Abstract
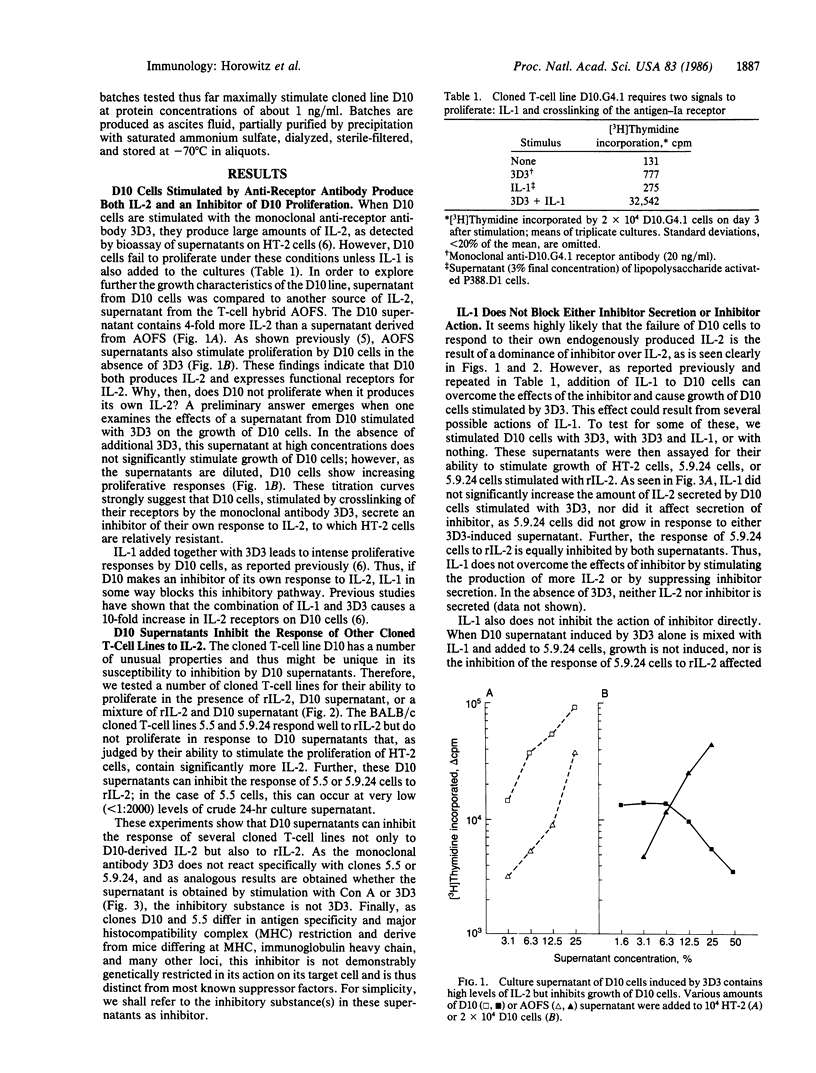
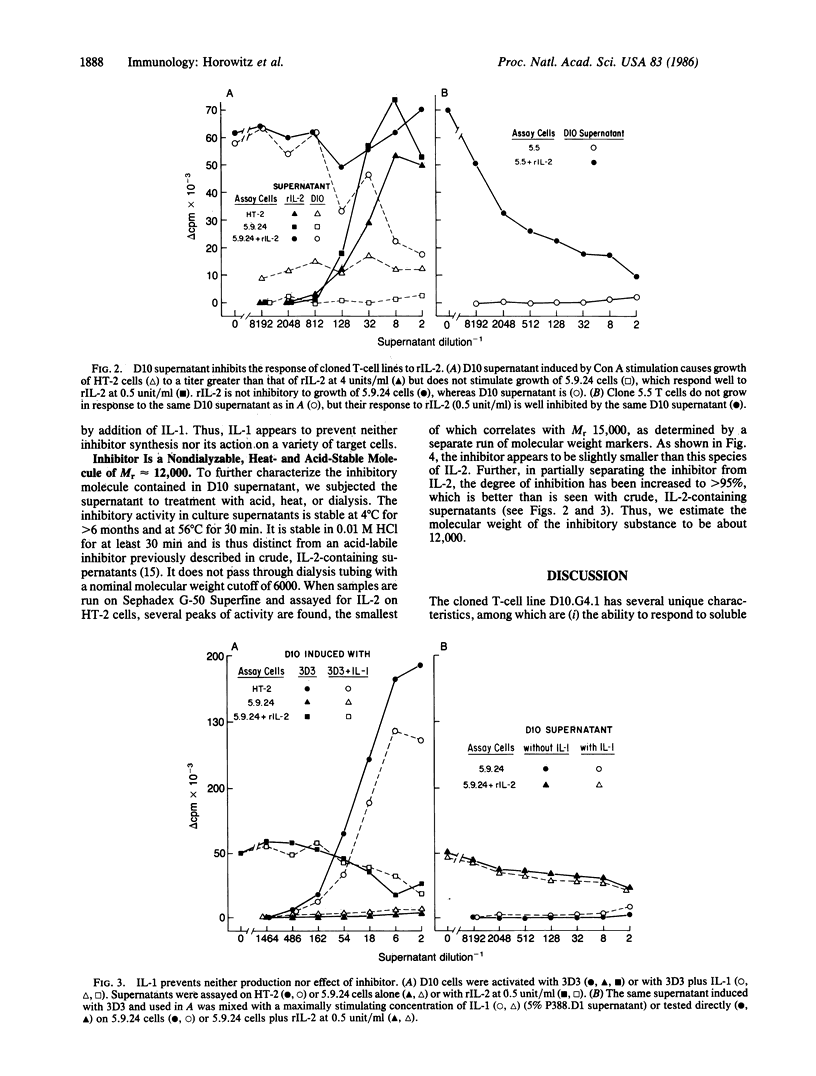
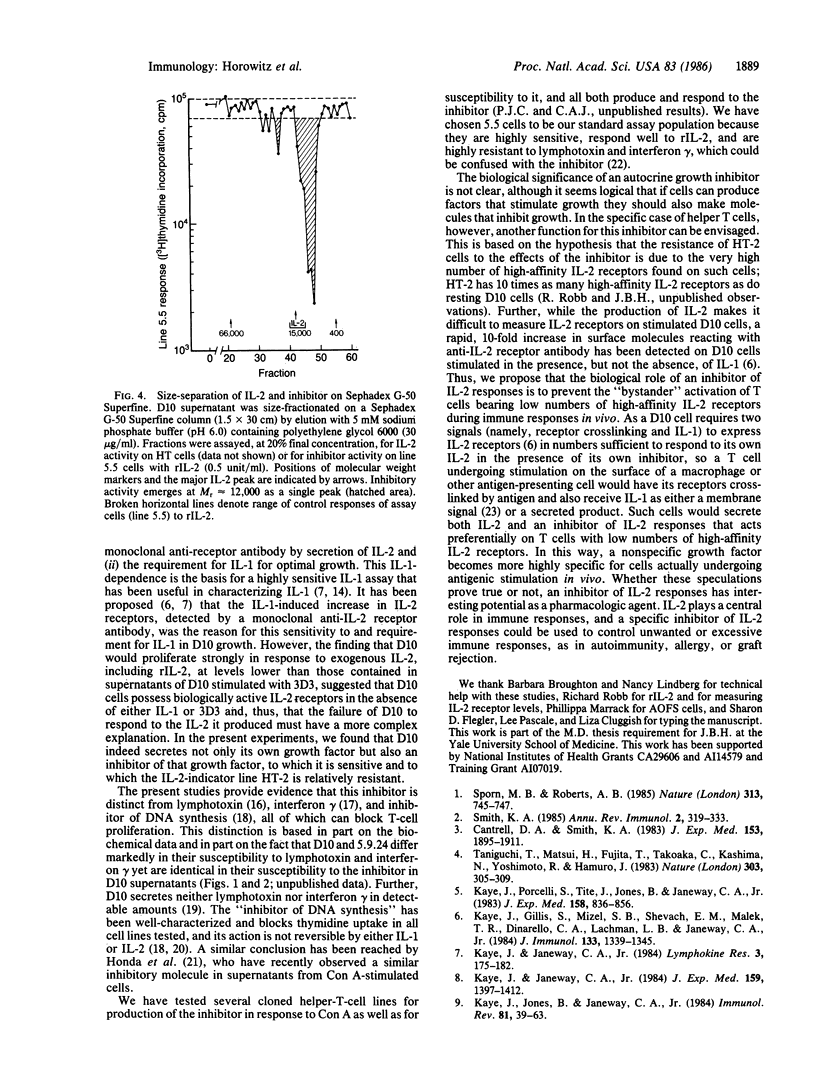
The growth of T lymphocytes is dependent on the T-cell growth factor interleukin 2 (IL-2), which causes T cells bearing high-affinity receptors for IL-2 to proliferate. Most cloned helper-T-cell lines can be shown to both produce and respond to IL-2; thus, growth of such cells is by an autocrine mechanism. We report that the failure of the cloned murine T-cell line D10.G4.1 to respond to its own IL-2 results from the secretion, by the same cells, of a potent inhibitor of the IL-2-driven T-cell proliferative response. This inhibition can be overcome by increasing the number of IL-2 receptors expressed by the target cell. In the cloned T-cell line producing the inhibitory substance, this increase in IL-2 receptors is driven by the monokine interleukin-1. We propose that this inhibitor of IL-2 responses may play a role in preventing "bystander" activation of T cells by IL-2 released in vivo and could be a potent pharmacologic agent.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auron P. E., Webb A. C., Rosenwasser L. J., Mucci S. F., Rich A., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Nucleotide sequence of human monocyte interleukin 1 precursor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7907–7911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. Transient expression of interleukin 2 receptors. Consequences for T cell growth. J Exp Med. 1983 Dec 1;158(6):1895–1911. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.6.1895. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conrad P. J., Janeway C. A., Jr The expression of I-Ed molecules in F1 hybrid mice detected with antigen-specific, I-Ed-restricted cloned T-cell lines. Immunogenetics. 1984;20(3):311–319. doi: 10.1007/BF00364212. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jegasothy B. V., Battles D. R. Immuno-suppressive lymphocyte factors-III. Complete purification and partial characterization of human inhibitor of DNA synthesis. Mol Immunol. 1981 May;18(5):395–401. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(81)90101-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jegasothy B. V., Battles D. R. Immuno-suppressive lymphocyte factors. I. Purification of inhibitor of DNA synthesis to homogeneity. J Exp Med. 1979 Sep 19;150(3):622–632. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.3.622. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Gillis S., Mizel S. B., Shevach E. M., Malek T. R., Dinarello C. A., Lachman L. B., Janeway C. A., Jr Growth of a cloned helper T cell line induced by a monoclonal antibody specific for the antigen receptor: interleukin 1 is required for the expression of receptors for interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1339–1345. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Janeway C. A., Jr Induction of receptors for interleukin 2 requires T cell Ag:Ia receptor crosslinking and interleukin 1. Lymphokine Res. 1984 Summer;3(4):175–182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Janeway C. A., Jr The Fab fragment of a directly activating monoclonal antibody that precipitates a disulfide-linked heterodimer from a helper T cell clone blocks activation by either allogeneic Ia or antigen and self-Ia. J Exp Med. 1984 May 1;159(5):1397–1412. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.5.1397. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Jones B., Janeway C. A., Jr The structure and function of T cell receptor complexes. Immunol Rev. 1984 Oct;81:39–63. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1984.tb01104.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaye J., Porcelli S., Tite J., Jones B., Janeway C. A., Jr Both a monoclonal antibody and antisera specific for determinants unique to individual cloned helper T cell lines can substitute for antigen and antigen-presenting cells in the activation of T cells. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):836–856. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.836. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurt-Jones E. A., Beller D. I., Mizel S. B., Unanue E. R. Identification of a membrane-associated interleukin 1 in macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1204–1208. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1204. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills B. J., Mitsky P. S., Todd C. W. Acid treatment enhances IL-2 activity of conditioned medium. J Immunol Methods. 1984 Feb 24;67(1):73–78. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(84)90086-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruddle N. H. Delayed hypersensitivity to soluble antigens in mice. II. Analysis in vitro. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1979;58(1):44–52. doi: 10.1159/000232172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. Interleukin 2. Annu Rev Immunol. 1984;2:319–333. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.02.040184.001535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sporn M. B., Roberts A. B. Autocrine growth factors and cancer. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):745–747. doi: 10.1038/313745a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stone-Wolff D. S., Yip Y. K., Kelker H. C., Le J., Henriksen-Destefano D., Rubin B. Y., Rinderknecht E., Aggarwal B. B., Vilcek J. Interrelationships of human interferon-gamma with lymphotoxin and monocyte cytotoxin. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):828–843. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.828. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taniguchi T., Matsui H., Fujita T., Takaoka C., Kashima N., Yoshimoto R., Hamuro J. Structure and expression of a cloned cDNA for human interleukin-2. Nature. 1983 Mar 24;302(5906):305–310. doi: 10.1038/302305a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tite J. P., Janeway C. A., Jr Antigen-dependent selection of B lymphoma cells varying in Ia density by cloned antigen-specific L3T4a+ T cells: a possible in vitro model for B cell adaptive differentiation. J Mol Cell Immunol. 1984;1(4):253–265. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tite J. P., Janeway C. A., Jr Cloned helper T cells can kill B lymphoma cells in the presence of specific antigen: Ia restriction and cognate vs. noncognate interactions in cytolysis. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):878–886. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tite J. P., Powell M. B., Ruddle N. H. Protein-antigen specific Ia-restricted cytolytic T cells: analysis of frequency, target cell susceptibility, and mechanism of cytolysis. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):25–33. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



