Abstract
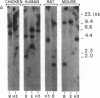
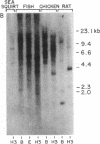
Mouse and rat small intestinal cDNA libraries were screened for recombinants derived from mRNAs whose concentration changed during the transition from suckling to weaning. cDNAs transcribed from a 570-nucleotide-long mRNA were isolated. Dot blot hybridization analyses of RNA recovered at various stages of rat gastrointestinal ontogeny indicated that the concentration of this mRNA begins to increase during the mid-suckling period, reaching a peak during weaning. There is considerable variation in the relative amount of this mRNA in adult tissues, with highest levels encountered in the rat small intestine and colon. Its concentration in duodenum, jejunum, and ileum is approximately the same. It is more concentrated in villi than in crypts. The rat mRNA encodes a 77 amino acid, 8.55-kDa polypeptide that has seven cysteine residues. This cysteine-rich intestinal protein (named CRIP) has two internal repeated sequence blocks. Computer-assisted comparisons of CRIP to proteins of known function disclosed that it is homologous to certain ferredoxins. Southern blot analyses revealed that sequences homologous to the rat gene are present in sea squirt, fish, bird, and human DNA, indicating that this gene is highly conserved and that related proteins may be present in many if not all vertebrates. Recombinant inbred mouse strains were utilized to show that the CRIP gene is closely linked to the immunoglobulin heavy chain constant region locus, Igh-c, on chromosome 12. CRIP mRNA is a molecular marker for the suckling-to-weaning transition of rodent intestinal development. The cloned cDNA may be a useful probe for identifying factors that regulate intestinal development during this period.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Birkenmeier E., Alpers D. H. Enzymatic properties of rat lactase-phlorizin hydrolase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1974 May 20;350(1):100–112. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(74)90207-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Boguski M. S., Elshourbagy N., Taylor J. M., Gordon J. I. Rat apolipoprotein A-IV contains 13 tandem repetitions of a 22-amino acid segment with amphipathic helical potential. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5021–5025. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5021. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels V. G., Hardy R. N., Malinowska K. W., Nathanielsz P. W. The influence of exogenous steroids on macromolecule uptake by the small intestine of the new-born rat. J Physiol. 1973 Mar;229(3):681–695. doi: 10.1113/jphysiol.1973.sp010160. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dayhoff M. O., Barker W. C., Hunt L. T. Establishing homologies in protein sequences. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:524–545. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91049-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson J. J., Messer M. Intestinal neuraminidase activity of suckling rats and other mammals. Relationship to the sialic acid content of milk. Biochem J. 1978 Feb 15;170(2):407–413. doi: 10.1042/bj1700407. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dietschy J. M., Siperstein M. D. Cholesterol synthesis by the gastrointestinal tract: localization and mechanisms of control. J Clin Invest. 1965 Aug;44(8):1311–1327. doi: 10.1172/JCI105237. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elshourbagy N. A., Boguski M. S., Liao W. S., Jefferson L. S., Gordon J. I., Taylor J. M. Expression of rat apolipoprotein A-IV and A-I genes: mRNA induction during development and in response to glucocorticoids and insulin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(23):8242–8246. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.23.8242. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fernando-Warnakulasuriya G. J., Staggers J. E., Frost S. C., Wells M. A. Studies on fat digestion, absorption, and transport in the suckling rat. I. Fatty acid composition and concentrations of major lipid components. J Lipid Res. 1981 May;22(4):668–674. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frost S. C., Clark W. A., Wells M. A. Studies on fat digestion, absorption, and transport in the suckling rat. IV. In vivo rates of triacylglycerol secretion by intestine and liver. J Lipid Res. 1983 Jul;24(7):899–903. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- George D. G., Hunt L. T., Yeh L. S., Barker W. C. New perspectives on bacterial ferredoxin evolution. J Mol Evol. 1985;22(1):20–31. doi: 10.1007/BF02105801. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gordon J. I., Elshourbagy N., Lowe J. B., Liao W. S., Alpers D. H., Taylor J. M. Tissue specific expression and developmental regulation of two genes coding for rat fatty acid binding proteins. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):1995–1998. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henning S. J. Postnatal development: coordination of feeding, digestion, and metabolism. Am J Physiol. 1981 Sep;241(3):G199–G214. doi: 10.1152/ajpgi.1981.241.3.G199. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herbst J. J., Sunshine P. Postnatal development of the small intestine of the rat. Changes in mucosal morphology at weaning. Pediatr Res. 1969 Jan;3(1):27–33. doi: 10.1203/00006450-196901000-00004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak L. P., Birkenmeier E. H. Mouse sn-glycerol-3-phosphate dehydrogenase: molecular cloning and genetic mapping of a cDNA sequence. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 May;80(10):3020–3024. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.10.3020. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLachlan A. D. Analysis of gene duplication repeats in the myosin rod. J Mol Biol. 1983 Sep 5;169(1):15–30. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(83)80173-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J. C., Barth R. K., Shaw P. H., Elliott R. W., Hastie N. D. Identification of a cDNA clone for mouse apoprotein A-1 (apo A-1) and its use in characterization of apo A-1 mRNA expression in liver and small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(6):1511–1515. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.6.1511. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nadeau J. H., Taylor B. A. Lengths of chromosomal segments conserved since divergence of man and mouse. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(3):814–818. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.3.814. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouellette A. J. Metallothionein mRNA expression in fetal mouse organs. Dev Biol. 1982 Jul;92(1):240–246. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(82)90168-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. S. Developmental studies of mouse hereditary anemias. Am J Med Genet. 1984 Aug;18(4):621–641. doi: 10.1002/ajmg.1320180410. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilbur W. J., Lipman D. J. Rapid similarity searches of nucleic acid and protein data banks. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Feb;80(3):726–730. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.3.726. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yeh K. Y., Moog F. Development of the small intestine in the hypophysectomized rat. I. Growth histology, and activity of alkaline phosphatase, maltase, and sucrase. Dev Biol. 1975 Nov;47(1):156–172. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(75)90270-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]