Abstract
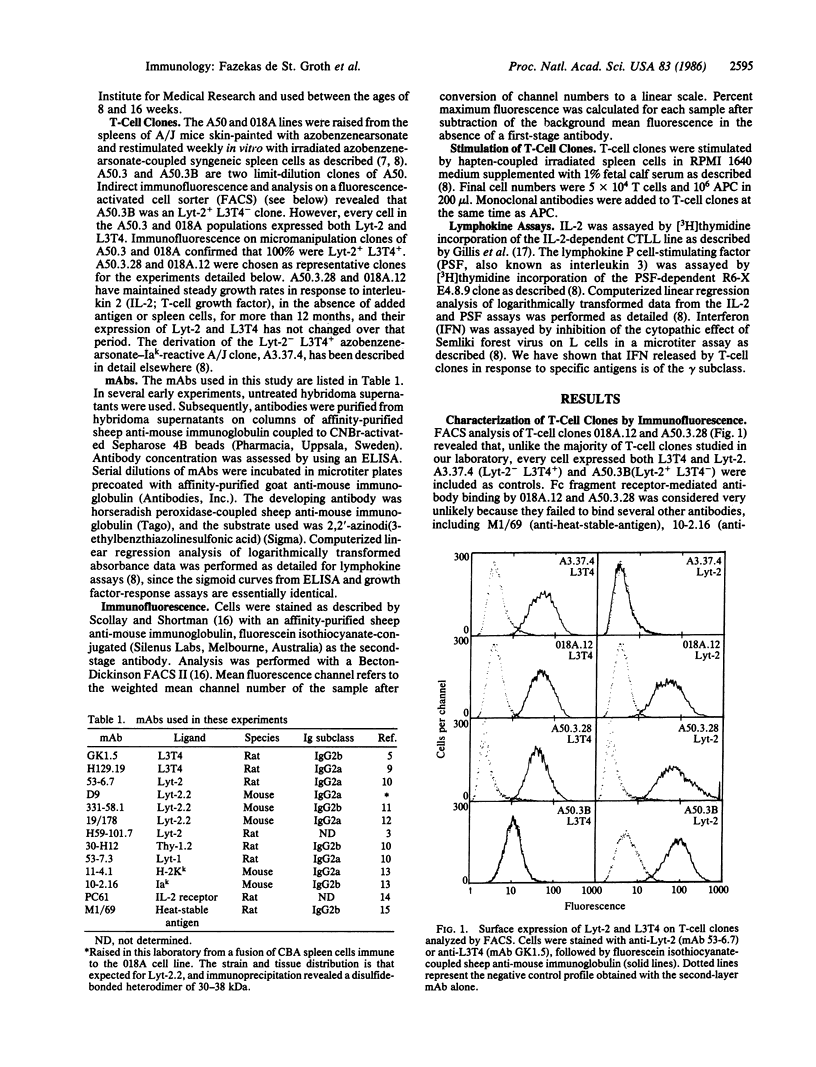
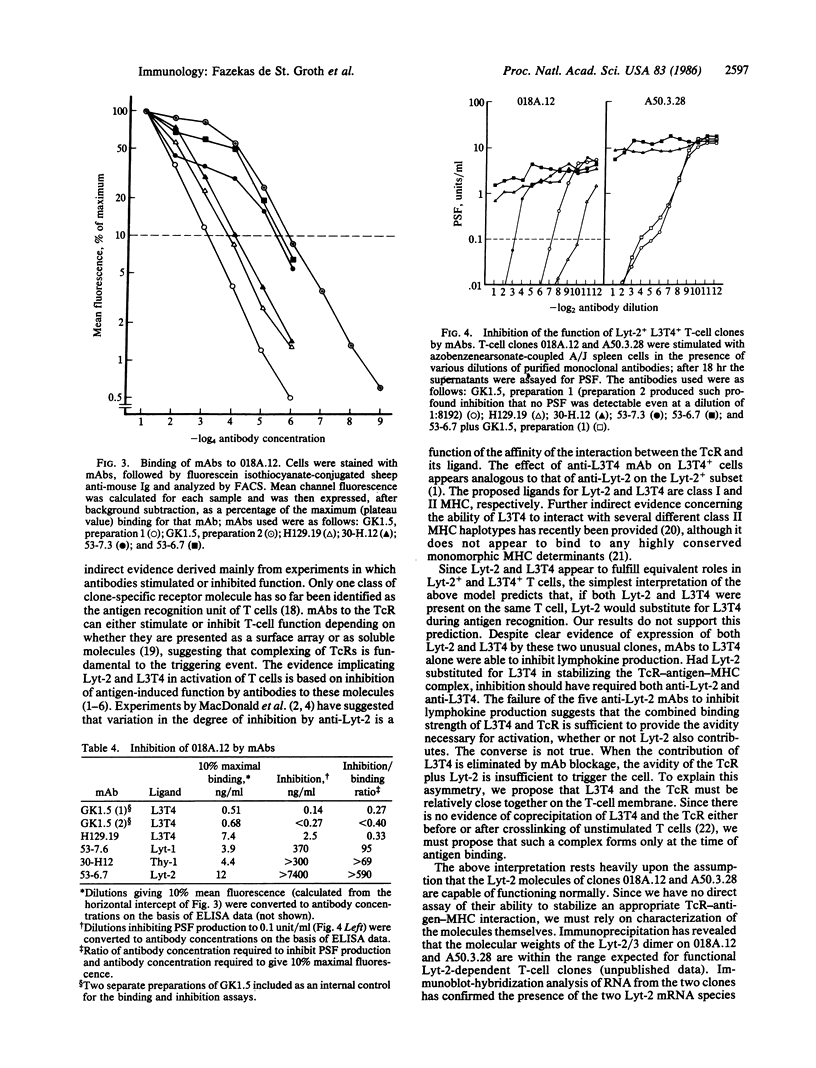
The murine T-cell surface molecules Lyt-2 and L3T4 play a role in the activation of antigen-specific T cells. The currently accepted model for the function of these molecules proposes that Lyt-2 and L3T4 increase the overall avidity of the interaction between the T-cell antigen receptor and antigen in association with the major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules on the antigen-presenting cell. We have used two unusual Lyt-2+ L3T4+ class II MHC-restricted T-cell clones to test whether Lyt-2 can substitute for L3T4 when the T-cell antigen receptor is class II MHC-restricted. Monoclonal antibodies against L3T4 profoundly inhibited antigen-induced lymphokine production by both T-cell clones. Anti-Lyt-2 monoclonal antibody had no effect. These results strongly suggest that L3T4 and the class II-restricted T-cell antigen receptors are physically close during antigen recognition, probably as part of a multimolecular complex from which Lyt-2 is excluded. The ability of L3T4 but not Lyt-2 to participate in such a complex with class II-restricted T-cell antigen receptors may explain the striking correlation between class II restriction and L3T4 expression in the peripheral T-cell pool.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allison J. P., Lanier L. L. Identification of antigen receptor-associated structures on murine T cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):107–109. doi: 10.1038/314107a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blue M. L., Daley J. F., Levine H., Schlossman S. F. Coexpression of T4 and T8 on peripheral blood T cells demonstrated by two-color fluorescence flow cytometry. J Immunol. 1985 Apr;134(4):2281–2286. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ceredig R., Lowenthal J. W., Nabholz M., MacDonald H. R. Expression of interleukin-2 receptors as a differentiation marker on intrathymic stem cells. Nature. 1985 Mar 7;314(6006):98–100. doi: 10.1038/314098a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dialynas D. P., Wilde D. B., Marrack P., Pierres A., Wall K. A., Havran W., Otten G., Loken M. R., Pierres M., Kappler J. Characterization of the murine antigenic determinant, designated L3T4a, recognized by monoclonal antibody GK1.5: expression of L3T4a by functional T cell clones appears to correlate primarily with class II MHC antigen-reactivity. Immunol Rev. 1983;74:29–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01083.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fazekas de St Groth B., Thomas W. R., McKimm-Breschkin J. L., Clark-Lewis I., Schrader J. W., Miller J. F. P cell stimulating factor release: a useful assay of T cell activation in vitro. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1986;79(2):169–177. doi: 10.1159/000233966. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gillis S., Ferm M. M., Ou W., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor: parameters of production and a quantitative microassay for activity. J Immunol. 1978 Jun;120(6):2027–2032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golding H., McCluskey J., Munitz T. I., Germain R. N., Margulies D. H., Singer A. T-cell recognition of a chimaeric class II/class I MHC molecule and the role of L3T4. Nature. 1985 Oct 3;317(6036):425–427. doi: 10.1038/317425a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Golstein P., Goridis C., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Hayot B., Pierres A., van Agthoven A., Kaufmann Y., Eshhar Z., Pierres M. Lymphoid cell surface interaction structures detected using cytolysis-inhibiting monoclonal antibodies. Immunol Rev. 1982;68:5–42. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb01058.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenstein J. L., Kappler J., Marrack P., Burakoff S. J. The role of L3T4 in recognition of Ia by a cytotoxic, H-2Dd-specific T cell hybridoma. J Exp Med. 1984 Apr 1;159(4):1213–1224. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.4.1213. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haas W., von Boehmer H. Surface markers of cytotoxic T lymphocyte clones. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Apr;14(4):383–384. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830140421. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haskins K., Kubo R., White J., Pigeon M., Kappler J., Marrack P. The major histocompatibility complex-restricted antigen receptor on T cells. I. Isolation with a monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1983 Apr 1;157(4):1149–1169. doi: 10.1084/jem.157.4.1149. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hämmerling G. J., Hämmerling U., Flaherty L. Qat-4 and Qat-5, new murine T-cell antigens governed by the Tla region and identified by monoclonal antibodies. J Exp Med. 1979 Jul 1;150(1):108–116. doi: 10.1084/jem.150.1.108. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kruisbeek A. M., Mond J. J., Fowlkes B. J., Carmen J. A., Bridges S., Longo D. L. Absence of the Lyt-2-,L3T4+ lineage of T cells in mice treated neonatally with anti-I-A correlates with absence of intrathymic I-A-bearing antigen-presenting cell function. J Exp Med. 1985 May 1;161(5):1029–1047. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.5.1029. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ledbetter J. A., Herzenberg L. A. Xenogeneic monoclonal antibodies to mouse lymphoid differentiation antigens. Immunol Rev. 1979;47:63–90. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1979.tb00289.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Glasebrook A. L., Bron C., Kelso A., Cerottini J. C. Clonal heterogeneity in the functional requirement for Lyt-2/3 molecules on cytolytic T lymphocytes (CTL): possible implications for the affinity of CTL antigen receptors. Immunol Rev. 1982;68:89–115. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1982.tb01061.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MacDonald H. R., Glasebrook A. L., Cerottini J. C. Clonal heterogeneity in the functional requirement for Lyt-2/3 molecules on cytolytic T lymphocytes: analysis by antibody blocking and selective trypsinization. J Exp Med. 1982 Dec 1;156(6):1711–1722. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.6.1711. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marrack P., Endres R., Shimonkevitz R., Zlotnik A., Dialynas D., Fitch F., Kappler J. The major histocompatibility complex-restricted antigen receptor on T cells. II. Role of the L3T4 product. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1077–1091. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1077. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hodgdon J. C., Hussey R. E., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. Antigen-like effects of monoclonal antibodies directed at receptors on human T cell clones. J Exp Med. 1983 Sep 1;158(3):988–993. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.3.988. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nakauchi H., Nolan G. P., Hsu C., Huang H. S., Kavathas P., Herzenberg L. A. Molecular cloning of Lyt-2, a membrane glycoprotein marking a subset of mouse T lymphocytes: molecular homology to its human counterpart, Leu-2/T8, and to immunoglobulin variable regions. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(15):5126–5130. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.15.5126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oi V. T., Jones P. P., Goding J. W., Herzenberg L. A., Herzenberg L. A. Properties of monoclonal antibodies to mouse Ig allotypes, H-2, and Ia antigens. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1978;81:115–120. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67448-8_18. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pierres A., Naquet P., Van Agthoven A., Bekkhoucha F., Denizot F., Mishal Z., Schmitt-Verhulst A. M., Pierres M. A rat anti-mouse T4 monoclonal antibody (H129.19) inhibits the proliferation of Ia-reactive T cell clones and delineates two phenotypically distinct (T4+, Lyt-2,3-, and T4-, Lyt-2,3+) subsets among anti-Ia cytolytic T cell clones. J Immunol. 1984 Jun;132(6):2775–2782. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Scollay R., Shortman K. Thymocyte subpopulations: an experimental review, including flow cytometric cross-correlations between the major murine thymocyte markers. Thymus. 1983 Sep;5(5-6):245–295. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sredni B., Schwartz R. H. Alloreactivity of an antigen-specific T-cell clone. Nature. 1980 Oct 30;287(5785):855–857. doi: 10.1038/287855a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swain S. L., Dialynas D. P., Fitch F. W., English M. Monoclonal antibody to L3T4 blocks the function of T cells specific for class 2 major histocompatibility complex antigens. J Immunol. 1984 Mar;132(3):1118–1123. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas W. R., Mottram P. L., Miller J. F. Hapten-specific T cell lines mediating delayed hypersensitivity to contact-sensitizing agents. J Exp Med. 1982 Jul 1;156(1):300–305. doi: 10.1084/jem.156.1.300. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Walker I. D., Murray B. J., Hogarth P. M., Kelso A., McKenzie I. F. Comparison of thymic and peripheral T cell Ly-2/3 antigens. Eur J Immunol. 1984 Oct;14(10):906–910. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830141009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



