Abstract
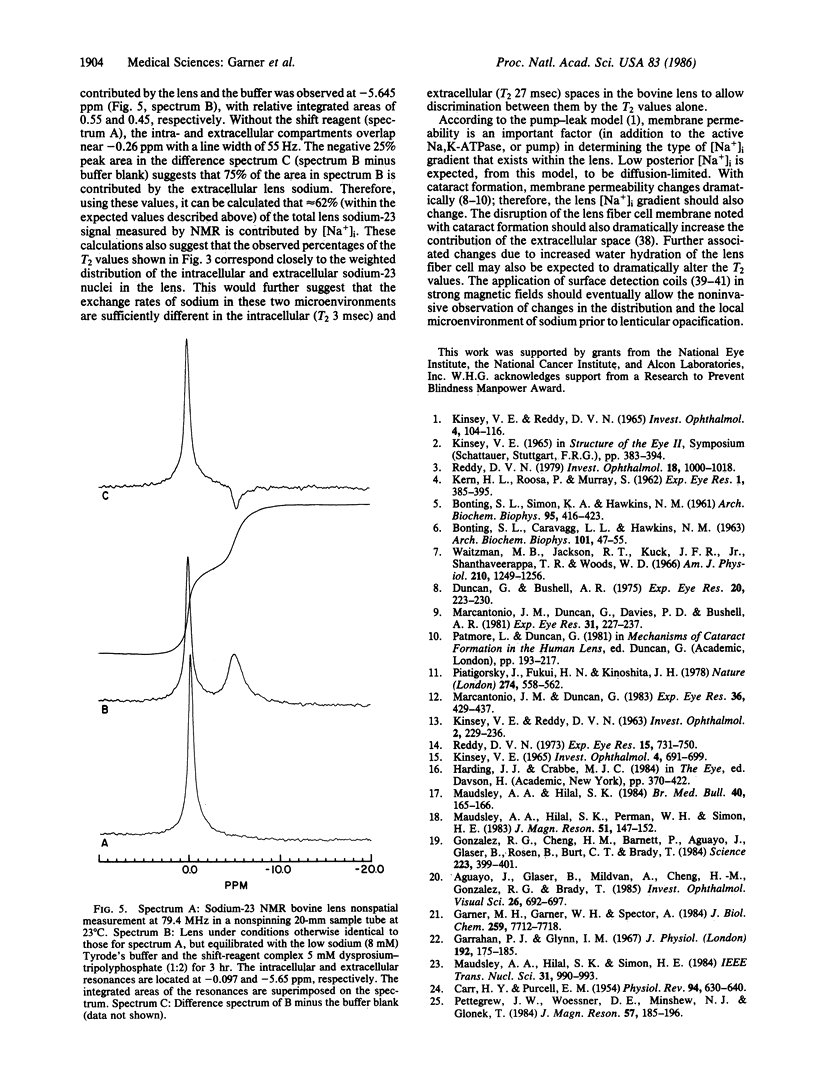
In order to develop a better understanding of cataract and to evaluate the effectiveness of potential drugs, noninvasive techniques must be devised to detect early metabolic changes. As a prelude to these goals, sodium-23 imaging experiments operating at 29.8 MHz (2.7 teslas) were performed on the bovine eye and lens. A spatially localized transverse relaxation time (T2)-weighted spin-density map of the sodium-23 within the lens is presented, with a resolution better than 250 micron. Due to the presence of short-T2 (3 msec) components within the lens, only the use of the planar-integral projection reconstruction (PPR) imaging scheme allowed sufficiently short echo-times (1 msec) to permit sodium-23 signal detection. These noninvasive imaging results show differences in the apparent sodium concentration within the lens that are consistent with separate, invasive measurements of sodium concentration. Separate analysis (with no spatial localization) at 79.4 MHz (7.2 teslas), using a shift reagent (dysprosium) to distinguish extracellular from intracellular sodium, indicates that approximately 62% of the detected sodium-23 signal is intracellular. These results are consistent with observations based on invasive measurements and further support the existence of the pump-leak system and a sodium gradient within the lens.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMOORE J. E., BARTLEY W., VAN HEYNINGEN R. Distribution of sodium and potassium within cattle lens. Biochem J. 1959 May;72(1):126–133. doi: 10.1042/bj0720126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman J. J., Grove T. H., Wong G. G., Gadian D. G., Radda G. K. Mapping of metabolites in whole animals by 31P NMR using surface coils. Nature. 1980 Jan 10;283(5743):167–170. doi: 10.1038/283167a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Aguayo J., Glaser B., Mildvan A., Cheng H. M., Gonzalez R. G., Brady T. Study of vitreous liquifaction by NMR spectroscopy and imaging. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1985 May;26(5):692–697. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONTING S. L., CARAVAGGIO L. L., HAWKINS N. M. Studies on sodium-potassium-activated adenosinetriphosphatase. VI. Its role in cation transport in the lens of cat, calf and rabbit. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1963 Apr;101:47–55. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(63)90532-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BONTING S. L., SIMON K. A., HAWKINS N. M. Studies on sodium-potassium-activated adenosine triphosphatase. I. Quantitative distribution in several tissues of the cat. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1961 Dec;95:416–423. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(61)90170-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berendsen H. J., Edzes H. T. The observation and general interpretation of sodium magnetic resonance in biological material. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1973 Mar 30;204:459–485. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1973.tb30799.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duncan G., Bushell A. R. Ion analyses of human cataractous lenses. Exp Eye Res. 1975 Mar;20(3):223–230. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(75)90136-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. H., Garner W. H., Spector A. Kinetic cooperativity change after H2O2 modification of (Na,K)-ATPase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 25;259(12):7712–7718. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garner M. H., Roy D., Rosenfeld L., Garner W. H., Spector A. Biochemical evidence for membrane disintegration in human cataracts. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Mar;78(3):1892–1895. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.3.1892. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrahan P. J., Glynn I. M. The sensitivity of the sodium pump to external sodium. J Physiol. 1967 Sep;192(1):175–188. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1967.sp008295. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- González R. G., Cheng H. M., Barnett P., Aguayo J., Glaser B., Rosen B., Burt C. T., Brady T. Nuclear magnetic resonance imaging of the vitreous body. Science. 1984 Jan 27;223(4634):399–400. doi: 10.1126/science.6318321. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilal S. K., Maudsley A. A., Simon H. E., Perman W. H., Bonn J., Mawad M. E., Silver A. J., Ganti S. R., Sane P., Chien I. C. In vivo NMR imaging of tissue sodium in the intact cat before and after acute cerebral stroke. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol. 1983 May-Jun;4(3):245–249. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KERN H. L., ROOSA P., MURRAY S. Evidence for active transport of alkali metal cations by calf lens. Exp Eye Res. 1962 Jun;1:385–395. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(62)80028-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINSEY V. E. AMINO ACID TRANSPORT IN THE LENS. Invest Ophthalmol. 1965 Aug;4:691–699. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINSEY V. E., REDDY D. V. STUDIES ON THE CRYSTALLINE LENS. XI. THE RELATIVE ROLE OF THE EPITHELIUM AND CAPSULE IN TRANSPORT. Invest Ophthalmol. 1965 Feb;4:104–116. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KINSEY V. E., REDDY D. V. Studies on the crystalline lens. X. Transport of amino acids. Invest Ophthalmol. 1963 Jun;2:229–236. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcantonio J. M., Duncan G. Amino acid transport and crystallin synthesis in the bovine lens. Exp Eye Res. 1983 Mar;36(3):429–440. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(83)90124-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marcantonio J. M., Duncan G., Davies P. D., Bushell A. R. Classification of human senile cataracts by nuclear colour and sodium content. Exp Eye Res. 1980 Aug;31(2):227–237. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(80)90080-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maudsley A. A., Hilal S. K. Biological aspects of sodium-23 imaging. Br Med Bull. 1984 Apr;40(2):165–166. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071964. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Monoi H. Nuclear magnetic resonance of tissue 23Na. II. Theoretical line shape. Biophys J. 1974 Sep;14(9):653–659. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85942-4. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson C. A. Distribution of sodium and potassium in ox lenses. Exp Eye Res. 1969 Oct;8(4):442–446. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4835(69)80011-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Paterson C. A. Extracellular space of the crystalline lens. Am J Physiol. 1970 Mar;218(3):797–802. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1970.218.3.797. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Piatigorsky J., Fukui H. N., Kinoshita J. H. Differential metabolism and leakage of protein in an inherited cataract and a normal lens cultured with ouabain. Nature. 1978 Aug 10;274(5671):558–562. doi: 10.1038/274558a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. N. Dynamics of transport systems in the eye. Friedenwald Lecture. Invest Ophthalmol Vis Sci. 1979 Oct;18(10):1000–1018. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reddy V. N. Transport of organic molecules in the lens. Exp Eye Res. 1973 May 24;15(6):731–750. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(73)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schleich T., Matson G. B., Willis J. A., Acosta G., Serdahl C., Campbell P., Garwood M. Surface coil phosphorus-31 nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the intact eye. Exp Eye Res. 1985 Mar;40(3):343–355. doi: 10.1016/0014-4835(85)90148-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shepp L. A. Computerized tomography and nuclear magnetic resonance. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 1980 Feb;4(1):94–107. doi: 10.1097/00004728-198002000-00018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waitzman M. B., Jackson R. T., Kuck J. F., Jr, Shanthaveerappa T. R., Woods W. D. Influences of metabolic-effective agents on nucleotide systems in ocular tissues. Am J Physiol. 1966 Jun;210(6):1249–1256. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1966.210.6.1249. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]






