Abstract
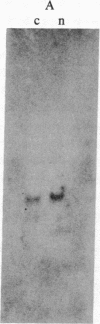
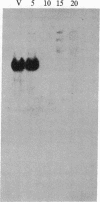
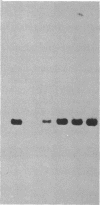
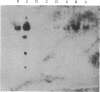
We describe the gene M4-1, whose unique pattern of developmental expression will allow us to study the molecular mechanisms controlling expression in undifferentiated cells in addition to repression in response to cAMP during development and reinduction during dedifferentiation. M4-1 is a Dictyostelium gene expressed in the undifferentiated cell. We have shown that M4-1 continues to be expressed very early during the developmental cycle but is repressed at a later stage of development, at a time coincident with the establishment of oscillations in the cAMP pool. Studies on the expression of the M4-1 gene in shaking culture, under conditions that mimic early development, have established that pulsatile stimulation of cells with cAMP is sufficient to repress M4-1 expression. Consistent with this, cells that are exposed to high levels of cAMP are unable to respond normally to cAMP oscillations and continue to express M4-1 at vegetative levels. These data indicate that low-level oscillations of cAMP are required for the repression of M4-1 expression rather than the continuous high levels of cAMP responsible for the regulation of a different class of Dictyostelium genes. We suggest that cAMP may mediate developmental expression of the Dictyostelium genome by different mechanisms. We also show that cell-cell interaction, a developmental event that occurs subsequent to the cAMP pulse, does not normally influence the regulation of M4-1. Finally, we have shown that when cAMP-pulsed cells are induced to dedifferentiate, M4-1 RNA sequences rapidly reappear in nuclei and cytoplasm, suggesting that regulation of M4-1 expression is primarily mediated at the level of transcription.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Alton T. H., Lodish H. F. Synthesis of developmentally regulated proteins in Dictyostelium discoideum which are dependent on continued cell-cell interaction. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):207–216. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90119-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barklis E., Lodish H. F. Regulation of dictyostelium discoideum mRNAs specific for prespore or prestalk cells. Cell. 1983 Apr;32(4):1139–1148. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90297-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berger E. A., Clark J. M. Specific cell-cell contact serves as the developmental signal to deactivate discoidin I gene expression in Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Aug;80(16):4983–4987. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.16.4983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg D. D., Lodish H. F. Changes in the messenger RNA population during differentiation of dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1980 Aug;78(2):285–300. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(80)90337-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg D. D., Margolskee J. P., Barklis E., Chung S. N., Cohen N. S., Lodish H. F. Specific cell-cell contacts are essential for induction of gene expression during differentiation of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jan;79(1):127–131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.1.127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cardelli J. A., Knecht D. A., Wunderlich R., Dimond R. L. Major changes in gene expression occur during at least four stages of development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Dev Biol. 1985 Jul;110(1):147–156. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90072-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Steck T. L., Devreotes P. N. Cyclic 3',5'-AMP relay in Dictyostelium discoideum IV. Recovery of the cAMP signaling response after adaptation to cAMP. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):545–553. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinauer M. C., Steck T. L., Devreotes P. N. Cyclic 3',5'-AMP relay in Dictyostelium discoideum V. Adaptation of the cAMP signaling response during cAMP stimulation. J Cell Biol. 1980 Aug;86(2):554–561. doi: 10.1083/jcb.86.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Finney R. E., Langtimm C. J., Soll D. R. Regulation of protein synthesis during the preaggregative period of Dictyostelium discoideum development: involvement of close cell associations and cAMP. Dev Biol. 1985 Jul;110(1):171–191. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(85)90074-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gerisch G., Wick U. Intracellular oscillations and release of cyclic AMP from Dictyostelium cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1975 Jul 8;65(1):364–370. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(75)80102-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R., Firtel R. A. A family of short, interspersed repeat sequences at the 5' end of a set of Dictyostelium single-copy mRNAs. Cell. 1979 Apr;16(4):787–796. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90094-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R., Firtel R. A. Intervening sequences in a Dictyostelium gene that encodes a low abundance class mRNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1980 Dec 11;8(23):5599–5610. doi: 10.1093/nar/8.23.5599. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R., Firtel R. A. Sequence organization and developmental expression of an interspersed, repetitive element and associated single-copy DNA sequences in Dictyostelium discoideum. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Aug;5(8):2123–2130. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.8.2123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimmel A. R., Firtel R. A. Sequence organization in Dictyostelium: unique structure at the 5'-ends of protein coding genes. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Jan 25;11(2):541–552. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.2.541. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konijn T. M. Microbiological assay of cyclic 3',5'-AMP. Experientia. 1970 Apr 15;26(4):367–369. doi: 10.1007/BF01896891. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lin M. C., Koh S. W., Dykman D. D., Beckner S. K., Shih T. Y. Loss and restoration of glucagon receptors and responsiveness in a transformed kidney cell line. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Nov;142(1):181–189. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90421-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malchow D., Gerisch G. Short-term binding and hydrolysis of cyclic 3':5'-adenosine monophosphate by aggregating Dictyostelium cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1974 Jun;71(6):2423–2427. doi: 10.1073/pnas.71.6.2423. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mehdy M. C., Ratner D., Firtel R. A. Induction and modulation of cell-type-specific gene expression in Dictyostelium. Cell. 1983 Mar;32(3):763–771. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90062-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palatnik C. M., Storti R. V., Capone A. K., Jacobson A. Messenger RNA stability in Dictyostelium discoideum: does poly(A) have a regulatory role? J Mol Biol. 1980 Aug 5;141(2):99–118. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(80)90379-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schaller K. L., Leichtling B. H., Majerfeld I. H., Woffendin C., Spitz E., Kakinuma S., Rickenberg H. V. Differential cellular distribution of cAMP-dependent protein kinase during development of Dictyostelium discoideum. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2127–2131. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2127. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomchik K. J., Devreotes P. N. Adenosine 3',5'-monophosphate waves in Dictyostelium discoideum: a demonstration by isotope dilution--fluorography. Science. 1981 Apr 24;212(4493):443–446. doi: 10.1126/science.6259734. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waddell D. R., Soll D. R. A characterization of the erasure phenomenon in dictyostelium. Dev Biol. 1977 Oct 1;60(1):83–92. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90111-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]