Abstract
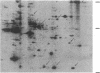
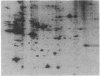
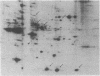
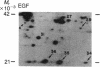
Epidermal growth factor (EGF) causes rapid increases in free intracellular Ca2+ and stimulates the phosphorylation of 11 cytosolic proteins in hepatocytes. Ten of the 11 cytosolic proteins altered by EGF are identical to those affected by angiotensin II, a hormone that stimulates the breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate. An increase in the phosphorylation of the other protein, spot c (Mr = 36,000, pI = 5.5), is observed only with EGF. Treatment of intact rats with pertussis toxin to ADP-ribosylate Ni, the inhibitory GTP-binding protein of the adenylate cyclase complex, abolished the effect of EGF on Ca2+ mobilization and on the phosphorylation of the 10 proteins affected in common with angiotensin II. This treatment had minimal effects on the ability of EGF to stimulate the phosphorylation of its unique substrate, spot c. In marked contrast, modification of Ni did not block the ability of angiotensin II to stimulate Ca2+ mobilization or protein phosphorylation. Pretreatment of normal hepatocytes with 4 beta-phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate blocked all responses to EGF, including the increased phosphorylation of spot c, but had no effect on the responses to angiotensin II. These results imply that Ni or a similar pertussis toxin substrate may mediate the apparent effects of EGF on phosphatidylinositol breakdown and that protein kinase C may regulate a site in the transduction pathway. Angiotensin II appears to use a different signal transduction mechanism to stimulate phosphatidylinositol metabolism in hepatocytes.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berridge M. J. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as second messengers. Biochem J. 1984 Jun 1;220(2):345–360. doi: 10.1042/bj2200345. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Gilman A. G. Inhibition of receptor-mediated release of arachidonic acid by pertussis toxin. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brandt S. J., Dougherty R. W., Lapetina E. G., Niedel J. E. Pertussis toxin inhibits chemotactic peptide-stimulated generation of inositol phosphates and lysosomal enzyme secretion in human leukemic (HL-60) cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(10):3277–3280. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.10.3277. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charest R., Blackmore P. F., Berthon B., Exton J. H. Changes in free cytosolic Ca2+ in hepatocytes following alpha 1-adrenergic stimulation. Studies on Quin-2-loaded hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jul 25;258(14):8769–8773. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cobb M. H., Rosen O. M. Description of a protein kinase derived from insulin-treated 3T3-L1 cells that catalyzes the phosphorylation of ribosomal protein S6 and casein. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 25;258(20):12472–12481. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cochet C., Gill G. N., Meisenhelder J., Cooper J. A., Hunter T. C-kinase phosphorylates the epidermal growth factor receptor and reduces its epidermal growth factor-stimulated tyrosine protein kinase activity. J Biol Chem. 1984 Feb 25;259(4):2553–2558. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cockcroft S., Gomperts B. D. Role of guanine nucleotide binding protein in the activation of polyphosphoinositide phosphodiesterase. Nature. 1985 Apr 11;314(6011):534–536. doi: 10.1038/314534a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper J. A., Sefton B. M., Hunter T. Diverse mitogenic agents induce the phosphorylation of two related 42,000-dalton proteins on tyrosine in quiescent chick cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):30–37. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.30. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper R. H., Coll K. E., Williamson J. R. Differential effects of phorbol ester on phenylephrine and vasopressin-induced Ca2+ mobilization in isolated hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3281–3288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Corvera S., Schwarz K. R., Graham R. M., García-Sáinz J. A. Phorbol esters inhibit alpha 1-adrenergic effects and decrease the affinity of liver cell alpha 1-adrenergic receptors for (-)-epinephrine. J Biol Chem. 1986 Jan 15;261(2):520–526. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Creba J. A., Downes C. P., Hawkins P. T., Brewster G., Michell R. H., Kirk C. J. Rapid breakdown of phosphatidylinositol 4-phosphate and phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate in rat hepatocytes stimulated by vasopressin and other Ca2+-mobilizing hormones. Biochem J. 1983 Jun 15;212(3):733–747. doi: 10.1042/bj2120733. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Evans T., Martin M. W., Hughes A. R., Harden T. K. Guanine nucleotide-sensitive, high affinity binding of carbachol to muscarinic cholinergic receptors of 1321N1 astrocytoma cells is insensitive to pertussis toxin. Mol Pharmacol. 1985 Jan;27(1):32–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison J. C., Haynes R. C., Jr The hormonal control of gluconeogenesis by regulation of mitochondrial pyruvate carboxylation in isolated rat liver cells. J Biol Chem. 1975 Apr 25;250(8):2769–2777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison J. C., Johnsen D. E., Campanile C. P. Evidence for the role of phosphorylase kinase, protein kinase C, and other Ca2+-sensitive protein kinases in the response of hepatocytes to angiotensin II and vasopressin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 10;259(5):3283–3292. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garrison J. C., Wagner J. D. Glucagon and the Ca2+-linked hormones angiotensin II, norepinephrine, and vasopressin stimulate the phosphorylation of distinct substrates in intact hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1982 Nov 10;257(21):13135–13143. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes A. R., Martin M. W., Harden T. K. Pertussis toxin differentiates between two mechanisms of attenuation of cyclic AMP accumulation by muscarinic cholinergic receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Sep;81(18):5680–5684. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.18.5680. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hunter T., Cooper J. A. Protein-tyrosine kinases. Annu Rev Biochem. 1985;54:897–930. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.54.070185.004341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lynch C. J., Charest R., Bocckino S. B., Exton J. H., Blackmore P. F. Inhibition of hepatic alpha 1-adrenergic effects and binding by phorbol myristate acetate. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2844–2851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Magun B. E., Matrisian L. M., Bowden G. T. Epidermal growth factor. Ability of tumor promoter to alter its degradation, receptor affinity and receptor number. J Biol Chem. 1980 Jul 10;255(13):6373–6381. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moolenaar W. H., Tertoolen L. G., de Laat S. W. Growth factors immediately raise cytoplasmic free Ca2+ in human fibroblasts. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jul 10;259(13):8066–8069. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murayama T., Ui M. Receptor-mediated inhibition of adenylate cyclase and stimulation of arachidonic acid release in 3T3 fibroblasts. Selective susceptibility to islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jun 25;260(12):7226–7233. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Borgeat P., White J. R., Sha'afi R. I. Phorbol esters inhibit the fMet-Leu-Phe- and leukotriene B4-stimulated calcium mobilization and enzyme secretion in rabbit neutrophils. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2125–2131. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakamura T., Ui M. Simultaneous inhibitions of inositol phospholipid breakdown, arachidonic acid release, and histamine secretion in mast cells by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin. A possible involvement of the toxin-specific substrate in the Ca2+-mobilizing receptor-mediated biosignaling system. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3584–3593. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neer E. J., Lok J. M., Wolf L. G. Purification and properties of the inhibitory guanine nucleotide regulatory unit of brain adenylate cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14222–14229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Novak-Hofer I., Thomas G. An activated S6 kinase in extracts from serum- and epidermal growth factor-stimulated Swiss 3T3 cells. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5995–6000. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Orellana S. A., Solski P. A., Brown J. H. Phorbol ester inhibits phosphoinositide hydrolysis and calcium mobilization in cultured astrocytoma cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5236–5239. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pobiner B. F., Hewlett E. L., Garrison J. C. Role of Ni in coupling angiotensin receptors to inhibition of adenylate cyclase in hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Dec 25;260(30):16200–16209. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sawyer S. T., Cohen S. Enhancement of calcium uptake and phosphatidylinositol turnover by epidermal growth factor in A-431 cells. Biochemistry. 1981 Oct 13;20(21):6280–6286. doi: 10.1021/bi00524a057. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternweis P. C., Robishaw J. D. Isolation of two proteins with high affinity for guanine nucleotides from membranes of bovine brain. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13806–13813. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsien R. Y., Pozzan T., Rink T. J. Calcium homeostasis in intact lymphocytes: cytoplasmic free calcium monitored with a new, intracellularly trapped fluorescent indicator. J Cell Biol. 1982 Aug;94(2):325–334. doi: 10.1083/jcb.94.2.325. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Volpi M., Naccache P. H., Molski T. F., Shefcyk J., Huang C. K., Marsh M. L., Munoz J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis toxin inhibits fMet-Leu-Phe- but not phorbol ester-stimulated changes in rabbit neutrophils: role of G proteins in excitation response coupling. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2708–2712. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2708. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson J. R., Cooper R. H., Joseph S. K., Thomas A. P. Inositol trisphosphate and diacylglycerol as intracellular second messengers in liver. Am J Physiol. 1985 Mar;248(3 Pt 1):C203–C216. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.3.C203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]