Abstract
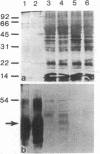
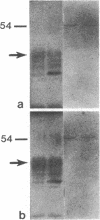
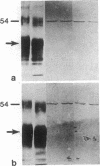
Scrapie is the best understood of the transmissible spongiform encephalopathies. These neurologic disorders include the human diseases kuru and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease and are caused by pathogens with unique biological and molecular properties. One major protein, protease-resistant protein (PrP)-27-30, is present in fractions isolated from scrapie-infected hamster brain that contain highly purified scrapie agent. PrP-27-30 appears to be the major protein component of the hamster scrapie agent. An antiserum generated to electrophoretically purified hamster scrapie PrP-27-30 identified higher molecular weight proteins in immunoblots of homogenates of uninfected hamster and mouse brains. Antibodies to hamster and mouse scrapie agent proteins were obtained by immunoaffinity purification of this antiserum. These antibodies to hamster and mouse PrPs recognized a 54-kDa protein present in uninfected brain homogenates. Antibodies immunoaffinity purified from this antiserum using whole immunoblots of normal brain antigens also identified the 54-kDa protein and PrPs. Our findings demonstrate that scrapie agent proteins share epitopes with normal proteins and suggest that the 54-kDa protein is the normal protein precursor of the scrapie agent PrPs.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alper T., Cramp W. A., Haig D. A., Clarke M. C. Does the agent of scrapie replicate without nucleic acid? Nature. 1967 May 20;214(5090):764–766. doi: 10.1038/214764a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Alper T., Haig D. A., Clarke M. C. The exceptionally small size of the scrapie agent. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1966 Feb 3;22(3):278–284. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(66)90478-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- BECK E., DANIEL P. M., PARRY H. B. DEGENERATION OF THE CEREBELLAR AND HYPOTHALAMONEUROHYPOPHYSIAL SYSTEMS IN SHEEP WITH SCRAPIE; AND ITS RELATIONSHIP TO HUMAN SYSTEM DEGENERATIONS. Brain. 1964 Mar;87:153–176. doi: 10.1093/brain/87.1.153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barry R. A., McKinley M. P., Bendheim P. E., Lewis G. K., DeArmond S. J., Prusiner S. B. Antibodies to the scrapie protein decorate prion rods. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):603–613. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendheim P. E., Barry R. A., DeArmond S. J., Stites D. P., Prusiner S. B. Antibodies to a scrapie prion protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 2;310(5976):418–421. doi: 10.1038/310418a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bendheim P. E., Bockman J. M., McKinley M. P., Kingsbury D. T., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie and Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease prion proteins share physical properties and antigenic determinants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):997–1001. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.997. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bockman J. M., Kingsbury D. T., McKinley M. P., Bendheim P. E., Prusiner S. B. Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease prion proteins in human brains. N Engl J Med. 1985 Jan 10;312(2):73–78. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198501103120202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Identification of a protein that purifies with the scrapie prion. Science. 1982 Dec 24;218(4579):1309–1311. doi: 10.1126/science.6815801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Molecular characteristics of the major scrapie prion protein. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 4;23(25):5898–5906. doi: 10.1021/bi00320a002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bolton D. C., Meyer R. K., Prusiner S. B. Scrapie PrP 27-30 is a sialoglycoprotein. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):596–606. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.596-606.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burnette W. N. "Western blotting": electrophoretic transfer of proteins from sodium dodecyl sulfate--polyacrylamide gels to unmodified nitrocellulose and radiographic detection with antibody and radioiodinated protein A. Anal Biochem. 1981 Apr;112(2):195–203. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90281-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesebro B., Race R., Wehrly K., Nishio J., Bloom M., Lechner D., Bergstrom S., Robbins K., Mayer L., Keith J. M. Identification of scrapie prion protein-specific mRNA in scrapie-infected and uninfected brain. Nature. 1985 May 23;315(6017):331–333. doi: 10.1038/315331a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cho H. J. Requirement of a protein component for scrapie infectivity. Intervirology. 1980;14(3-4):213–216. doi: 10.1159/000149185. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeArmond S. J., McKinley M. P., Barry R. A., Braunfeld M. B., McColloch J. R., Prusiner S. B. Identification of prion amyloid filaments in scrapie-infected brain. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):221–235. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90076-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dees C., McMillan B. C., Wade W. F., German T. L., Marsh R. F. Characterization of nucleic acids in membrane vesicles from scrapie-infected hamster brain. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):126–132. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.126-132.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickinson A. G., Meikle V. M. Host-genotype and agent effects in scrapie incubation: change in allelic interaction with different strains of agent. Mol Gen Genet. 1971;112(1):73–79. doi: 10.1007/BF00266934. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diener T. O., McKinley M. P., Prusiner S. B. Viroids and prions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Sep;79(17):5220–5224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.17.5220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diringer H., Gelderblom H., Hilmert H., Ozel M., Edelbluth C., Kimberlin R. H. Scrapie infectivity, fibrils and low molecular weight protein. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):476–478. doi: 10.1038/306476a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek D. C. Unconventional viruses and the origin and disappearance of kuru. Science. 1977 Sep 2;197(4307):943–960. doi: 10.1126/science.142303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- German T. L., McMillan B. C., Castle B. E., Dees C., Wade W. F., Marsh R. F. Comparison of RNA from healthy and scrapie-infected hamster brain. J Gen Virol. 1985 Apr;66(Pt 4):839–844. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-4-839. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis. The beta-fibrilloses (first of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 5;302(23):1283–1292. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006053022305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G. Amyloid deposits and amyloidosis: the beta-fibrilloses (second of two parts). N Engl J Med. 1980 Jun 12;302(24):1333–1343. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198006123022403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goudsmit J., Morrow C. H., Asher D. M., Yanagihara R. T., Masters C. L., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Evidence for and against the transmissibility of Alzheimer disease. Neurology. 1980 Sep;30(9):945–950. doi: 10.1212/wnl.30.9.945. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hilmert H., Diringer H. A rapid and efficient method to enrich SAF-protein from scrapie brains of hamsters. Biosci Rep. 1984 Feb;4(2):165–170. doi: 10.1007/BF01120313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kascsak R. J., Rubenstein R., Merz P. A., Carp R. I., Wisniewski H. M., Diringer H. Biochemical differences among scrapie-associated fibrils support the biological diversity of scrapie agents. J Gen Virol. 1985 Aug;66(Pt 8):1715–1722. doi: 10.1099/0022-1317-66-8-1715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimberlin R. H. Scrapie agent: prions or virinos? Nature. 1982 May 13;297(5862):107–108. doi: 10.1038/297107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornfeld R., Kornfeld S. Comparative aspects of glycoprotein structure. Annu Rev Biochem. 1976;45:217–237. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.45.070176.001245. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Legocki R. P., Verma D. P. Multiple immunoreplica Technique: screening for specific proteins with a series of different antibodies using one polyacrylamide gel. Anal Biochem. 1981 Mar 1;111(2):385–392. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90577-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Masters C. L., Gajdusek D. C., Gibbs C. J., Jr Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease virus isolations from the Gerstmann-Sträussler syndrome with an analysis of the various forms of amyloid plaque deposition in the virus-induced spongiform encephalopathies. Brain. 1981 Sep;104(3):559–588. doi: 10.1093/brain/104.3.559. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McKinley M. P., Bolton D. C., Prusiner S. B. A protease-resistant protein is a structural component of the scrapie prion. Cell. 1983 Nov;35(1):57–62. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90207-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merril C. R., Goldman D., Sedman S. A., Ebert M. H. Ultrasensitive stain for proteins in polyacrylamide gels shows regional variation in cerebrospinal fluid proteins. Science. 1981 Mar 27;211(4489):1437–1438. doi: 10.1126/science.6162199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Rohwer R. G., Kascsak R., Wisniewski H. M., Somerville R. A., Gibbs C. J., Jr, Gajdusek D. C. Infection-specific particle from the unconventional slow virus diseases. Science. 1984 Jul 27;225(4660):437–440. doi: 10.1126/science.6377496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Somerville R. A., Wisniewski H. M., Iqbal K. Abnormal fibrils from scrapie-infected brain. Acta Neuropathol. 1981;54(1):63–74. doi: 10.1007/BF00691333. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Somerville R. A., Wisniewski H. M., Manuelidis L., Manuelidis E. E. Scrapie-associated fibrils in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):474–476. doi: 10.1038/306474a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oesch B., Westaway D., Wälchli M., McKinley M. P., Kent S. B., Aebersold R., Barry R. A., Tempst P., Teplow D. B., Hood L. E. A cellular gene encodes scrapie PrP 27-30 protein. Cell. 1985 Apr;40(4):735–746. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90333-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olmsted J. B. Affinity purification of antibodies from diazotized paper blots of heterogeneous protein samples. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):11955–11957. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D. F., Bolton D. C., Kent S. B., Hood L. E. Purification and structural studies of a major scrapie prion protein. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):127–134. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90533-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., Groth D. F., Cochran S. P., McKinley M. P., Masiarz F. R. Gel electrophoresis and glass permeation chromatography of the hamster scrapie agent after enzymatic digestion and detergent extraction. Biochemistry. 1980 Oct 14;19(21):4892–4898. doi: 10.1021/bi00562a029. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B., McKinley M. P., Bowman K. A., Bolton D. C., Bendheim P. E., Groth D. F., Glenner G. G. Scrapie prions aggregate to form amyloid-like birefringent rods. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(2 Pt 1):349–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90168-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Prusiner S. B. Novel proteinaceous infectious particles cause scrapie. Science. 1982 Apr 9;216(4542):136–144. doi: 10.1126/science.6801762. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohwer R. G. Scrapie infectious agent is virus-like in size and susceptibility to inactivation. Nature. 1984 Apr 12;308(5960):658–662. doi: 10.1038/308658a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rohwer R. G. Virus like sensitivity of the scrapie agent to heat inactivation. Science. 1984 Feb 10;223(4636):600–602. doi: 10.1126/science.6420887. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somerville R. A. Ultrastructural links between scrapie and Alzheimer's disease. Lancet. 1985 Mar 2;1(8427):504–506. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(85)92097-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spiro R. G. Glycoproteins. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:599–638. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.003123. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tateishi J., Nagara H., Hikita K., Sato Y. Amyloid plaques in the brains of mice with Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Ann Neurol. 1984 Mar;15(3):278–280. doi: 10.1002/ana.410150313. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiche G., Briones E., Koszka C., Artlieb U., Krepler R. Widespread occurrence of polypeptides related to neurotubule-associated proteins (MAP-1 and MAP-2) in non-neuronal cells and tissues. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):991–998. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01918.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Merz G. S., Carp R. I. Senile dementia of the Alzheimer type: possibility of infectious etiology in genetically susceptible individuals. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl. 1984;99:91–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-0404.1984.tb05673.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]