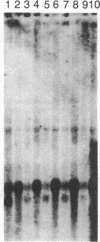
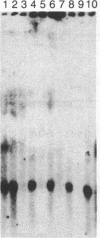
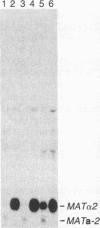
Abstract
We have excised a 28-base-pair DNA fragment from the MAT alpha intergenic region and tested its ability to direct diploid-specific transcriptional repression. This fragment (1643-1671, 5'-GCTTCCCAATGTAGAAAAGTACA-TCATA-3') lies within a region required for the normal diploid-specific repression of the MAT alpha transcripts. First, the fragment was inserted into a 53-base-pair MAT alpha deletion that expresses alpha 1 and alpha 2 constitutively. Insertion of the fragment restores proper diploid regulation to the MAT alpha transcripts: alpha 1 mRNA is strongly repressed and alpha 2 mRNA is reduced by a factor of approximately equal to 10 from its haploid level. The fragment works equally well in either orientation, and two copies of the fragment do not lead to stronger repression than a single copy. We also inserted the fragment at three sites upstream of the CYC1-lacZ fusion gene. Insertions placing the regulatory fragment between the CYC1 upstream activator sequence (UAS) and the coding region make beta-galactosidase efficiently in alpha haploids but produce 1/40th the enzyme in a/alpha diploids. This diploid-specific repression requires functional MATa-1 gene product. Insertion of the MAT fragment on the opposite side of the UAS (37 base pairs upstream of the UAS) also caused diploid repression of the fusion gene, but only by a factor of 7. When the regulatory fragment is inserted at a large distance on the far side of the UAS (375 base pairs), it has little if any effect on beta-galactosidase expression. We postulate that this sequence is the operator recognized by the diploid-specific repressor.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Astell C. R., Ahlstrom-Jonasson L., Smith M., Tatchell K., Nasmyth K. A., Hall B. D. The sequence of the DNAs coding for the mating-type loci of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):15–23. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90356-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Cardillo T. S., Sherman F., Dubois E., Deschamps J., Wiame J. M. Mating signals control expression of mutations resulting from insertion of a transposable repetitive element adjacent to diverse yeast genes. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(2 Pt 2):427–436. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90353-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Errede B., Company M., Ferchak J. D., Hutchison C. A., 3rd, Yarnell W. S. Activation regions in a yeast transposon have homology to mating type control sequences and to mammalian enhancers. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5423–5427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Lalonde B., Gifford P., Alani E. Distinctly regulated tandem upstream activation sites mediate catabolite repression of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):503–511. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90243-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Mason T. Heme regulates transcription of the CYC1 gene of S. cerevisiae via an upstream activation site. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1279–1286. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90309-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L., Ptashne M. Fusion of Escherichia coli lacZ to the cytochrome c gene of Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2199–2203. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guarente L. Yeast promoters and lacZ fusions designed to study expression of cloned genes in yeast. Methods Enzymol. 1983;101:181–191. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(83)01013-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Hereford L., Herskowitz I. Targeting of E. coli beta-galactosidase to the nucleus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):1057–1065. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90055-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson A. D., Herskowitz I. A repressor (MAT alpha 2 Product) and its operator control expression of a set of cell type specific genes in yeast. Cell. 1985 Aug;42(1):237–247. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80119-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klar A. J., Strathern J. N., Broach J. R., Hicks J. B. Regulation of transcription in expressed and unexpressed mating type cassettes of yeast. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):239–244. doi: 10.1038/289239a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. M., MacKay V. L., Nasmyth K. A. Identification and comparison of two sequence elements that confer cell-type specific transcription in yeast. Nature. 1985 Apr 18;314(6012):598–603. doi: 10.1038/314598a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A. Molecular genetics of yeast mating type. Annu Rev Genet. 1982;16:439–500. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.16.120182.002255. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nasmyth K. A., Tatchell K., Hall B. D., Astell C., Smith M. A position effect in the control of transcription at yeast mating type loci. Nature. 1981 Jan 22;289(5795):244–250. doi: 10.1038/289244a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Siliciano P. G., Tatchell K. Transcription and regulatory signals at the mating type locus in yeast. Cell. 1984 Jul;37(3):969–978. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90431-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J., Hicks J., Herskowitz I. Control of cell type in yeast by the mating type locus. The alpha 1-alpha 2 hypothesis. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 15;147(3):357–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90488-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taguchi A. K., Ciriacy M., Young E. T. Carbon source dependence of transposable element-associated gene activation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Mol Cell Biol. 1984 Jan;4(1):61–68. doi: 10.1128/mcb.4.1.61. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tatchell K., Nasmyth K. A., Hall B. D., Astell C., Smith M. In vitro mutation analysis of the mating-type locus in yeast. Cell. 1981 Nov;27(1 Pt 2):25–35. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90357-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williamson V. M., Cox D., Young E. T., Russell D. W., Smith M. Characterization of transposable element-associated mutations that alter yeast alcohol dehydrogenase II expression. Mol Cell Biol. 1983 Jan;3(1):20–31. doi: 10.1128/mcb.3.1.20. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]