Abstract
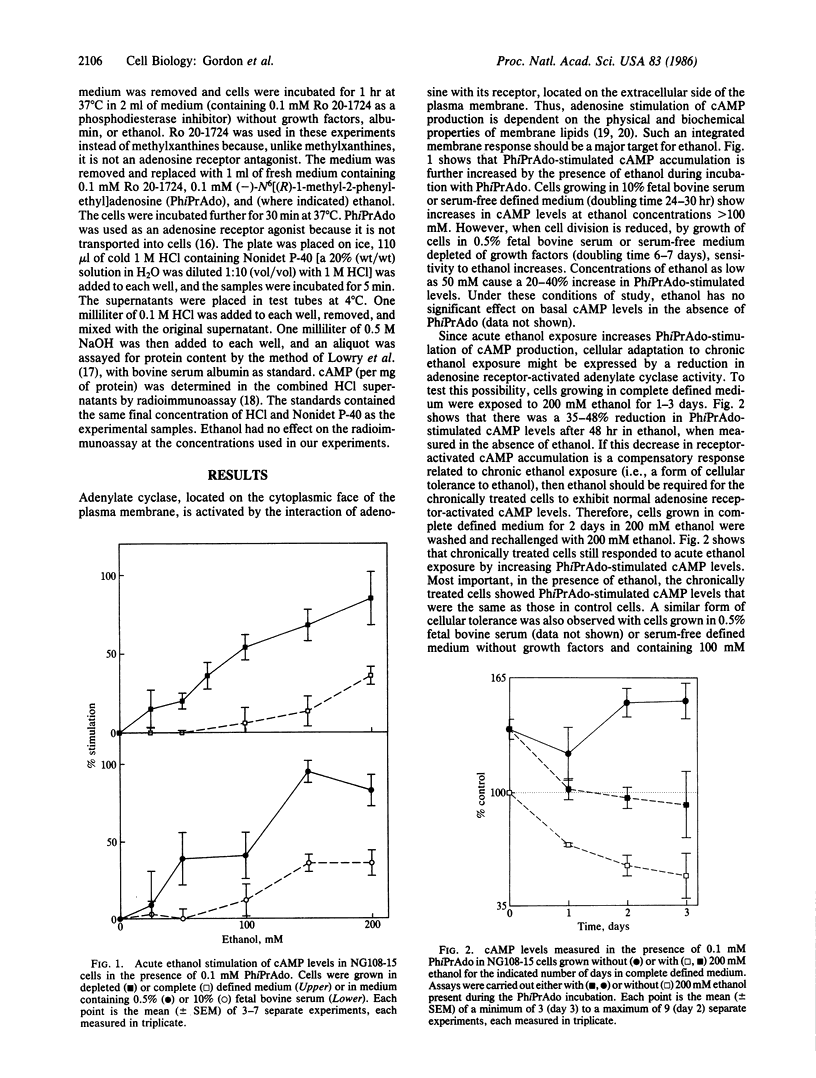
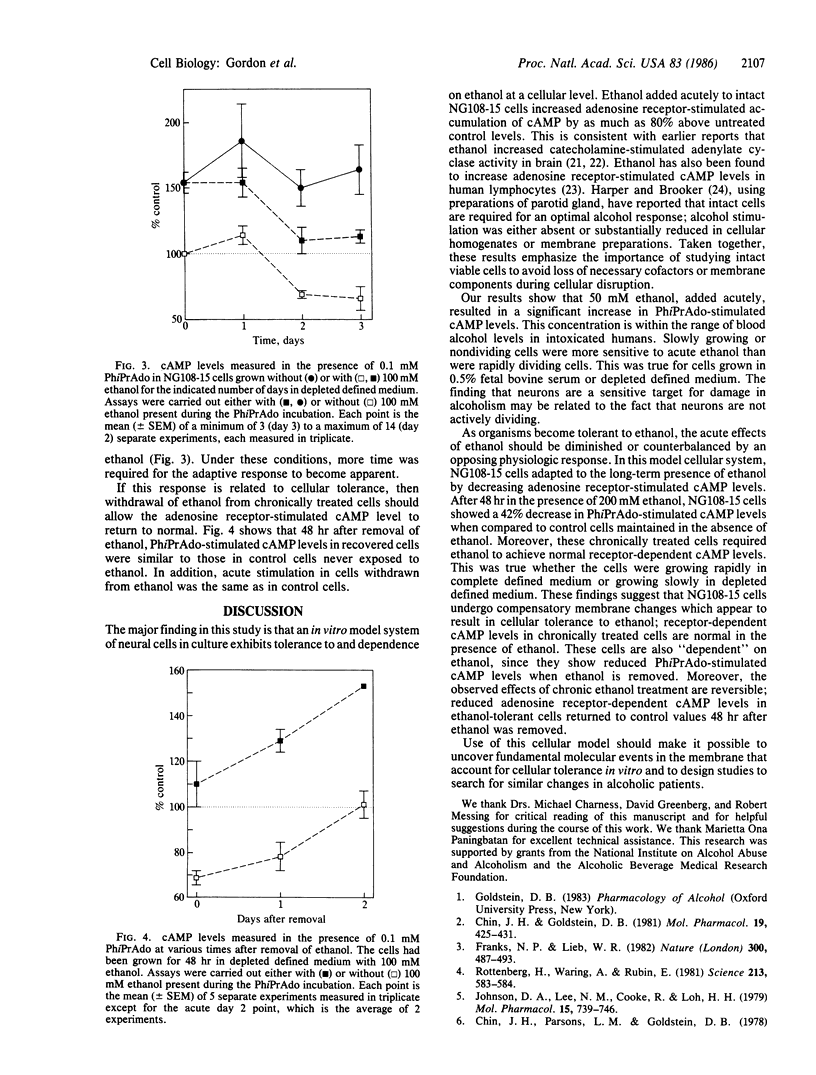
The acute and chronic neurologic effects of ethanol appear to be due to its interaction with neural cell membranes. Chronic exposure to ethanol induces changes in the membrane that lead to tolerance to the effects of ethanol. However, the actual membrane changes that account for tolerance to ethanol are not understood. We have developed a model cell culture system, using NG108-15 neuroblastoma-glioma hybrid cells, to study cellular tolerance to ethanol. We have found that adenosine receptor-stimulated cAMP levels increased markedly upon acute exposure to ethanol. However, the cells became tolerant to ethanol, since chronically treated cells required ethanol to maintain normal adenosine-stimulated cAMP levels. Moreover, the cells appeared to be dependent on ethanol, as evidenced by reduced adenosine-stimulated cAMP levels in the absence of ethanol. Recovery occurred after ethanol was withdrawn. These cellular changes appear to parallel the clinical events of acute ethanol intoxication, tolerance, and dependence.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Charness M. E., Gordon A. S., Diamond I. Ethanol modulation of opiate receptors in cultured neural cells. Science. 1983 Dec 16;222(4629):1246–1248. doi: 10.1126/science.6316506. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chin J. H., Goldstein D. B. Membrane-disordering action of ethanol: variation with membrane cholesterol content and depth of the spin label probe. Mol Pharmacol. 1981 May;19(3):425–431. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daly J. W., Bruns R. F., Snyder S. H. Adenosine receptors in the central nervous system: relationship to the central actions of methylxanthines. Life Sci. 1981 May 11;28(19):2083–2097. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(81)90614-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dar M. S., Mustafa S. J., Wooles W. R. Possible role of adenosine in the CNS effects of ethanol. Life Sci. 1983 Oct 3;33(14):1363–1374. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(83)90819-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Engelhard V. H., Glaser M., Storm D. R. Effect of membrane phospholipid compositional changes on adenylate cyclase in LM cells. Biochemistry. 1978 Aug 8;17(16):3191–3200. doi: 10.1021/bi00609a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franks N. P., Lieb W. R. Molecular mechanisms of general anaesthesia. Nature. 1982 Dec 9;300(5892):487–493. doi: 10.1038/300487a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper J. F., Brooker G. Alcohol potentiation of isoproterenol-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation in rat parotid. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1980;6(1):51–62. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hynie S., Lanefelt F., Fredholm B. B. Effects of ethanol on human lymphocyte levels of cyclic AMP. In vitro: Potentiation of the response to isoproterenol, prostaglandin E2 or adenosine stimulation. Acta Pharmacol Toxicol (Copenh) 1980 Jul;47(1):58–65. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0773.1980.tb02026.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson D. A., Lee N. M., Cooke R., Loh H. H. Ethanol-induced fluidization of brain lipid bilayers: required presence of cholesterol in membranes for the expression of tolerance. Mol Pharmacol. 1979 May;15(3):739–746. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch T. K., Gordon A. S., Diamond I. Phospholipid methylation in myogenic cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Jul 18;114(1):339–347. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)91633-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Littleton J. M., John G. Synaptosomal membrane lipids of mice during continuous exposure to ethanol. J Pharm Pharmacol. 1977 Sep;29(9):579–580. doi: 10.1111/j.2042-7158.1977.tb11407.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon R. C., Goldstein D. B. Changes in synaptic membrane order associated with chronic ethanol treatment in mice. Mol Pharmacol. 1983 Jan;23(1):86–91. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parsons L. M., Gallaher E. J., Goldstein D. B. Rapidly developing functional tolerance to ethanol is accompanied by increased erythrocyte cholesterol in mice. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1982 Nov;223(2):472–476. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Proctor W. R., Dunwiddie T. V. Behavioral sensitivity to purinergic drugs parallels ethanol sensitivity in selectively bred mice. Science. 1984 May 4;224(4648):519–521. doi: 10.1126/science.6324348. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin R. A., Molinoff P. B. Activation of adenylate cyclase by ethanol in mouse striatal tissue. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1981 Jan;216(1):129–134. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reitz R. C., Wang L., Schilling R. J., Starich G. H., Bergstrom J. D., Thompson J. A. Effects of ethanol ingestion on the unsaturated fatty acids from various tissues. Prog Lipid Res. 1981;20:209–213. doi: 10.1016/0163-7827(81)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rottenberg H., Waring A., Rubin E. Tolerance and cross-tolerance in chronic alcoholics: reduced membrane binding of ethanol and other drugs. Science. 1981 Jul 31;213(4507):583–585. doi: 10.1126/science.6264608. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito T., Lee J. M., Tabakoff B. Ethanol's effects on cortical adenylate cyclase activity. J Neurochem. 1985 Apr;44(4):1037–1044. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1985.tb08722.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sinensky M., Pinkerton F., Sutherland E., Simon F. R. Rate limitation of (Na+ + K+)-stimulated adenosinetriphosphatase by membrane acyl chain ordering. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Oct;76(10):4893–4897. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.10.4893. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith T. L., Gerhart M. J. Alterations in brain lipid composition of mice made physically dependent to ethanol. Life Sci. 1982 Oct 4;31(14):1419–1425. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(82)90002-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waring A. J., Rottenberg H., Ohnishi T., Rubin E. Membranes and phospholipids of liver mitochondria from chronic alcoholic rats are resistant to membrane disordering by alcohol. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2582–2586. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2582. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



