Abstract
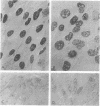
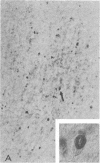
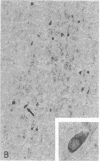
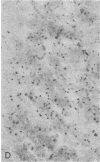
Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML) is a JC papovavirus infection of the central nervous system in immunocompromised patients. It is well established that demyelination in PML is caused by JC virus infection of oligodendroglia, but whether the nonstructural regulatory protein, large tumor (T) antigen, is detectable in infected human tissue was not known. Using a modification of the peroxidase-antiperoxidase technique, we found T antigen expressed in the nuclei of cells in virus-infected sites in five cases of PML studied, including two with acquired immune deficiency syndrome (AIDS). PML occurs in AIDS at a much higher frequency than in other immunosuppressive disorders, and PML in AIDS may represent a more severe form of JC virus infection of the central nervous system.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- ASTROM K. E., MANCALL E. L., RICHARDSON E. P., Jr Progressive multifocal leuko-encephalopathy; a hitherto unrecognized complication of chronic lymphatic leukaemia and Hodgkin's disease. Brain. 1958 Mar;81(1):93–111. doi: 10.1093/brain/81.1.93. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Arakaki Y., Watanabe S., Ikeda S., Iwamoto H., Oda T. Detection of T-antigen and surface antigen by immunoperoxidase staining of simian virus 40 transformed cells. Cell Mol Biol. 1983;29(5):461–463. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brooks B. R., Walker D. L. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. Neurol Clin. 1984 May;2(2):299–313. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chan K. F., Stoner G. L., Hashim G. A., Huang K. P. Substrate specificity of rat brain calcium-activated and phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1986 Feb 13;134(3):1358–1364. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(86)90399-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chesters P. M., Heritage J., McCance D. J. Persistence of DNA sequences of BK virus and JC virus in normal human tissues and in diseased tissues. J Infect Dis. 1983 Apr;147(4):676–684. doi: 10.1093/infdis/147.4.676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coleman D. V., Gardner S. D., Mulholland C., Fridiksdottir V., Porter A. A., Lilford R., Valdimarsson H. Human polyomavirus in pregnancy. A model for the study of defence mechanisms to virus reactivation. Clin Exp Immunol. 1983 Aug;53(2):289–296. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Deppert W., Hanke K., Henning R. Simian virus 40 T-antigen-related cell surface antigen: serological demonstration on simian virus 40-transformed monolayer cells in situ. J Virol. 1980 Aug;35(2):505–518. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.2.505-518.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frisque R. J., Bream G. L., Cannella M. T. Human polyomavirus JC virus genome. J Virol. 1984 Aug;51(2):458–469. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.2.458-469.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan T. F., Borden E. C., McBain J. A., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L. Human polyomavirus infections with JC virus and BK virus in renal transplant patients. Ann Intern Med. 1980 Mar;92(3):373–378. doi: 10.7326/0003-4819-92-3-373. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hogan T. F., Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., Borden E. C., McBain J. A. Rapid detection and identification of JC virus and BK virus in human urine by using immunofluorescence microscopy. J Clin Microbiol. 1980 Feb;11(2):178–183. doi: 10.1128/jcm.11.2.178-183.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoyama Y., Sternberger N. H., Kies M. W., Cohen S. R., Richardson E. P., Jr, Webster H. Immunocytochemical method to identify myelin basic protein in oligodendroglia and myelin sheaths of the human nervous system. Ann Neurol. 1980 Feb;7(2):157–166. doi: 10.1002/ana.410070211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Itoyama Y., Webster H. D., Sternberger N. H., Richardson E. P., Jr, Walker D. L., Quarles R. H., Padgett B. L. Distribution of papovavirus, myelin-associated glycoprotein, and myelin basic protein in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy lesions. Ann Neurol. 1982 Apr;11(4):396–407. doi: 10.1002/ana.410110414. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosaka H., Sano Y., Matsukado Y., Sairenji T., Hinuma Y. Failure to detect papovavirus-associated T antigens in human brain tumor cells by anticomplement immunofluorescence. J Neurosurg. 1980 Mar;52(3):367–370. doi: 10.3171/jns.1980.52.3.0367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krupp L. B., Lipton R. B., Swerdlow M. L., Leeds N. E., Llena J. Progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy: clinical and radiographic features. Ann Neurol. 1985 Apr;17(4):344–349. doi: 10.1002/ana.410170407. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane H. C., Fauci A. S. Immunologic abnormalities in the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:477–500. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.002401. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levy R. M., Bredesen D. E., Rosenblum M. L. Neurological manifestations of the acquired immunodeficiency syndrome (AIDS): experience at UCSF and review of the literature. J Neurosurg. 1985 Apr;62(4):475–495. doi: 10.3171/jns.1985.62.4.0475. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mázló M., Tariska I. Are astrocytes infected in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy (PML)? Acta Neuropathol. 1982;56(1):45–51. doi: 10.1007/BF00691181. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Padgett B. L., Walker D. L., ZuRhein G. M., Hodach A. E., Chou S. M. JC Papovavirus in progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy. J Infect Dis. 1976 Jun;133(6):686–690. doi: 10.1093/infdis/133.6.686. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shaw G. M., Harper M. E., Hahn B. H., Epstein L. G., Gajdusek D. C., Price R. W., Navia B. A., Petito C. K., O'Hara C. J., Groopman J. E. HTLV-III infection in brains of children and adults with AIDS encephalopathy. Science. 1985 Jan 11;227(4683):177–182. doi: 10.1126/science.2981429. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snider W. D., Simpson D. M., Nielsen S., Gold J. W., Metroka C. E., Posner J. B. Neurological complications of acquired immune deficiency syndrome: analysis of 50 patients. Ann Neurol. 1983 Oct;14(4):403–418. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140404. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stoner G. L. Predicted folding of beta-structure in myelin basic protein. J Neurochem. 1984 Aug;43(2):433–447. doi: 10.1111/j.1471-4159.1984.tb00919.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tabuchi K., Lehman J. M., Kirsch W. M. Immunocytochemical localization of simian virus 40 T antigen with peroxidase-labeled antibody fragments. J Virol. 1976 Feb;17(2):668–671. doi: 10.1128/jvi.17.2.668-671.1976. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tsuboi M. Immunocytochemical localization of T antigen in cells of BK virus-induced hamster brain tumor. Acta Med Okayama. 1983 Aug;37(4):353–366. doi: 10.18926/AMO/32388. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zu Rhein G. M. Association of papova-virions with a human demyelinating disease (progressive multifocal leukoencephalopathy). Prog Med Virol. 1969;11:185–247. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]