6.1844. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Larson S. M., Carrasquillo J. A., Krohn K. A., Brown J. P., McGuffin R. W., Ferens J. M., Graham M. M., Hill L. D., Beaumier P. L., Hellström K. E. Localization of 131I-labeled p97-specific Fab fragments in human melanoma as a basis for radiotherapy. J Clin Invest. 1983 Dec;72(6):2101–2114. doi: 10.1172/JCI111175. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGillivray R. T., Mendez E., Shewale J. G., Sinha S. K., Lineback-Zins J., Brew K. The primary structure of human serum transferrin. The structures of seven cyanogen bromide fragments and the assembly of the complete structure. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3543–3553. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacGillivray R. T., Mendez E., Sinha S. K., Sutton M. R., Lineback-Zins J., Brew K. The complete amino acid sequence of human serum transferrin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Apr;79(8):2504–2508. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.8.2504. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mazurier J., Metz-Boutigue M. H., Jollès J., Spik G., Montreuil J., Jollès P. Human lactotransferrin: molecular, functional and evolutionary comparisons with human serum transferrin and hen ovotransferrin. Experientia. 1983 Feb 15;39(2):135–141. doi: 10.1007/BF01958861. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metz-Boutigue M. H., Jollès J., Mazurier J., Schoentgen F., Legrand D., Spik G., Montreuil J., Jollès P. Human lactotransferrin: amino acid sequence and structural comparisons with other transferrins. Eur J Biochem. 1984 Dec 17;145(3):659–676. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1984.tb08607.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palmiter R. D. Magnesium precipitation of ribonucleoprotein complexes. Expedient techniques for the isolation of undergraded polysomes and messenger ribonucleic acid. Biochemistry. 1974 Aug 13;13(17):3606–3615. doi: 10.1021/bi00714a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelham H. R., Jackson R. J. An efficient mRNA-dependent translation system from reticulocyte lysates. Eur J Biochem. 1976 Aug 1;67(1):247–256. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10656.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plowman G. D., Brown J. P., Enns C. A., Schröder J., Nikinmaa B., Sussman H. H., Hellström K. E., Hellström I. Assignment of the gene for human melanoma-associated antigen p97 to chromosome 3. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):70–72. doi: 10.1038/303070a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schneider C., Owen M. J., Banville D., Williams J. G. Primary structure of human transferrin receptor deduced from the mRNA sequence. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):675–678. doi: 10.1038/311675b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taub F., Thompson E. B. An improved method for preparing large arrays of bacterial colonies containing plasmids for hybridization: in situ purification and stable binding of DNA on paper filters. Anal Biochem. 1982 Oct;126(1):222–230. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(82)90133-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Villa-Komaroff L., Efstratiadis A., Broome S., Lomedico P., Tizard R., Naber S. P., Chick W. L., Gilbert W. A bacterial clone synthesizing proinsulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Aug;75(8):3727–3731. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.8.3727. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J., Elleman T. C., Kingston I. B., Wilkins A. G., Kuhn K. A. The primary structure of hen ovotransferrin. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Feb;122(2):297–303. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb05880.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams J. The formation of iron-binding fragments of hen ovotransferrin by limited proteolysis. Biochem J. 1974 Sep;141(3):745–752. doi: 10.1042/bj1410745. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Brown J. P., Yeh M. Y., Hellström I., Hellström K. E. Identification of a cell surface protein, p97, in human melanomas and certain other neoplasms. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Apr;77(4):2183–2187. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.4.2183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang F., Lum J. B., McGill J. R., Moore C. M., Naylor S. L., van Bragt P. H., Baldwin W. D., Bowman B. H. Human transferrin: cDNA characterization and chromosomal localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(9):2752–2756. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.9.2752. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]