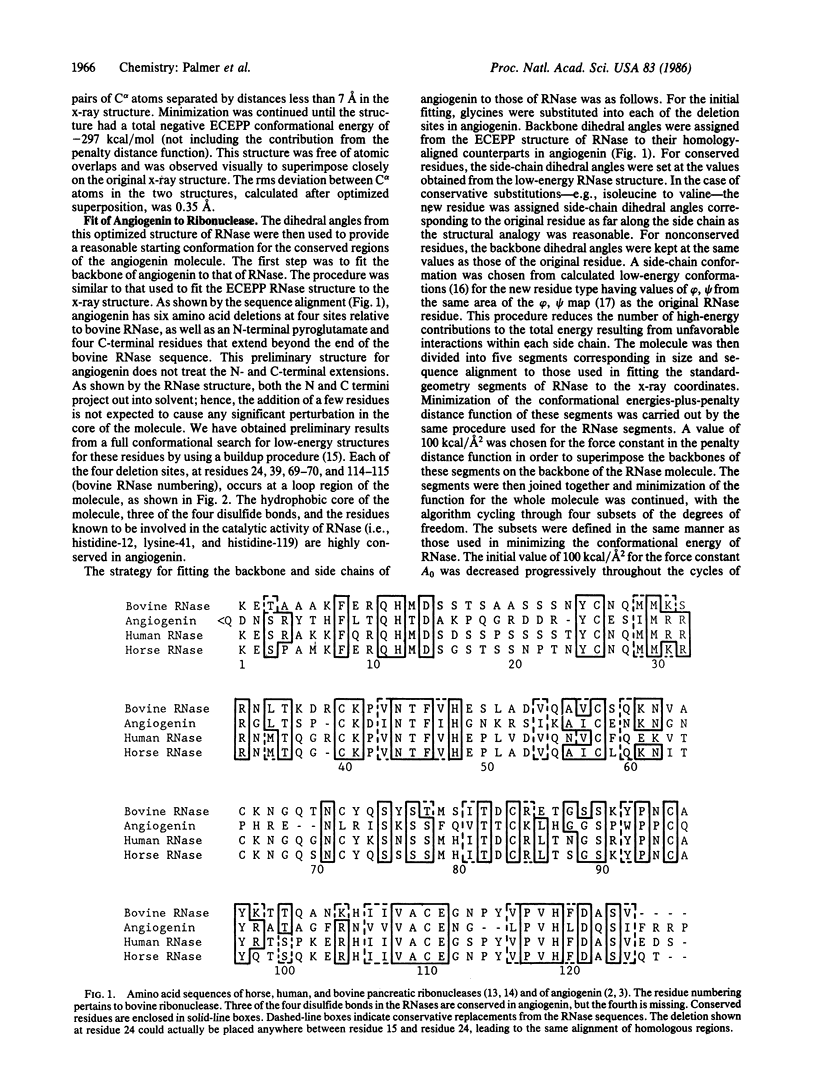
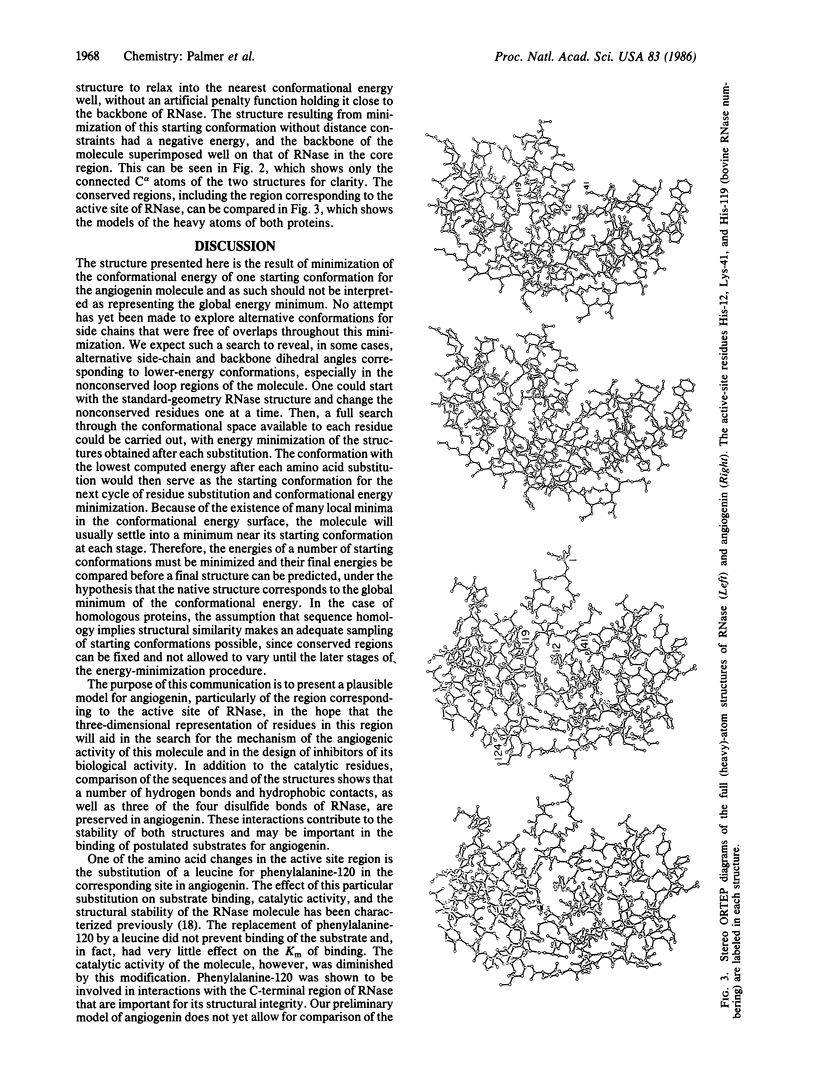
Abstract
A preliminary three-dimensional structure of angiogenin has been computed, based on its homology to bovine pancreatic ribonuclease A. A standard-geometry structure of ribonuclease was first obtained from its x-ray coordinates. The fit of the backbone of angiogenin to that of ribonuclease was then optimized by taking account of amino acid deletions and by minimizing its conformational energy-plus-a-penalty distance function constraining its backbone to that of ribonuclease. Side-chain and backbone dihedral angles were allowed to vary throughout the cycles of energy minimization. In the last stages of minimization, the penalty distance function was removed. A low-energy structure resembling ribonuclease was obtained.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Beintema J. J., Wietzes P., Weickmann J. L., Glitz D. G. The amino acid sequence of human pancreatic ribonuclease. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):48–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernstein F. C., Koetzle T. F., Williams G. J., Meyer E. F., Jr, Brice M. D., Rodgers J. R., Kennard O., Shimanouchi T., Tasumi M. The Protein Data Bank: a computer-based archival file for macromolecular structures. J Mol Biol. 1977 May 25;112(3):535–542. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(77)80200-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blake C. C., Mair G. A., North A. C., Phillips D. C., Sarma V. R. On the conformation of the hen egg-white lysozyme molecule. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1967 Apr 18;167(1009):365–377. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1967.0034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chavez L. G., Scherage H. A. Immunological determination of the order of folding of portions of the molecule during air oxidation of reduced ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1977 May 3;16(9):1849–1856. doi: 10.1021/bi00628a014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fett J. W., Strydom D. J., Lobb R. R., Alderman E. M., Bethune J. L., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Isolation and characterization of angiogenin, an angiogenic protein from human carcinoma cells. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5480–5486. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurachi K., Davie E. W., Strydom D. J., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Sequence of the cDNA and gene for angiogenin, a human angiogenesis factor. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5494–5499. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a032. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. C., Gutte B., Caldi D. G., Moore S., Merrifield R. B. Reactivation of des (119-124) ribonuclease A by mixture with synthetic COOH-terminal peptides; the role of phenylalanine-120. J Biol Chem. 1972 Aug 10;247(15):4768–4774. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meadows D. H., Roberts G. C., Jardetzky O. Nuclear magnetic resonance studies of the structure and binding sites of enzymes. 8. Inhibitor binding to ribonuclease. J Mol Biol. 1969 Nov 14;45(3):491–511. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(69)90308-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Némethy G., Scheraga H. A. A possible folding pathway of bovine pancreatic RNase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6050–6054. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6050. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stern M. S., Doscher M. S. Aspartic acid-121 functions at the active site of bovine pancreatic ribonuclease. FEBS Lett. 1984 Jun 11;171(2):253–256. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80498-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J., Fett J. W., Lobb R. R., Alderman E. M., Bethune J. L., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Amino acid sequence of human tumor derived angiogenin. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5486–5494. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vásquez M., Scheraga H. A. Use of buildup and energy-minimization procedures to compute low-energy structures of the backbone of enkephalin. Biopolymers. 1985 Aug;24(8):1437–1447. doi: 10.1002/bip.360240803. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warme P. K., Momany F. A., Rumball S. V., Tuttle R. W., Scheraga H. A. Computation of structures of homologous proteins. Alpha-lactalbumin from lysozyme. Biochemistry. 1974 Feb 12;13(4):768–782. doi: 10.1021/bi00701a020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zimmerman S. S., Pottle M. S., Némethy G., Scheraga H. A. Conformational analysis of the 20 naturally occurring amino acid residues using ECEPP. Macromolecules. 1977 Jan-Feb;10(1):1–9. doi: 10.1021/ma60055a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



