Abstract
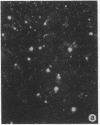
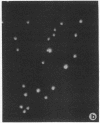
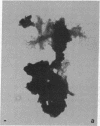
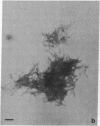
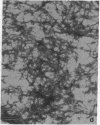
Isolation of Alzheimer disease amyloid plaque core protein (APCP) was carried out by repetitive NaDodSO4/EDTA/sucrose extractions and by Ficoll-400 density-gradient centrifugations. The enriched APCP-Ficoll interface was labeled with the fluorochrome thioflavin T and separated from the contaminating lipofuscin by fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Electron microscopy demonstrated that APCP is made of two different kinds of filaments measuring 5.5-6 nm and 10-12 nm, respectively, and of variable length. Purified APCP and lipofuscin were chemically modified by performic acid oxidation. The amino acid composition of APCP revealed a high content of glycine and valine (30%) and 1% cysteine. By contrast, the protein moiety of the copurified lipofuscin contained 16% cysteine. The amino acid composition of APCP did not resemble that of any known protein.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Allsop D., Landon M., Kidd M. The isolation and amino acid composition of senile plaque core protein. Brain Res. 1983 Jan 24;259(2):348–352. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91273-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J., Pennock C. A., Stoward P. J. The specificity of the staining of amyloid deposits with thioflavine T. J Pathol Bacteriol. 1967 Oct;94(2):337–344. doi: 10.1002/path.1700940211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gajdusek D. C. Hypothesis: interference with axonal transport of neurofilament as a common pathogenetic mechanism in certain diseases of the central nervous system. N Engl J Med. 1985 Mar 14;312(11):714–719. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198503143121110. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenner G. G., Wong C. W. Alzheimer's disease: initial report of the purification and characterization of a novel cerebrovascular amyloid protein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 May 16;120(3):885–890. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80190-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herzenberg L. A., Sweet R. G., Herzenberg L. A. Fluorescence-activated cell sorting. Sci Am. 1976 Mar;234(3):108–117. doi: 10.1038/scientificamerican0376-108. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIDD M. ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE--AN ELECTRON MICROSCOPICAL STUDY. Brain. 1964 Jun;87:307–320. doi: 10.1093/brain/87.2.307. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KRIGMAN M. R., FELDMAN R. G., BENSCH K. ALZHEIMER'S PRESENILE DEMENTIA. A HISTOCHEMICAL AND ELECTRON MICROSCOPIC STUDY. Lab Invest. 1965 Apr;14:381–396. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Karin M., Richards R. I. Human metallothionein genes--primary structure of the metallothionein-II gene and a related processed gene. Nature. 1982 Oct 28;299(5886):797–802. doi: 10.1038/299797a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelényi G. On the histochemistry of azo group-free thiazole dyes. J Histochem Cytochem. 1967 Mar;15(3):172–180. doi: 10.1177/15.3.172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Konigsberg W. H., Henderson L. Removal of sodium dodecyl sulfate from proteins by ion-pair extraction. Methods Enzymol. 1983;91:254–259. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(83)91022-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Luse S. A., Smith K. R., Jr The ultrastructure of senile plaques. Am J Pathol. 1964 Apr;44(4):553–563. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merz P. A., Wisniewski H. M., Somerville R. A., Bobin S. A., Masters C. L., Iqbal K. Ultrastructural morphology of amyloid fibrils from neuritic and amyloid plaques. Acta Neuropathol. 1983;60(1-2):113–124. doi: 10.1007/BF00685355. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Narang H. K. High-resolution electron microscopic analysis of the amyloid fibril in Alzheimer's disease. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1980 Nov;39(6):621–631. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198011000-00001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Austin J., Rinehart R., Trueb L., Hutchinson J., Stukenbrok H., Miles B. Studies in ageing of the brain. I. Isolation and preliminary characterization of Alzheimer plaques and cores. Arch Neurol. 1971 Sep;25(3):198–211. doi: 10.1001/archneur.1971.00490030024002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Ihara Y., Salazar F. J. Alzheimer's disease: insolubility of partially purified paired helical filaments in sodium dodecyl sulfate and urea. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1243–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.6120571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY R. D., GONATAS N. K., WEISS M. ULTRASTRUCTURAL STUDIES IN ALZHEIMER'S PRESENILE DEMENTIA. Am J Pathol. 1964 Feb;44:269–297. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY R. D. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF NEUROFIBRILLARY TANGLES IN ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1963 Oct;22:629–642. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196310000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Terry R. D., Katzman R. Senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Ann Neurol. 1983 Nov;14(5):497–506. doi: 10.1002/ana.410140502. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waldrop F. S., Puchtler H., Valentine L. S. Fluorescence microscopy of amyloid using mixed illumination. Arch Pathol. 1973 Jan;95(1):37–41. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wischik C. M., Crowther R. A., Stewart M., Roth M. Subunit structure of paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease. J Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;100(6):1905–1912. doi: 10.1083/jcb.100.6.1905. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wisniewski H. M., Merz P. A., Iqbal K. Ultrastructure of paired helical filaments of Alzheimer's neurofibrillary tangle. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1984 Nov;43(6):643–656. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198411000-00008. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]