Abstract
Background and Purpose:
Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients with severe cirrhosis are usually treated with supportive care because of their poor prognosis. However, the survival of severe cirrhotic patients has recently improved due to advanced treatments. The aim of this study was to define the role of proton beam therapy for HCC patients with severe cirrhosis.
Patients and Methods:
19 HCC patients with Child-Pugh class C cirrhosis received proton beam therapy. The hepatic tumors were solitary in 14 patients and multiple in five, and the tumor size was 25–80 mm (median 40 mm) in maximum diameter. No patient had regional lymph node or distant metastasis. Total doses of 50–84 Gy (median 72 Gy) in ten to 24 fractions (median 16) were delivered to the tumors.
Results:
Of the 19 patients, six, eight and four died of cancer, liver failure and intercurrent diseases, respectively, during the follow-up period of 3–63 months (median 17 months) after treatment. A remaining patient was alive with no evidence of disease 33 months after treatment. All but one of irradiated tumors were controlled during the follow-up period. Ten patients had new intrahepatic tumors outside the irradiated volume. The overall and progression-free survival rates were 53% and 47% at 1 year, respectively, and 42% each at 2 years. Performance status and Child-Pugh score were significant prognostic factors for survival. Therapy-related toxicity of grade 3 or more was not observed.
Conclusion:
Proton beam therapy for HCC patients with severe cirrhosis was tolerable. It may improve survival for patients with relatively good general condition and liver function.
Key Words: Hepatocellular carcinoma, Proton beam therapy, Radiation therapy, Severe cirrhosis
Schlüsselwörter: Leberzellkarzinom, Protonentherapie, Strahlentherapie, Schwere Zirrhose
Abstract
Hintergrund und Ziel:
Patienten mit Leberzellkarzinom (HCC [„hepatocellular carcinoma“]) und schwerer Zirrhose werden aufgrund der schlechten Prognose gewöhnlich konservativ behandelt. Allerdings haben fortschrittliche Therapien in letzter Zeit zu einer Verbesserung der Überlebenszeit von Patienten mit schwerer Zirrhose geführt. Das Ziel der vorliegenden Studie war die Bestimmung der Rolle einer Protonentherapie für HCC-Patienten mit schwerer Zirrhose.
Patienten und Methodik:
19 HCC-Patienten mit Zirrhose der Child-Pugh-Klasse C wurden mit Protonenstrahlen behandelt. 14 Patienten wiesen einzelne und fünf Patienten multiple Lebertumoren auf. Hinsichtlich der Tumorgröße variierte der maximale Durchmesser dabei zwischen 25 und 80 mm (durchschnittlich 40 mm). Keiner der Patienten hatte regionäre Lymphknoten- oder Fernmetastasen in regionären oder entfernten Lymphknoten. Die Gesamtstrahlendosis betrug 50–84 Gy (durchschnittlich 72 Gy) und wurde in zehn bis 24 Fraktionen (durchschnittlich 16 Fraktionen) verabreicht.
Ergebnisse:
Im Nachuntersuchungszeitraum von 3–63 Monaten (durchschnittlich 17 Monate) verstarben sechs der insgesamt 19 Patienten an Krebs, acht an Leberversagen und vier an interkurrierenden Erkrankungen. Ein Patient war 33 Monate nach der Behandlung ohne Krankheitszeichen am Leben. Mit einer Ausnahme wurden alle Tumoren während der Nachuntersuchung mit entsprechenden Kontrollen verglichen. Zehn Patienten hatten intrahepatische Tumoren, die außerhalb des bestrahlten Bereichs lagen. Die Gesamt- und die progressionsfreie Überlebensrate betrugen nach 1 Jahr 53% und 47% und nach 2 Jahren 42%. Der Performance-Status und die Child-Pugh-Bewertung waren wichtige prognostische Faktoren für das Überleben.
Schlussfolgerung:
Die Protonentherapie war für Patienten mit Leberzellkarzinom und schwerer Zirrhose tolerabel. Die Behandlung könnte das Überleben von Patienten mit relativ gutem Allgemeinzustand und guter Leberfunktion verbessern.
Introduction
Currently, hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) patients can be effectively treated with various modalities, i.e., surgical resection, transcatheter arterial embolization (TAE) and infusion chemotherapy (TAI), percutaneous ethanol injection (PEI) and microwave coagulation (PMC), and radiofrequency ablation (RFA) [16]. However, these treatment modalities are often unsuitable for patients with severe cirrhosis because of the potential risk of liver failure or bleeding; furthermore, their prognosis is poor due to severe cirrhosis [8]. Therefore, HCC patients with severe cirrhosis are usually treated with palliative or supportive care [3].
At our institute, University of Tsukuba, Japan, proton beams have been employed in treatment for a variety of malignancies including HCC since 1983 [4, 11, 19, 30]. Proton beam irradiation yields theoretically excellent dose localization to the target due to sharp distal fall-off of the Bragg peak compared with photon irradiation, and consequently can reduce the irradiated volume and dose given to the hepatic parenchyma and digestive tract for HCC patients, while increasing the dose to the tumor [12, 21, 26, 28].
We present herein the treatment results of proton beam therapy for HCC patients with severe cirrhosis.
Patients and Methods
Patients
Between November 1990 and January 2000, 197 HCC patients received proton beam therapy. Of these patients, 19 had severe cirrhosis categorized as Child-Pugh class C at the initiation of proton beam therapy [25]. All patients were inoperable, and TAE and TAI were contraindicated due to the potential risk of liver failure. PEI, PMC and RFA were unfeasible because of bleeding tendency, large-sized tumors, or unfavorable tumor location. There were no other available treatment modalities for these patients. Exclusion criteria for proton beam therapy included extrahepatic metastasis, diffusely infiltrated tumor, and poor general condition of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group (ECOG) performance status ≥3 [23].
HCCs were diagnosed histopathologically by biopsy in eight patients, and clinically by medical imaging; contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), and elevated serum α-fetoprotein (AFP) values in eleven patients. None had regional lymph node enlargement or distant metastasis. 14 and five patients were diagnosed clinically as stage I (T1 N0 M0) and stage II (T2 N0 M0), respectively, based on the TNM classification defined by the International Union Against Cancer (UICC), at the time of proton beam irradiation [27].
Patient and tumor characteristics are summarized in Table 1. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients before initiation of proton beam therapy.
Table 1.
Patient and tumor characteristics. HBV:hepatitis B virus; HCV: hepatitis C virus; AFP: α-fetoprotein.
| Total number of patients | 19 |
| Gender | |
| • Male | 14 |
| • Female | 5 |
| Age (years) | |
| • Range | 51–69 |
| • Median | 61 |
| Performance status | |
| • 0 | 1 |
| • 1 | 10 |
| • 2 | 8 |
| Etiology of cirrhosis | |
| • HBV | 1 |
| • HCV | 16 |
| • Alcohol | 2 |
| Child-Pugh score | |
| • 10 | 4 |
| • 11 | 2 |
| • 12 | 8 |
| • 13 | 3 |
| • 14 | 2 |
| Number of tumors | |
| • Solitary | 14 |
| • Multiple | 5 |
| Tumor size (mm) | |
| • Range | 25–80 |
| • Median | 40 |
| Serum AFP value (ng/ml) | |
| • Range | 2–12,539 |
| • Median | 93 |
Proton Beam Therapy
Metallic fiducial markers for proton beam therapy were implanted percutaneously into the hepatic parenchyma beside the tumors. Treatment planning for proton beam therapy was based on CT images at 5-mm intervals in the treatment position. Clinical target volume (CTV) was defined as gross tumor volume plus 5-mm margin. Planning target volume, which included CTV with 5-mm margin, was homogeneously set at the 100% dose level by utilizing the spread-out Bragg peak (SOBP) of proton beams (Figure 1). Multiple hepatic tumors, which were observed in five patients, were entirely included within the target volume.
Figure 1.
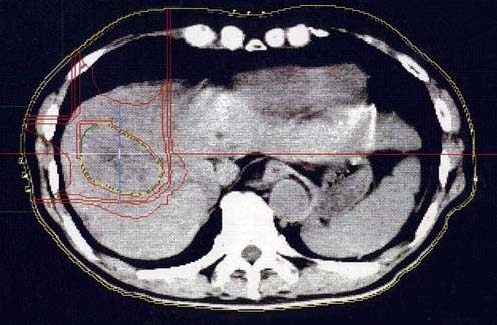
Isodose distribution with the anterior and right lateral proton beams in a hepatocellular carcinoma patient with severe cirrhosis. Each isodose line corresponds to 90%, 50%, 30%, and 10% dose levels from the inside out, respectively. The critical organs such as the spinal cord and the digestive tracts are located entirely outside the irradiated volume due to sharp distal fall-off of the Bragg peak of proton beams.
Proton beams generated by a booster synchrotron of the High Energy Accelerator Research Organization were degraded to ≤ 250 MeV for clinical use. The beams synchronized with respiration were delivered through the horizontal or vertical port for treatment. Respiratory gating was controlled by means of a strain gauge (Kyowa Electronic Instruments, Tokyo, Japan) attached to the abdominal surface of the patients, so that proton beams were delivered to the tumors in expiratory phase when the tumor position was considered to be most stable and reproducible [13, 22]. For each treatment session, the positional relationship between the center of the target and the fiducial markers was examined, with the patients lying in the treatment position, by the fluoroscopy unit attached to the treatment unit.
Fraction size was 3–5 Gy daily, 3–5 days per week; total doses were 50–84 Gy (median 72 Gy) in ten to 24 fractions (median 16). A relative biological effectiveness value of 1.0 was utilized in accordance with data obtained from fibrosarcoma NFSa cells [2]. Evaluation by doses of 2 Gy per fraction-equivalent calculated using a linear-quadratic model with α/β ratios of 10 and 3 for early and late responding tissues revealed total doses equivalent to 63–95 Gy (median 87 Gy) and 79–109 Gy (median 107 Gy), respectively [31].
Follow-up Procedure and Evaluation Criteria
The patients had serum AFP value measurements and abdominal imaging studies (CT or MRI) approximately 1 and 2 months after completion of proton beam therapy, respectively, and then were followed at intervals of 1–3 months. Local responses to proton beam therapy were classified according to the World Health Organization (WHO) response evaluation criteria [20]. No growth of the irradiated tumors was defined as progression-free.
Acute and late toxicities associated with treatment were evaluated with RTOG acute radiation morbidity scoring criteria and RTOG/EORTC late radiation morbidity scoring scheme, respectively [5].
Statistical Analysis
The actuarial survival rates and the progression- and disease-free rates were calculated according to the Kaplan-Meier method [14]. The prognostic factors for survival were evaluated by the log-rank test [1]. The changes of variables in blood tests were examined by the paired t-test. p < 0.05 was considered statistically significant. All statistical analyses were performed using the statistical software SPSS 11.0J (SPSS Inc., Chicago, IL, USA).
Results
Tumor Control and Failure Patterns
Tumor responses were complete response (CR) in nine patients, partial response (PR) in three, no change (NC) in six, and progressive disease (PD) in one. The objective response (CR and PR) rate was 63%. The pre- and posttreatment CT images of a patient are shown in Figure 2. Consequently, all but one of irradiated tumors were controlled at the median follow-up period of 17 months (range, 3–63 months) after treatment; the progression-free rate was 91%. AFP values of 14 patients which had shown high levels of 30–12,539 ng/ml (median 145 ng/ml) beyond the upper normal limit of 20 ng/ml before irradiation decreased to 1–2,141 ng/ml (median 19 ng/ml), to normal range in seven patients, after irradiation.
Figures 2a and 2b.
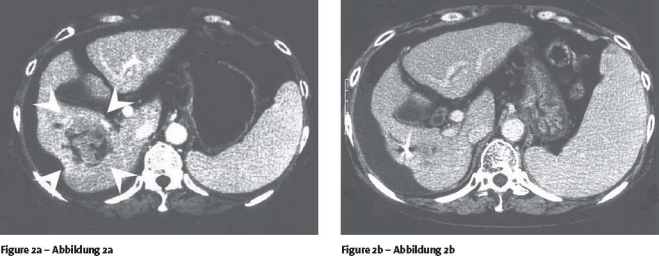
Contrast-enhanced CT in arterial phase of a hepatocellular carcinoma patient with severe cirrhosis. a) Just before initiation of proton beam therapy. Arrowheads represent position of the hepatic tumor enhanced inhomogeneously. b) 7 months after completion of proton beam therapy. The marked reduction of the tumor volume is demonstrated. The intrahepatic high-density region corresponds to an implanted metallic fiducial marker.
Ten patients had new hepatic tumors outside the irradiated volume 4–30 months after treatment. None had distant metastases. Of the ten patients with recurrence, two (patients # 1 and 2) received second courses of proton beam therapy and all recurrent tumors were controlled after reirradiation. For the remaining eight patients, radical treatment was considered contraindicated due to further deteriorated cirrhosis.
The disease-free rates were 51% at 1 year and 31% at 2 years (Figure 3). The summaries of all patients divided into two groups according to survival time (over or within 1 year) are shown in Tables 2 and 3.
Figure 3.
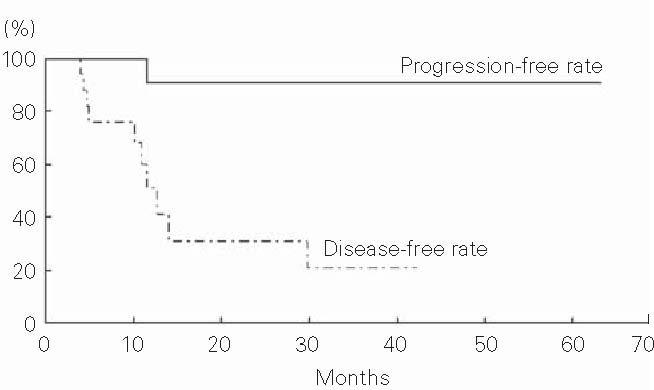
Progression-free and disease-free rates of 19 hepatocellular carcinoma patients with severe cirrhosis treated with proton beams.
Table 2.
Summary of ten hepatocellular carcinoma patients with severe cirrhosis who survived for > 1 year after proton beam therapy. CR: complete response; F: female; HBV: hepatitis B virus; HCV: hepatitis C virus; ICH: intracranial hemorrhage; IOIV: inside and outside of the irradiated volume; M: male; NED: no evidence of disease; OIV: outside of the irradiated volume; PD: progressive disease; PR: partial response; PS: performance status.
| Patient # | Age (years)/gender | PS | Etiology of cirrhosis | Child-Pugh score | Number of tumors | Tumor size (mm) | Total dose (Gy/fractions) | Tumor response | Pattern of failure | Follow-up (months) and status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 67/M | 1 | HCV | 10 | Solitary | 50 | 84/24 | CR | Liver (OIV) | 63, dead of trauma |
| 2 | 54/M | 1 | HCV | 10 | Multiple | 25 | 84/24 | CR | Liver (OIV) | 56, dead of cancer |
| 3 | 68/M | 2 | HCV | 13 | Solitary | 35 | 72.5/19 | CR | None | 42, dead of liver failure |
| 4 | 66/F | 0 | Alcohol | 12 | Solitary | 30 | 72/16 | CR | Liver (OIV) | 37, dead of cancer |
| 5 | 63/F | 2 | HCV | 12 | Solitary | 60 | 67.5/15 | PR | Liver (OIV) | 17, dead of cancer |
| 6 | 60/F | 1 | HCV | 11 | Solitary | 40 | 72/16 | CR | Liver (OIV) | 57, dead of ICH |
| 7 | 52/M | 2 | HCV | 14 | Solitary | 35 | 50/10 | PD | Liver (OIV) | 19, dead of liver failure |
| 8 | 59/M | 1 | HCV | 10 | Solitary | 35 | 72/16 | CR | Liver (OIV) | 32, dead of cancer |
| 9 | 66/M | 1 | HCV | 11 | Solitary | 30 | 72/16 | CR | Liver (OIV) | 45, dead of liver failure |
| 10 | 53/M | 1 | HCV | 12 | Solitary | 35 | 50/10 | CR | None | 33, alive with NED |
Table 3.
Summary of nine hepatocellular carcinoma patients with severe cirrhosis who died within 1 year after proton beam therapy. CR: complete response; F: female; HBV: hepatitis B virus; HCV: hepatitis C virus; ICH: intracranial hemorrhage; IP: interstitial pneumonitis; M: male; NC: no change; OIV: outside of the irradiated volume; PR: partial response; PS: performance status.
| Patient # | Age (years)/gender | PS | Etiology of cirrhosis | Child-Pugh score | Number of tumors | Tumor size (mm) | Total dose (Gy/fractions) | Tumor response | Pattern of failure | Follow-up (months) and status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 60/M | 2 | HCV | 12 | Multiple | 45 | 77/22 | CR | None | 4, dead of ICH |
| 12 | 62/M | 1 | HBV | 13 | Solitary | 36 | 84/24 | NC | None | 5, dead of liver failure |
| 13 | 57/M | 2 | HCV | 10 | Solitary | 80 | 64/15 | NC | None | 3, dead of IP |
| 14 | 62/M | 1 | HCV | 12 | Multiple | 55 | 72/18 | PR | None | 10, dead of liver failure |
| 15 | 62/M | 2 | HCV | 12 | Solitary | 30 | 68.8/16 | PR | Liver (OIV) | 6, dead of cancer |
| 16 | 58/F | 1 | Alcohol | 12 | Solitary | 40 | 68/14 | NC | Liver (OIV) | 6, dead of cancer |
| 17 | 69/M | 2 | HCV | 14 | Multiple | 41 | 72/16 | NC | None | 5, dead of liver failure |
| 18 | 66/M | 1 | HCV | 13 | Solitary | 57 | 72/16 | NC | None | 12, dead of liver failure |
| 19 | 61/F | 2 | HCV | 12 | Multiple | 55 | 66/22 | NC | None | 6, dead of liver failure |
Pre- and Posttreatment Liver Function
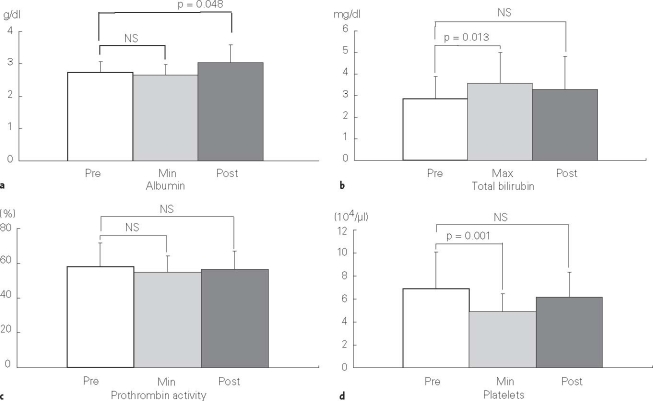
Pre- and posttreatment (1 month after treatment) mean ± standard deviation (SD) values of serum albumin and total bilirubin, prothrombin activity, and platelets, and those during treatment in all patients are summarized in Table 4. Although the mean value of total bilirubin increased and that of platelets decreased transiently during treatment, in comparison with each pretreatment mean value, there were no significant differences between the pre- and posttreatment mean values (Figure 4).
Table 4.
Mean values ± SD in serum albumin, total bilirubin, prothrombin activity, and platelets before, during and at 1 month after proton beam therapy. SD: standard deviation.
| Variable | Before treatment Mean ± SD | During treatmenta | After treatment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Albumin (g/dl) | 2.7 ± 0.3 | 2.6 ± 0.3 | 3.0 ± 0.6 |
| Total bilirubin (mg/dl) | 2.8 ± 1.1 | 3.6 ± 1.5 | 3.3 ± 1.5 |
| Prothrombin activity (%) | 58.0 ± 13.8 | 55.1 ± 9.4 | 56.8 ± 10.0 |
| Platelets (× 104/μl) | 6.9 ± 3.2 | 4.9 ± 1.5 | 6.2 ± 2.2 |
a mean ± SD of minimum values in albumin, prothrombin activity and platelets and of maximum values in total bilirubin for individuals
Figures 4a to 4d.
Pretreatment (Pre), maximum (Max) or minimum (Min) during treatment, and posttreatment (Post) mean values ± SD of a) serum albumin, b) total bilirubin, c) prothrombin activity, and d) platelets. NS: not significant.
There was no deterioration in Child-Pugh score, but rather an improvement in 14 patients.
Survival and Prognostic Factors
Of 19 patients, six and eight died of cancer 6–56 months and liver failure 5–45 months after treatment, respectively. Of the remaining five patients, four died of intercurrent diseases (n = 2 intracranial hemorrhage, n = 1 trauma, and n = 1 interstitial pneumonitis due to coexisting pulmonary fibrosis) and another was alive with no evidence of disease 33 months after treatment. The progression-free survival rates were 47% at 1 year and 42% at 2 years, and the median progression-free survival time was 12 months (Figure 5). The overall survival rates were 53% and 42% at 1 and 2 years, respectively, and the median overall survival time was 17 months (Figure 6).
Figure 5.
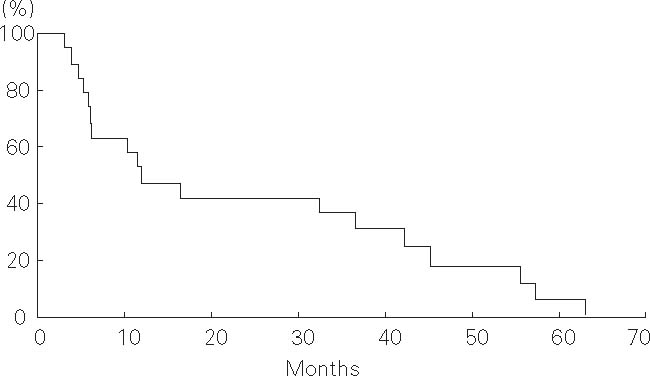
Progression-free survival of 19 hepatocellular carcinoma patients with severe cirrhosis treated with proton beams.
Figure 6.
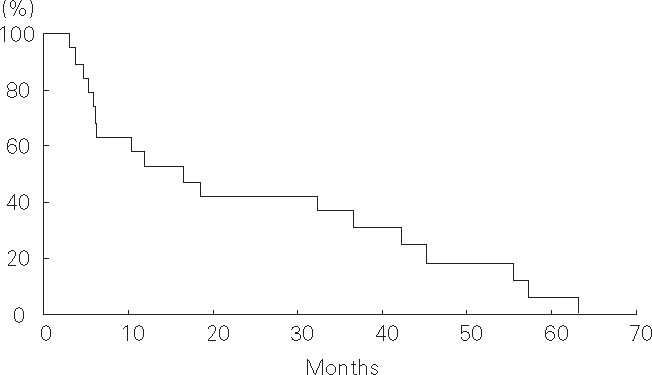
Overall survival of 19 hepatocellular carcinoma patients with severe cirrhosis treated with proton beams.
Performance status and Child-Pugh score were significant prognostic factors for survival (Table 5).
Table 5.
Results of Kaplan-Meier estimate and univariate analysis of prognostic factors for survival. AFP: α-fetoprotein.
| Prognostic factor | Patients (n) | Overall survival rates (%) | p-value | |
| 1 year | 2 years | |||
| Gender | ||||
| • Male | 14 | 50 | 43 | 0.976 |
| • Female | 5 | 60 | 40 | |
| Age (years) | ||||
| • < 61 | 9 | 67 | 56 | 0.544 |
| • ≥ 61 | 10 | 40 | 30 | |
| Performance status | ||||
| • 0–1 | 11 | 64 | 64 | 0.014 |
| • 2 | 8 | 38 | 13 | |
| Child-Pugh score | ||||
| • 10–11 | 6 | 83 | 83 | 0.015 |
| • 12–14 | 13 | 38 | 23 | |
| Number of tumors | ||||
| • Solitary | 14 | 64 | 50 | 0.234 |
| • Multiple | 5 | 20 | 20 | |
| Tumor size (mm) | ||||
| • < 40 | 9 | 78 | 67 | 0561 |
| • ≥ 40 | 10 | 30 | 20 | |
| Serum AFP value (ng/ml) | ||||
| • < 93 | 9 | 56 | 44 | 0.522 |
| • ≥ 93 | 10 | 50 | 40 | |
| Irradiated dose (α/β = 10, Gy) | ||||
| • < 87 | 9 | 44 | 22 | 0.162 |
| • ≥ 87 | 10 | 60 | 60 | |
Toxicity
Acute reactions of grade 2 or less occurred in six patients (Table 6). These toxicities were transient and easily manageable and caused no interruption of the treatment.
Table 6.
Therapy-related acute toxicity according to the acute radiation morbidity scoring criteria (RTOG). GI: gastrointestinal.
| Toxicity | Grade | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 2 | |
| Skin | ||
| • Erythema | 5 | 1 |
| Upper GI tract | ||
| • Appetite loss | 3 | 0 |
| Lower GI tract including pelvis | ||
| • Diarrhea | 1 | 0 |
No late toxicities associated with the treatment were observed.
Discussion
Although the clinical significance of treatment for HCC in patients with severe cirrhosis is still unknown, it is currently believed that radical treatment for HCC hardly ever contributes to prolonging survival of the patients. This hypothesis is based on the poor prognosis of severe cirrhosis itself. However, according to some reports the prognosis of severe cirrhotic patients has recently improved due to advanced treatments for liver dysfunction or esophageal varices. Planas et al. reported that the 1-year survival rate in Child-Pugh class C cirrhotic patients was 75% and some patients survived for > 5 years [24].
On the other hand, the median survival time of HCC patients with Child-Pugh class C cirrhosis treated only with supportive care was 3–9 months and all such patients died within 3 years [3, 17, 18]. These data suggest that the control of HCC may result in improvement of prognosis even for patients with severe cirrhosis. However, surgical resection is generally unfeasible because of the high risk of liver failure or bleeding [6, 9]. Aggressive transcatheter arterial chemoembolization (TACE) resulted in the death of 25% of Child-Pugh class C cirrhotic patients due to fatal complications including gastroduodenal bleeding within 1 month after treatment [18]. PEI may be one of the most feasible modalities for small HCC with favorable tumor location. Nevertheless, the overall survival rates were 40–81% at 1 year and none survived for > 2 years. Furthermore, severe and fatal complications such as hemoperitoneum, hepatic infarction and abscess, and tumoral seeding occurred in some cases, along with uncomfortable symptoms such as fever and pain in many cases [7, 10, 15]. Although RFA is also anticipated to be a less invasive modality, its efficacy has never been demonstrated in patients with severe cirrhosis [29]. To our knowledge, there was no detailed report on radiation therapy for HCC patients with severe cirrhosis.
In the current study, proton beam therapy appeared to have achieved an improvement in survival for some HCC patients with severe cirrhosis due to excellent local control and reduced toxicity. The overall survival rates of 53% at 1 year and 42% at 2 years were better than those of natural course [3, 17, 18]. Performance status and Child-Pugh score were significant prognostic factors for survival. In particular, five of six patients with Child-Pugh scores of 10 and 11 survived for > 2 years after treatment. By contrast, eight of nine patients who died within 1 year after treatment had Child-Pugh scores of ≥ 12.
All but one patients (95%) had no growth of the irradiated tumor while the tumor sizes were ≥30 mm in all patients except one and ≥ 50 mm in six patients. The objective response rate was 90% in ten patients who survived for > 1 year after treatment, and 33% in nine patients who died within 1 year after treatment. Usually, the tumor volume of HCC reduces gradually over several months, or occasionally over several years, on medical imaging after irradiation. All of the irradiated tumors of six NC patients tended to reduce in the final imaging studies. Since all NC patients died within 1 year after treatment, the intervals between completion of treatment and the last evaluation of treatment efficacy may have been insufficient to achieve an objective response. The dose of 50 Gy in ten fractions delivered to the one PD patient was the lowest among the present series. This irradiated dose may not have been sufficient for tumor control.
The severe or fatal toxicities which occurred in previous studies with other treatment modalities were not observed at all in this series.
Conclusion
Proton beam therapy for HCC patients with severe cirrhosis was tolerable. It may improve survival for the patients with relatively good general condition and liver function.
Acknowledgment
The present study was supported in part by a Grant-in-Aid for Cancer Research (15-9) from the Ministry of Health, Labor, and Welfare of the Japanese Government.
References
- 1.Altman D.G. Practical statistics for medical research. 2nd edn. London: Chapman & Hall; 2004. [Google Scholar]
- 2.Ando K., Koike S., Kawachi K., et al. Relative biological effectiveness of the therapeutic proton beam at NIRS and Tsukuba University. Nippon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi. 1985;45:531–535. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 3.Blum H.E. Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol. 2005;19:129–145. doi: 10.1016/j.bpg.2004.11.008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 4.Chiba T., Tokuuye K., Matsuzaki Y., et al. Proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma: a retrospective review of 162 patients. Clin Cancer Res. 2005;11:3799–3805. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-04-1350. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 5.Cox J.D., Stetz J., Pajak T.F. Toxicity criteria of the Radiation Therapy Oncology Group (RTOG) and the European Organization for Research and Treatment of Cancer (EORTC) Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1995;31:1341–1346. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(95)00060-C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 6.Carlo V., Ferrari G., Castoldi R., et al. Surgical treatment and prognostic variables of hepatocellular carcinoma in 122 cirrhotics. Hepatogastroenterology. 1995;42:222–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 7.Stasi M., Buscarini L., Livraghi T., et al. Percutaneous ethanol injection in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma. A multicenter survey of evaluation practices and complication rates. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1997;32:1168–1173. doi: 10.3109/00365529709002998. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 8.Ferro D., Saliola M., Quintarelli C., et al. 1-year survey of patients with advanced liver cirrhosis: prognostic value of clinical and laboratory indexes identified by the Cox regression model. Scand J Gastroenterol. 1992;27:852–856. doi: 10.3109/00365529209000153. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 9.Franco D., Capussotti L., Smadja C., et al. Resection of hepatocellular carcinoma. Results in 72 European patients with cirrhosis. Gastroenterology. 1990;98:733–738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 10.Giorgio A., Tarantino L., Francica G., et al. Percutaneous ethanol injection under sonographic guidance of hepatocellular carcinoma in compensated and decompensated cirrhotic patients. J Ultrasound Med. 1992;11:587–595. doi: 10.7863/jum.1992.11.11.587. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 11.Hata M., Tokuuye K., Sugahara S., et al. Proton beam therapy for hepatocellular carcinoma with portal vein tumor thrombus. Cancer. 2005;104:794–801. doi: 10.1002/cncr.21237. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 12.Höcht S., Stark R., Seiler F., et al. Proton or stereotactic photon irradiation for posterior uveal melanoma? A planning intercomparison. Strahlenther Onkol. 2005;181:783–788. doi: 10.1007/s00066-005-1395-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 13.Inada T., Tsuji H., Hayakawa Y., et al. Proton irradiation synchronized with respiratory cycle. Nippon Igaku Hoshasen Gakkai Zasshi. 1992;52:1161–1167. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 14.Kaplan E.L., Meier P. Nonparametric estimation from incomplete observations. J Am Stat Assoc. 1958;53:457–481. doi: 10.2307/2281868. [DOI] [Google Scholar]
- 15.Livraghi T., Bolondi L., Lazzaroni S., et al. Percutaneous ethanol injection in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in cirrhosis. A study on 207 patients. Cancer. 1992;69:925–929. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19920215)69:4<925::AID-CNCR2820690415>3.0.CO;2-G. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 16.Llovet J.M. Updated treatment approach to hepatocellular carcinoma. J Gastroenterol. 2005;40:225–235. doi: 10.1007/s00535-005-1566-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 17.Llovet J.M., Bustamante J., Castells A., et al. Natural history of untreated nonsurgical hepatocellular carcinoma: rationale for the design and evaluation of therapeutic trials. Hepatology. 1999;29:62–67. doi: 10.1002/hep.510290145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 18.Markovič S., Gadžijev E., Štabuc B., et al. Treatment options in Western hepatocellular carcinoma: a prospective study of 224 patients. J Hepatol. 1998;29:650–659. doi: 10.1016/S0168-8278(98)80162-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 19.Matsuzaki Y., Osuga T., Saito Y., et al. A new, effective, and safe therapeutic option using proton irradiation for hepatocellular carcinoma. Gastroenterology. 1994;106:1032–1041. doi: 10.1016/0016-5085(94)90764-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 20.Miller A.B., Hoogstraten B., Staquet M., et al. Reporting results of cancer treatment. Cancer. 1981;47:207–214. doi: 10.1002/1097-0142(19810101)47:1<207::AID-CNCR2820470134>3.0.CO;2-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 21.Mock U., Bogner J., Georg D., et al. Comparative treatment planning on localized prostate carcinoma. Strahlenther Onkol. 2005;181:448–455. doi: 10.1007/s00066-005-1317-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 22.Ohara K., Okumura T., Akisada M., et al. Irradiation synchronized with respiration gate. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1989;17:853–857. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(89)90078-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 23.Oken M.M., Creech R.H., Tormey D.C., et al. Toxicity and response criteria of the Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group. Am J Clin Oncol. 1982;5:649–655. doi: 10.1097/00000421-198212000-00014. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 24.Planas R., Ballesté B., Álvarez M.A., et al. Natural history of decompensated hepatitis C virus-related cirrhosis. A study of 200 patients. J Hepatol. 2004;40:823–830. doi: 10.1016/j.jhep.2004.01.005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 25.Pugh R.N., Murray-Lyon I.M., Dawson J.L., et al. Transection of the oesophagus for bleeding oesophageal varices. Br J Surg. 1973;60:646–649. doi: 10.1002/bjs.1800600817. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 26.Rutz H.P., Lomax A.J. Donut-shaped high-dose configuration for proton beam radiation therapy. Strahlenther Onkol. 2004;181:49–53. doi: 10.1007/s00066-005-1280-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 27.Sobin L.H., Wittekind C. TNM classification of malignant tumours. 6th edn. New York: Wiley-Liss; 2002. pp. 81–3. [Google Scholar]
- 28.Suit H., Goldberg S., Niemierko A., et al. Proton beams to replace photon beams in radical dose treatments. Acta Oncol. 2003;42:800–808. doi: 10.1080/02841860310017676. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 29.Tateishi R., Shiina S., Teratani T., et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma. An analysis of 1000 cases. Cancer. 2005;103:1201–1209. doi: 10.1002/cncr.20892. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 30.Tokuuye K., Akine Y., Kagei K., et al. Proton therapy for head and heck malignancies at Tsukuba. Strahlenther Onkol. 2004;180:96–101. doi: 10.1007/s00066-004-1132-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- 31.Withers H.R., Thames H.D., Jr, Peters L.J. A new isoeffect curve for change in dose per fraction. Radiother Oncol. 1983;1:187–191. doi: 10.1016/S0167-8140(83)80021-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]