Abstract
Rapid mixing of ferrocytochrome c peroxidase [cyt c peroxidase(II)] and ferricytochrome c [cyt c(III)] results in the reduction of cyt c(III) by cyt c peroxidase(II). In 10 mM phosphate, pH 7.0, the rate of decay of cyt c peroxidase(II) and the rate of accumulation of cyt c(II) give equal first-order rate constants: k = 0.23 +/- 0.02 s-1. Equivalent results are obtained by pulse radiolysis using isopropanol radical as the reducing agent. This rate is independent of the initial cyt c(III):cyt c peroxidase(II) ratios. These results are consistent with unimolecular electron transfer occurring within a cyt c(III)-cyt c peroxidase(II) complex. When cyt c is replaced by porphyrin cyt c (iron-free cyt c), a complex still forms with cyt c peroxidase. On radiolysis, using e-aq as the reducing agent, intracomplex electron transfer occurs from the porphyrin cyt c anion radical to cyt c peroxidase(III) with k = 150 s-1. This large rate increase with increasing delta G degrees suggests that the barrier for intracomplex electron transfer is large. Finally, we have briefly investigated how the cyt c peroxidase(II)----cyt c(III) rate depends on the primary structure of cyt c(III). We find the reactivity order to be as follows: yeast (k = 3.4 s-1) greater than horse (k = 0.3 s-1) greater than tuna (k = 0.2 s-1). These results mirror a report [Ho, P. S., Sutoris, C., Liang, N., Margoliash, E. & Hoffman, B. M. (1985) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 107, 1070-1071] on excited state reactions of the cyt c/cyt c peroxidase couple.
Full text
PDF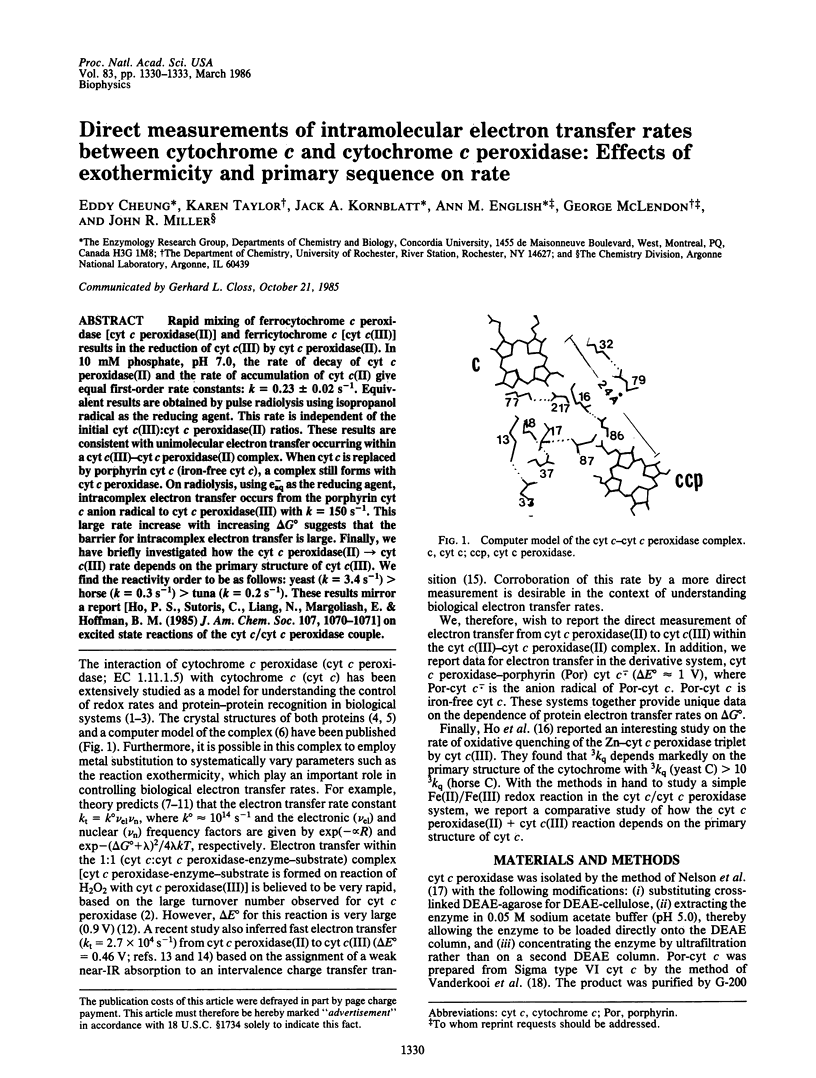

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Clark RK, Barlow PM, Diamond RN, Hagopian V, V, Lannutti JE, Spencer CM, Ferguson M, Glanzman T, Goshaw AT, Lucas P. Triggered-bubble-chamber study of the reaction pi +p--> Delta ++ pi 0 pi 0 at 16 GeV/c. Phys Rev D Part Fields. 1985 Sep 1;32(5):1061–1070. doi: 10.1103/physrevd.32.1061. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conroy C. W., Tyma P., Daum P. H., Erman J. E. Oxidation-reduction potential measurements of cytochrome c peroxidase and pH dependent spectral transitions in the ferrous enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1978 Nov 20;537(1):62–69. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(78)90602-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devault D. Quantum mechanical tunnelling in biological systems. Q Rev Biophys. 1980 Nov;13(4):387–564. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000175x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erman J. E., Vitello L. B. The binding of cytochrome c peroxidase and ferricytochrome c. A spectrophotometric determination of the equilibrium association constant as a function of ionic strength. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6224–6227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. J. Electron transfer between biological molecules by thermally activated tunneling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Sep;71(9):3640–3644. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.9.3640. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iizuka T., Makino R., Ishimura Y., Yonetani T. Reversible acidic-alkaline transition of the carbon monoxide complex of cytochrome c peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1407–1412. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kang C. H., Ferguson-Miller S., Margoliash E. Steady state kinetics and binding of eukaryotic cytochromes c with yeast cytochrome c peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 1977 Feb 10;252(3):919–926. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C. E., Sitzman E. V., Kang C. H., Margoliash E. Preparation of cytochrome c peroxidase from baker's yeast. Anal Biochem. 1977 Dec;83(2):622–631. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(77)90066-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potasek M. J. Investigation of electron tunneling between cytochrome c peroxidase and cytochrome c. Science. 1978 Jul 14;201(4351):151–153. doi: 10.1126/science.208146. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Freer S. T., Alden R. A., Edwards S. L., Skogland U., Takio K., Eriksson B., Xuong N., Yonetani T., Kraut J. The crystal structure of cytochrome c peroxidase. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jan 25;255(2):575–580. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulos T. L., Kraut J. A hypothetical model of the cytochrome c peroxidase . cytochrome c electron transfer complex. J Biol Chem. 1980 Nov 10;255(21):10322–10330. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Purcell W. L., Erman J. E. Cytochrome c peroxidase catalyzed oxidations of substitution inert iron(II) complexes. J Am Chem Soc. 1976 Oct 27;98(22):7033–7037. doi: 10.1021/ja00438a049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swanson R., Trus B. L., Mandel N., Mandel G., Kallai O. B., Dickerson R. E. Tuna cytochrome c at 2.0 A resolution. I. Ferricytochrome structure analysis. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):759–775. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vanderkooi J. M., Adar F., Erecińska M. Metallocytochromes c: characterization of electronic absorption and emission spectra of Sn4+ and Zn2+ cytochromes c. Eur J Biochem. 1976 May 1;64(2):381–387. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1976.tb10312.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ward B., Chang C. K. A convenient photochemical method for reduction of ferric hemes. Photochem Photobiol. 1982 May;35(5):757–759. doi: 10.1111/j.1751-1097.1982.tb02643.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Kok J., Butler J., Braams R., van Gelder B. F. The reduction of porphyrin cytochrome c by hydrated electrons and the subsequent electron transfer reaction from reduced porphyrin cytochrome c to ferricytochrome c. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1977 May 11;460(2):290–298. doi: 10.1016/0005-2728(77)90215-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



