Abstract
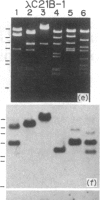
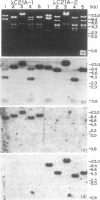
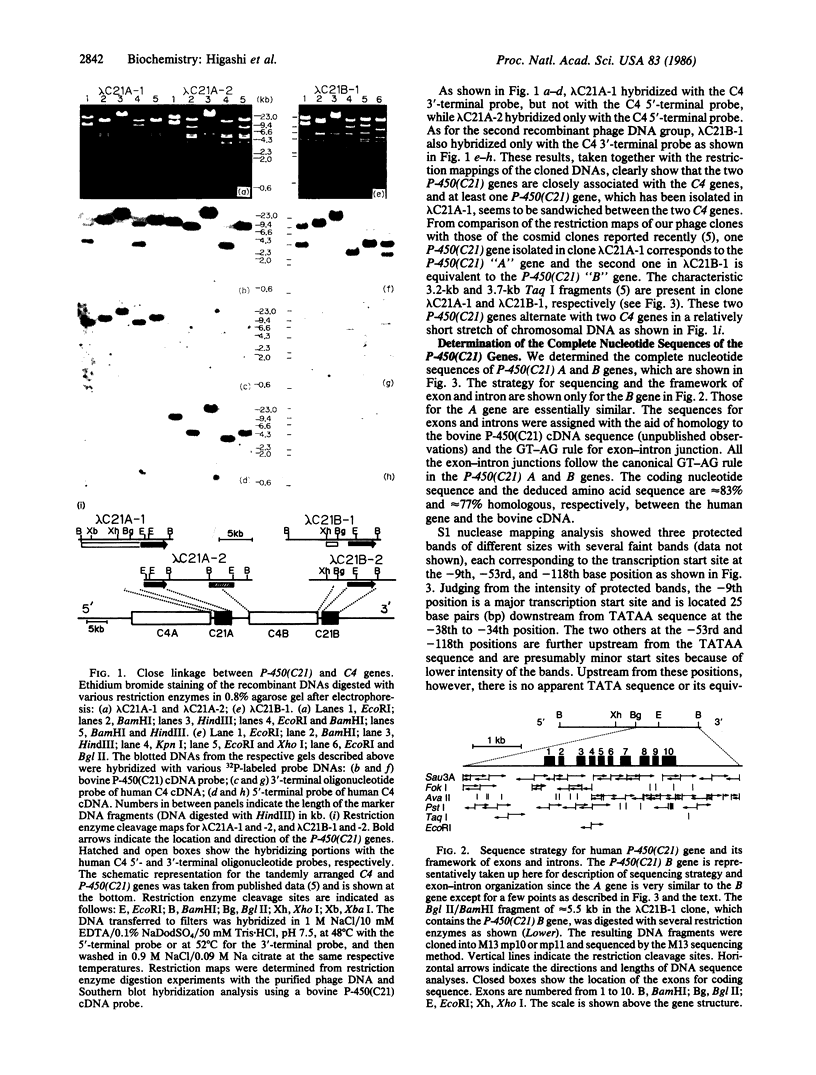
Two 21-hydroxylase [P-450(C21)] genes have been isolated from a human genomic library using a bovine P-450(C21) cDNA. The insert DNAs containing the P-450(C21) genes were also hybridized with the sequences of the 5' or 3' end regions of human C4 cDNA, indicating a close linkage of the P-450(C21) gene to the C4 gene. Sequence analysis has revealed that the two P-450(C21) genes are both approximately equal to 3.4 kilobases long and split into 10 exons. Comparing the two sequences, we found that the two genes are highly homologous including their introns and flanking sequences, but that three mutations render one of the two P-450(C21) genes nonfunctional--1 base insertion, an 8-base deletion, and a transition mutation--all of which may cause premature termination of the translation. Tandem arrangement of the highly homologous pseudo- and genuine genes in close proximity could account for the high incidence of P-450(C21) gene deficiency by homologous gene recombination.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Belt K. T., Carroll M. C., Porter R. R. The structural basis of the multiple forms of human complement component C4. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):907–914. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90040-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benton W. D., Davis R. W. Screening lambdagt recombinant clones by hybridization to single plaques in situ. Science. 1977 Apr 8;196(4286):180–182. doi: 10.1126/science.322279. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carroll M. C., Campbell R. D., Porter R. R. Mapping of steroid 21-hydroxylase genes adjacent to complement component C4 genes in HLA, the major histocompatibility complex in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):521–525. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.521. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chung B. C., Matteson K. J., Miller W. L. Cloning and characterization of the bovine gene for steroid 21-hydroxylase (P-450c21). DNA. 1985 Jun;4(3):211–219. doi: 10.1089/dna.1985.4.211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gonzalez F. J., Kimura S., Nebert D. W. Comparison of the flanking regions and introns of the mouse 2,3,7,8-tetrachlorodibenzo-p-dioxin-inducible cytochrome P1-450 and P3-450 genes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5040–5049. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hines R. N., Levy J. B., Conrad R. D., Iversen P. L., Shen M. L., Renli A. M., Bresnick E. Gene structure and nucleotide sequence for rat cytochrome P-450c. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Mar;237(2):465–476. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90300-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hood L., Steinmetz M., Malissen B. Genes of the major histocompatibility complex of the mouse. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:529–568. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.002525. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kioussis D., Eiferman F., van de Rijn P., Gorin M. B., Ingram R. S., Tilghman S. M. The evolution of alpha-fetoprotein and albumin. II. The structures of the alpha-fetoprotein and albumin genes in the mouse. J Biol Chem. 1981 Feb 25;256(4):1960–1967. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lawn R. M., Fritsch E. F., Parker R. C., Blake G., Maniatis T. The isolation and characterization of linked delta- and beta-globin genes from a cloned library of human DNA. Cell. 1978 Dec;15(4):1157–1174. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(78)90043-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Messing J., Crea R., Seeburg P. H. A system for shotgun DNA sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 1981 Jan 24;9(2):309–321. doi: 10.1093/nar/9.2.309. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mizukami Y., Sogawa K., Suwa Y., Muramatsu M., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Gene structure of a phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 in rat liver. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(13):3958–3962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.13.3958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nonaka M., Takahashi M., Natsuume-Sakai S., Nonaka M., Tanaka S., Shimizu A., Honjo T. Isolation of cDNA clones specifying the fourth component of mouse complement and its isotype, sex-limited protein. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(21):6822–6826. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.21.6822. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reynolds G. A., Basu S. K., Osborne T. F., Chin D. J., Gil G., Brown M. S., Goldstein J. L., Luskey K. L. HMG CoA reductase: a negatively regulated gene with unusual promoter and 5' untranslated regions. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):275–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90549-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sharp P. A. On the origin of RNA splicing and introns. Cell. 1985 Sep;42(2):397–400. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90092-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Slightom J. L., Blechl A. E., Smithies O. Human fetal G gamma- and A gamma-globin genes: complete nucleotide sequences suggest that DNA can be exchanged between these duplicated genes. Cell. 1980 Oct;21(3):627–638. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90426-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Gotoh O., Kawajiri K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Distinct organization of methylcholanthrene- and phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 genes in the rat. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5066–5070. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5066. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sogawa K., Gotoh O., Kawajiri K., Harada T., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Complete nucleotide sequence of a methylcholanthrene-inducible cytochrome P-450 (P-450d) gene in the rat. J Biol Chem. 1985 Apr 25;260(8):5026–5032. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern E. M. Detection of specific sequences among DNA fragments separated by gel electrophoresis. J Mol Biol. 1975 Nov 5;98(3):503–517. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(75)80083-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Suwa Y., Mizukami Y., Sogawa K., Fujii-Kuriyama Y. Gene structure of a major form of phenobarbital-inducible cytochrome P-450 in rat liver. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 5;260(13):7980–7984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Chaplin D. D., Weis J. H., Dupont B., New M. I., Seidman J. G. Two steroid 21-hydroxylase genes are located in the murine S region. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):465–467. doi: 10.1038/312465a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., Grossberger D., Onufer B. J., Chaplin D. D., New M. I., Dupont B., Strominger J. L. Two genes encoding steroid 21-hydroxylase are located near the genes encoding the fourth component of complement in man. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(4):1089–1093. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- White P. C., New M. I., Dupont B. HLA-linked congenital adrenal hyperplasia results from a defective gene encoding a cytochrome P-450 specific for steroid 21-hydroxylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(23):7505–7509. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.23.7505. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]