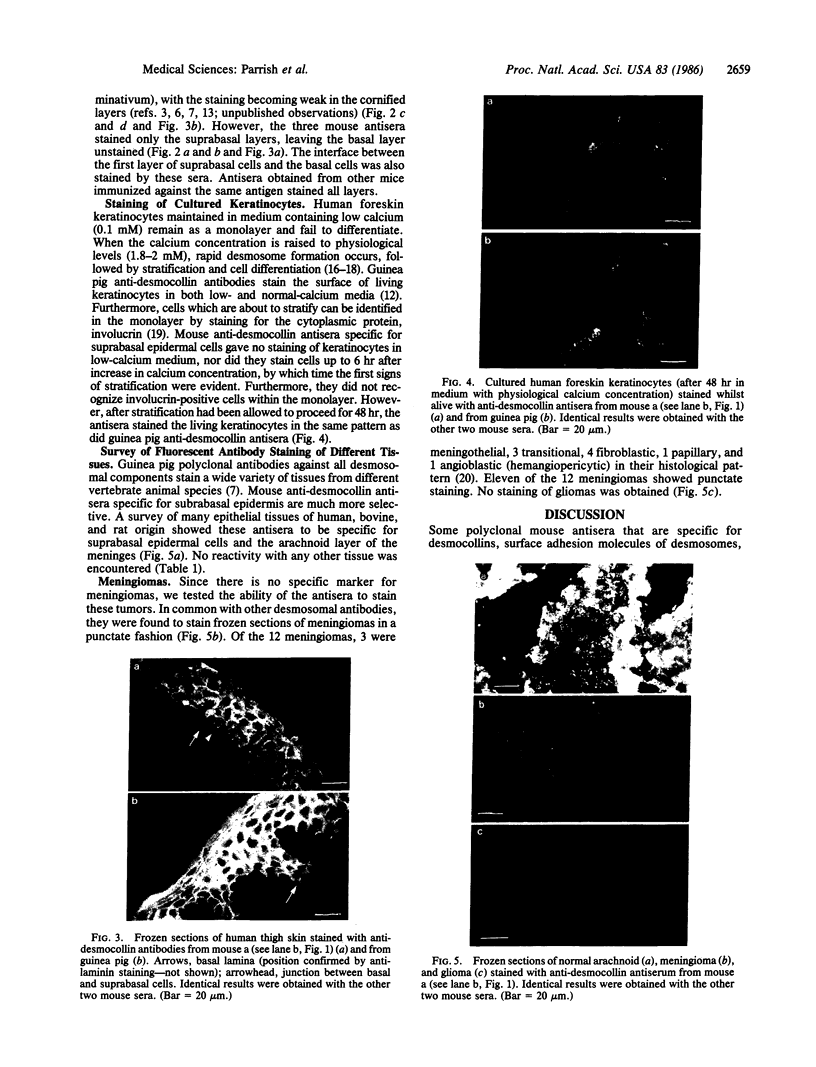
Abstract
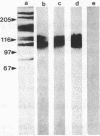
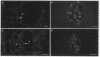
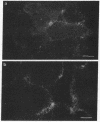
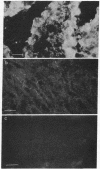
Mouse polyclonal antisera were raised to the Mr 130,000 and Mr 115,000 cell surface glycoproteins, desmocollins, of desmosomes from bovine nasal epithelium. Immunoblotting confirmed that the antisera were specific for the desmocollins. An immunofluorescence study showed that the antisera distinguished between the basal and suprabasal layers of bovine and human epidermis. The antibodies reacted with cultured keratinocytes only after calcium-induced stratification. In epidermis, therefore, there appears to be a difference between the desmocollins of basal and suprabasal cells that may be important in relation to epidermal differentiation. Previous work has shown that polyclonal antisera raised in other animals (guinea pigs and rabbits) against desmocollins, as well as against other desmosomal components, react with all desmosome-containing epithelia. In contrast, an immunofluorescence survey of bovine, rat, and human tissues showed that the present mouse antisera stained only suprabasal skin cells and the arachnoid layer of the meninges, demonstrating that these have common determinants that distinguished their desmocollins from those of all other tissues. The antibodies also stained 11 of 12 meningiomas and, therefore, may be useful as a marker not only for the diagnosis of these tumors but also for investigation of their histogenesis.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allen T. D., Potten C. S. Desmosomal form, fate, and function in mammalian epidermis. J Ultrastruct Res. 1975 Apr;51(1):94–105. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(75)80011-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Banks-Schlegel S., Green H. Involucrin synthesis and tissue assembly by keratinocytes in natural and cultured human epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):732–737. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.732. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breathnach A. S. Aspects of epidermal ultrastructure. J Invest Dermatol. 1975 Jul;65(1):2–15. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12598018. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen S. M., Gorbsky G., Steinberg M. S. Immunochemical characterization of related families of glycoproteins in desmosomes. J Biol Chem. 1983 Feb 25;258(4):2621–2627. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowin P., Garrod D. R. Antibodies to epithelial desmosomes show wide tissue and species cross-reactivity. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):148–150. doi: 10.1038/302148a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowin P., Mattey D., Garrod D. Distribution of desmosomal components in the tissues of vertebrates, studied by fluorescent antibody staining. J Cell Sci. 1984 Mar;66:119–132. doi: 10.1242/jcs.66.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowin P., Mattey D., Garrod D. Identification of desmosomal surface components (desmocollins) and inhibition of desmosome formation by specific Fab'. J Cell Sci. 1984 Aug;70:41–60. doi: 10.1242/jcs.70.1.41. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- FARQUHAR M. G., PALADE G. E. Junctional complexes in various epithelia. J Cell Biol. 1963 May;17:375–412. doi: 10.1083/jcb.17.2.375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Farquhar M. G., Palade G. E. Cell junctions in amphibian skin. J Cell Biol. 1965 Jul;26(1):263–291. doi: 10.1083/jcb.26.1.263. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Moll R., Schiller D. L., Schmid E., Kartenbeck J., Mueller H. Desmoplakins of epithelial and myocardial desmosomes are immunologically and biochemically related. Differentiation. 1982;23(2):115–127. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1982.tb01274.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schmid E., Grund C., Müller H., Engelbrecht I., Moll R., Stadler J., Jarasch E. D. Antibodies to high molecular weight polypeptides of desmosomes: specific localization of a class of junctional proteins in cells and tissue. Differentiation. 1981;20(3):217–241. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1981.tb01178.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giudice G. J., Cohen S. M., Patel N. H., Steinberg M. S. Immunological comparison of desmosomal components from several bovine tissues. J Cell Biochem. 1984;26(1):35–45. doi: 10.1002/jcb.240260104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbsky G., Cohen S. M., Shida H., Giudice G. J., Steinberg M. S. Isolation of the non-glycosylated proteins of desmosomes and immunolocalization of a third plaque protein: desmoplakin III. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):810–814. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.810. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gorbsky G., Steinberg M. S. Isolation of the intercellular glycoproteins of desmosomes. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):243–248. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hennings H., Michael D., Cheng C., Steinert P., Holbrook K., Yuspa S. H. Calcium regulation of growth and differentiation of mouse epidermal cells in culture. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):245–254. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90406-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones J. C., Goldman A. E., Steinert P. M., Yuspa S., Goldman R. D. Dynamic aspects of the supramolecular organization of intermediate filament networks in cultured epidermal cells. Cell Motil. 1982;2(3):197–213. doi: 10.1002/cm.970020302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kapprell H. P., Cowin P., Franke W. W., Ponstingl H., Opferkuch H. J. Biochemical characterization of desmosomal proteins isolated from bovine muzzle epidermis: amino acid and carbohydrate composition. Eur J Cell Biol. 1985 Mar;36(2):217–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kartenbeck J., Schwechheimer K., Moll R., Franke W. W. Attachment of vimentin filaments to desmosomal plaques in human meningiomal cells and arachnoidal tissue. J Cell Biol. 1984 Mar;98(3):1072–1081. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.3.1072. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mattey D. L., Garrod D. R. Mutual desmosome formation between all binary combinations of human, bovine, canine, avian and amphibian cells: desmosome formation is not tissue- or species-specific. J Cell Sci. 1985 Apr;75:377–399. doi: 10.1242/jcs.75.1.377. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Overton J. Formation of junctions and cell sorting in aggregates of chick and mouse cells. Dev Biol. 1977 Jan;55(1):103–116. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(77)90323-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rice R. H., Green H. Presence in human epidermal cells of a soluble protein precursor of the cross-linked envelope: activation of the cross-linking by calcium ions. Cell. 1979 Nov;18(3):681–694. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90123-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimono M., Clementi F. Intercellular junctions of oral epithelium. I. Studies with freeze-fracture and tracing methods of normal rat keratinized oral epithelium. J Ultrastruct Res. 1976 Jul;56(1):121–136. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5320(76)80145-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerrow C. J. Intercellular adhesion and its role in epidermal differentiation. Invest Cell Pathol. 1978 Jan-Mar;1(1):23–37. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Skerrow C. J., Matoltsy A. G. Isolation of epidermal desmosomes. J Cell Biol. 1974 Nov;63(2 Pt 1):515–523. doi: 10.1083/jcb.63.2.515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suhrbier A., Garrod D. An investigation of the molecular components of desmosomes in epithelial cells of five vertebrates. J Cell Sci. 1986 Mar;81:223–242. doi: 10.1242/jcs.81.1.223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sun T. T., Eichner R., Nelson W. G., Tseng S. C., Weiss R. A., Jarvinen M., Woodcock-Mitchell J. Keratin classes: molecular markers for different types of epithelial differentiation. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jul;81(1 Suppl):109s–115s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12540831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thacher S. M., Rice R. H. Keratinocyte-specific transglutaminase of cultured human epidermal cells: relation to cross-linked envelope formation and terminal differentiation. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):685–695. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90217-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Delouvée A., Gallin W. J., Cunningham B. A., Edelman G. M. Ontogenetic expression of cell adhesion molecules: L-CAM is found in epithelia derived from the three primary germ layers. Dev Biol. 1984 Mar;102(1):61–78. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(84)90175-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F. M., Green H. Involucrin synthesis is correlated with cell size in human epidermal cultures. J Cell Biol. 1981 Sep;90(3):738–742. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.3.738. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F. M., Green H. Stratification and terminal differentiation of cultured epidermal cells. Nature. 1982 Feb 4;295(5848):434–436. doi: 10.1038/295434a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F. M. Involucrin and other markers of keratinocyte terminal differentiation. J Invest Dermatol. 1983 Jul;81(1 Suppl):100s–103s. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12540786. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watt F. M., Mattey D. L., Garrod D. R. Calcium-induced reorganization of desmosomal components in cultured human keratinocytes. J Cell Biol. 1984 Dec;99(6):2211–2215. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.6.2211. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White F. H., Gohari K. Desmosomes in hamster cheek pouch epithelium: their quantitative characterization during epithelial differentiation. J Cell Sci. 1984 Mar;66:411–429. doi: 10.1242/jcs.66.1.411. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White F. H., Gohari K. Some aspects of desmosomal morphology during differentiation of hamster cheek pouch epithelium. J Submicrosc Cytol. 1984 Jul;16(3):407–422. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodcock-Mitchell J., Eichner R., Nelson W. G., Sun T. T. Immunolocalization of keratin polypeptides in human epidermis using monoclonal antibodies. J Cell Biol. 1982 Nov;95(2 Pt 1):580–588. doi: 10.1083/jcb.95.2.580. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]