Abstract
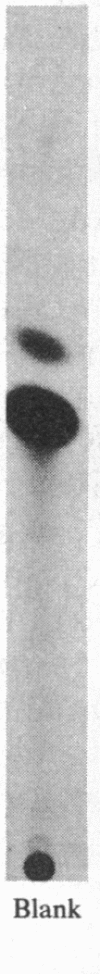
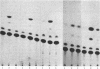
Numerous studies of cell hybrids have indicated that somatic cells produce negative regulators (extinguishers) that prevent the expression of functions foreign to their own differentiation. Here, we report genetic evidence of such control. In microcell hybrids between well-differentiated rat hepatoma cells and microcells of mouse fibroblast L cells, the extinction of albumin synthesis is directly related to the presence of a single specific chromosome of the mouse fibroblast parent. The expression of several other hepatic functions is not affected. Transfection of these hybrids with a recombinant plasmid, containing a tissue-specific control element of the upstream region of the rat albumin gene linked to coding sequences of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene, reveals that extinction acts on or via this cis-control element.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Banerji J., Olson L., Schaffner W. A lymphocyte-specific cellular enhancer is located downstream of the joining region in immunoglobulin heavy chain genes. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):729–740. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90015-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bergman Y., Rice D., Grosschedl R., Baltimore D. Two regulatory elements for immunoglobulin kappa light chain gene expression. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7041–7045. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolotti R. A selective system for hepatoma cells producing gluconeogenic enzymes. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Jul;3(4):365–380. doi: 10.1007/BF01542966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bertolotti R. Expression of differentiated functions in hepatoma cell hybrids: selection in glucose-free media of segregated hybrid cells which reexpress gluconeogenic enzymes. Somatic Cell Genet. 1977 Nov;3(6):579–602. doi: 10.1007/BF01539067. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borrelli E., Hen R., Chambon P. Adenovirus-2 E1A products repress enhancer-induced stimulation of transcription. Nature. 1984 Dec 13;312(5995):608–612. doi: 10.1038/312608a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brand A. H., Breeden L., Abraham J., Sternglanz R., Nasmyth K. Characterization of a "silencer" in yeast: a DNA sequence with properties opposite to those of a transcriptional enhancer. Cell. 1985 May;41(1):41–48. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90059-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cassio D., Weiss M. C., Ott M. O., Sala-Trepat J. M., Friès J., Erdos T. Expression of the albumin gene in rat hepatoma cells and their dedifferentiated variants. Cell. 1981 Dec;27(2 Pt 1):351–358. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Charnay P., Treisman R., Mellon P., Chao M., Axel R., Maniatis T. Differences in human alpha- and beta-globin gene expression in mouse erythroleukemia cells: the role of intragenic sequences. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):251–263. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90547-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chepelinsky A. B., King C. R., Zelenka P. S., Piatigorsky J. Lens-specific expression of the chloramphenicol acetyltransferase gene promoted by 5' flanking sequences of the murine alpha A-crystallin gene in explanted chicken lens epithelia. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2334–2338. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2334. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ciliberto G., Dente L., Cortese R. Cell-specific expression of a transfected human alpha 1-antitrypsin gene. Cell. 1985 Jun;41(2):531–540. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80026-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coon H. G., Weiss M. C. A quantitative comparison of formation of spontaneous and virus-produced viable hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1969 Mar;62(3):852–859. doi: 10.1073/pnas.62.3.852. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DUBBS D. R., KIT S. EFFECT OF HALOGENATED PYRIMIDINES AND THYMIDINE ON GROWTH OF L-CELLS AND A SUBLINE LACKING THYMIDINE KINASE. Exp Cell Res. 1964 Jan;33:19–28. doi: 10.1016/s0014-4827(64)81006-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L., Ephrussi B., Yamamoto K. Regulation of pigment synthesis in mammalian cells, as studied by somatic hybridization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1966 Nov;56(5):1437–1440. doi: 10.1073/pnas.56.5.1437. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L. Gene expression in somatic cell hybrids. Annu Rev Genet. 1974;8:195–218. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ge.08.120174.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R. L. Regulation of malanin synthesis in mammalian cells: effect of gene dosage on the expression of differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Apr;69(4):951–955. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.4.951. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davidson R., Ephrussi B., Yamamoto K. Regulation of melanin synthesis in mammalian cells, as studied by somatic hybridization. I. Evidence for negative control. J Cell Physiol. 1968 Oct;72(2):115–127. doi: 10.1002/jcp.1040720206. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Episkopou V., Murphy A. J., Efstratiadis A. Cell-specified expression of a selectable hybrid gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4657–4661. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4657. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fougère C., Ruiz F., Ephrussi B. Gene dosage dependence of pigment synthesis in melanoma x fibroblast hybrids (hamster cells-mouse fibroblast-DOPA-oxidase-irradiation). Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Feb;69(2):330–334. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.2.330. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fournier R. E. A general high-efficiency procedure for production of microcell hybrids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Oct;78(10):6349–6353. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.10.6349. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallimore P. H., Richardson C. R. An improved banding technique exemplified in the karyotype analysis of two strains of rat. Chromosoma. 1973;41(3):259–263. doi: 10.1007/BF00344020. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillies S. D., Morrison S. L., Oi V. T., Tonegawa S. A tissue-specific transcription enhancer element is located in the major intron of a rearranged immunoglobulin heavy chain gene. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):717–728. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90014-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gopalakrishnan T. V., Anderson W. F. Epigenetic activation of phenylalanine hydroxylase in mouse erythroleukemia cells by the cytoplast of rat hepatoma cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Aug;76(8):3932–3936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.8.3932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorman C. M., Moffat L. F., Howard B. H. Recombinant genomes which express chloramphenicol acetyltransferase in mammalian cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1982 Sep;2(9):1044–1051. doi: 10.1128/mcb.2.9.1044. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HAM R. G. CLONAL GROWTH OF MAMMALIAN CELLS IN A CHEMICALLY DEFINED, SYNTHETIC MEDIUM. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1965 Feb;53:288–293. doi: 10.1073/pnas.53.2.288. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heberlein U., England B., Tjian R. Characterization of Drosophila transcription factors that activate the tandem promoters of the alcohol dehydrogenase gene. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):965–977. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80077-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kahn C. R., Bertolotti R., Ninio M., Weiss M. C. Short-lived cytoplasmic regulators of gene expression in cell cybrids. Nature. 1981 Apr 23;290(5808):717–720. doi: 10.1038/290717a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Killary A. M., Fournier R. E. A genetic analysis of extinction: trans-dominant loci regulate expression of liver-specific traits in hepatoma hybrid cells. Cell. 1984 Sep;38(2):523–534. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90507-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klebe R. J., Chen T., Ruddle R. H. Mapping of a human genetic regulator element by somatic cell genetic analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1970 Aug;66(4):1220–1227. doi: 10.1073/pnas.66.4.1220. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak C. A., Lawrence J. B., Ruddle F. H. A sequential staining technique for the chromosomal analysis of the interspecific mouse/hamster and mouse/human somatic cell hybrids. Exp Cell Res. 1977 Mar 1;105(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(77)90156-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LITTLEFIELD J. W. SELECTION OF HYBRIDS FROM MATINGS OF FIBROBLASTS IN VITRO AND THEIR PRESUMED RECOMBINANTS. Science. 1964 Aug 14;145(3633):709–710. doi: 10.1126/science.145.3633.709. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laurell C. B. Quantitative estimation of proteins by electrophoresis in agarose gel containing antibodies. Anal Biochem. 1966 Apr;15(1):45–52. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(66)90246-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Melloul D., Aloni B., Calvo J., Yaffe D., Nudel U. Developmentally regulated expression of chimeric genes containing muscle actin DNA sequences in transfected myogenic cells. EMBO J. 1984 May;3(5):983–990. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb01917.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mével-Ninio M. Immunofluorescence analysis of reexpression and activation: the origin of phenotypic diversity of rat hepatoma-mouse fibroblast hybrid colonies. Differentiation. 1984;26(1):68–76. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb01376.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mével-Ninio M., Weiss M. C. Immunofluorescence analysis of the time-course of extinction, reexpression, and activation of albumin production in rat hepatoma-mouse fibroblast heterokaryons and hybrids. J Cell Biol. 1981 Aug;90(2):339–350. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.2.339. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ornitz D. M., Palmiter R. D., Hammer R. E., Brinster R. L., Swift G. H., MacDonald R. J. Specific expression of an elastase-human growth hormone fusion gene in pancreatic acinar cells of transgenic mice. Nature. 1985 Feb 14;313(6003):600–602. doi: 10.1038/313600a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ott M. O., Sperling L., Herbomel P., Yaniv M., Weiss M. C. Tissue-specific expression is conferred by a sequence from the 5' end of the rat albumin gene. EMBO J. 1984 Nov;3(11):2505–2510. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02164.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- PITOT H. C., PERAINO C., MORSE P. A., Jr, POTTER V. R. HEPATOMAS IN TISSUE CULTURE COMPARED WITH ADAPTING LIVER IN VIVO. Natl Cancer Inst Monogr. 1964 Apr;13:229–245. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Queen C., Baltimore D. Immunoglobulin gene transcription is activated by downstream sequence elements. Cell. 1983 Jul;33(3):741–748. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90016-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- REUBER M. D. A transplantable bile-secreting hepatocellular carcinoma in the rat. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1961 Apr;26:891–899. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strathern J., Hicks J., Herskowitz I. Control of cell type in yeast by the mating type locus. The alpha 1-alpha 2 hypothesis. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 15;147(3):357–372. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90488-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker M. D., Edlund T., Boulet A. M., Rutter W. J. Cell-specific expression controlled by the 5'-flanking region of insulin and chymotrypsin genes. Nature. 1983 Dec 8;306(5943):557–561. doi: 10.1038/306557a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss M. C., Chaplain M. Expression of differentiated functions in hepatoma cell hybrids: reappearance of tyrosine aminotransferase inducibility after the loss of chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Dec;68(12):3026–3030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.12.3026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wright S., Rosenthal A., Flavell R., Grosveld F. DNA sequences required for regulated expression of beta-globin genes in murine erythroleukemia cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):265–273. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90548-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]