Abstract
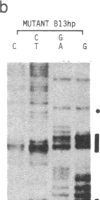
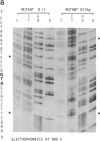
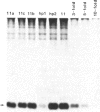
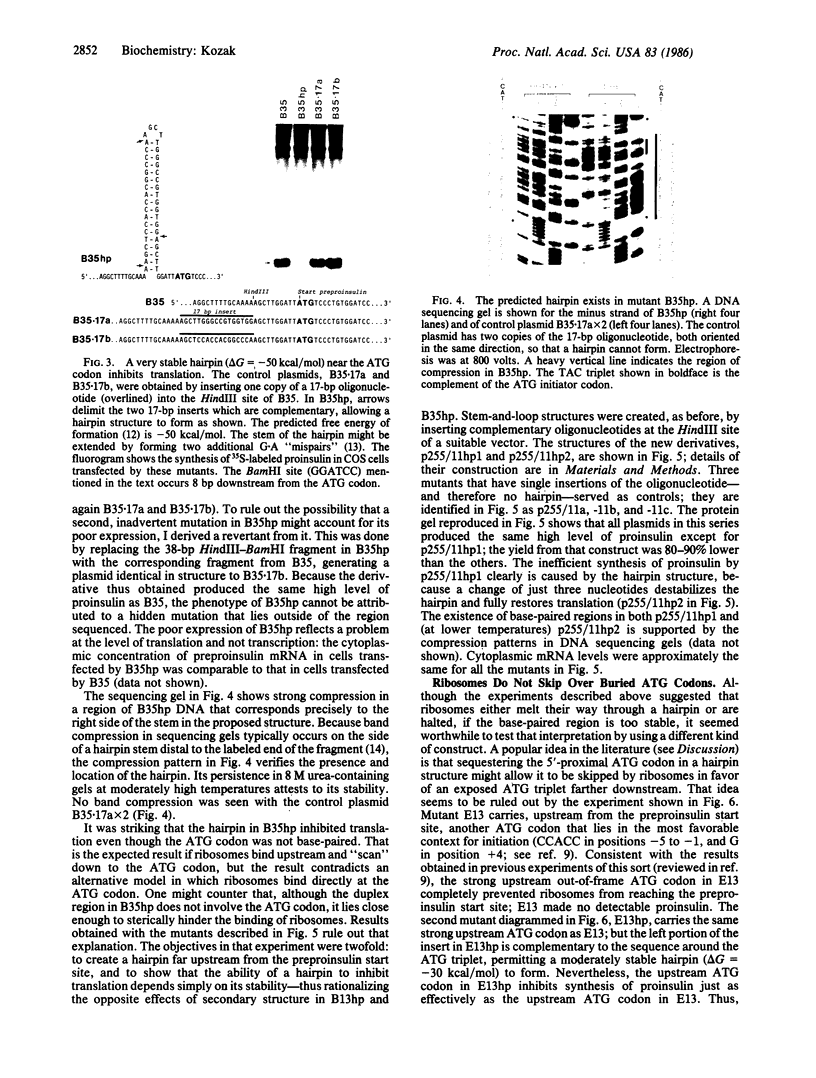
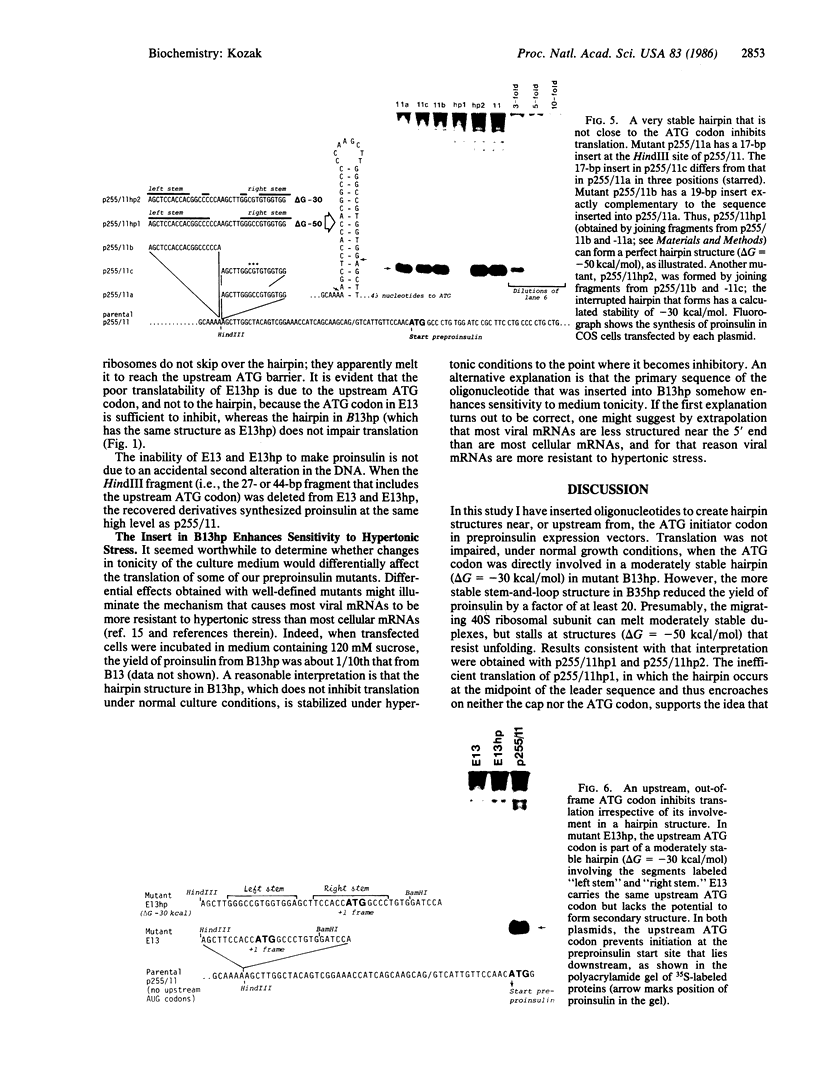
Oligonucleotides designed to create hairpin structures were inserted upstream from the ATG initiator codon in several plasmids that encode preproinsulin, and the effects on translation were monitored in COS cells transfected by the vectors. Creation of a hairpin (delta G = -30 kcal/mol) that directly involves the ATG triplet at the start of the preproinsulin coding sequence does not reduce the yield of proinsulin. However, a more stable stem-and-loop structure (delta G = -50 kcal/mol) reduces the proinsulin yield by 85-95%. The stable hairpin inhibits even when it occurs at the midpoint of the 5' untranslated sequence and thus involves neither the cap nor the ATG codon. Presumably the migrating 40S ribosomal subunit can melt moderately stable duplexes but stalls at structures (delta G = -50 kcal/mol) that resist unfolding. Other experiments argue against the idea that sequestering the 5'-proximal ATG codon in a hairpin structure might allow it to be skipped by ribosomes in favor of an exposed ATG triplet farther downstream: when the primary sequence around the first ATG triplet is favorable for initiation, no translation from a downstream site can be detected, irrespective of whether the first ATG codon is single-stranded or base-paired.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ahlquist P., Dasgupta R., Kaesberg P. Near identity of 3- RNA secondary structure in bromoviruses and cucumber mosaic virus. Cell. 1981 Jan;23(1):183–189. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(81)90283-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienz B., Zakut-Houri R., Givol D., Oren M. Analysis of the gene coding for the murine cellular tumour antigen p53. EMBO J. 1984 Sep;3(9):2179–2183. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1984.tb02110.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chu M. L., de Wet W., Bernard M., Ramirez F. Fine structural analysis of the human pro-alpha 1 (I) collagen gene. Promoter structure, AluI repeats, and polymorphic transcripts. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2315–2320. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darlix J. L., Zuker M., Spahr P. F. Structure-function relationship of Rous sarcoma virus leader RNA. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 Sep 11;10(17):5183–5196. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.17.5183. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ghosh P. K., Reddy V. B., Swinscoe J., Lebowitz P., Weissman S. M. Heterogeneity and 5'-terminal structures of the late RNAs of simian virus 40. J Mol Biol. 1978 Dec 25;126(4):813–846. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(78)90022-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gough N. M., Metcalf D., Gough J., Grail D., Dunn A. R. Structure and expression of the mRNA for murine granulocyte-macrophage colony stimulating factor. EMBO J. 1985 Mar;4(3):645–653. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03678.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haarr L., Marsden H. S., Preston C. M., Smiley J. R., Summers W. C., Summers W. P. Utilization of internal AUG codons for initiation of protein synthesis directed by mRNAs from normal and mutant genes encoding herpes simplex virus-specified thymidine kinase. J Virol. 1985 Nov;56(2):512–519. doi: 10.1128/jvi.56.2.512-519.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hall M. N., Gabay J., Débarbouillé M., Schwartz M. A role for mRNA secondary structure in the control of translation initiation. Nature. 1982 Feb 18;295(5850):616–618. doi: 10.1038/295616a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hay N., Aloni Y. Attenuation of late simian virus 40 mRNA synthesis is enhanced by the agnoprotein and is temporally regulated in isolated nuclear systems. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jun;5(6):1327–1334. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.6.1327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hickey D. R., Turner D. H. Effects of terminal mismatches on RNA stability: thermodynamics of duplex formation for ACCGGGp, ACCGGAp, and ACCGGCp. Biochemistry. 1985 Jul 16;24(15):3987–3991. doi: 10.1021/bi00336a028. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnston H. M., Roth J. R. DNA sequence changes of mutations altering attenuation control of the histidine operon of Salmonella typhimurium. J Mol Biol. 1981 Feb 5;145(4):735–756. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90312-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Comparison of initiation of protein synthesis in procaryotes, eucaryotes, and organelles. Microbiol Rev. 1983 Mar;47(1):1–45. doi: 10.1128/mr.47.1.1-45.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Evaluation of the "scanning model" for initiation of protein synthesis in eucaryotes. Cell. 1980 Nov;22(1 Pt 1):7–8. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90148-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Influence of mRNA secondary structure on binding and migration of 40S ribosomal subunits. Cell. 1980 Jan;19(1):79–90. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90390-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations close to the AUG initiator codon affect the efficiency of translation of rat preproinsulin in vivo. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):241–246. doi: 10.1038/308241a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kozak M. Point mutations define a sequence flanking the AUG initiator codon that modulates translation by eukaryotic ribosomes. Cell. 1986 Jan 31;44(2):283–292. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90762-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Liau G., Mudryj M., de Crombrugghe B. Identification of the promoter and first exon of the mouse alpha 1 (III) collagen gene. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3773–3777. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macdonald P. M., Kutter E., Mosig G. Regulation of a bacteriophage T4 late gene, soc, which maps in an early region. Genetics. 1984 Jan;106(1):17–27. doi: 10.1093/genetics/106.1.17. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
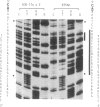
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munson L. M., Stormo G. D., Niece R. L., Reznikoff W. S. lacZ translation initiation mutations. J Mol Biol. 1984 Aug 25;177(4):663–683. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90043-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nomoto A., Omata T., Toyoda H., Kuge S., Horie H., Kataoka Y., Genba Y., Nakano Y., Imura N. Complete nucleotide sequence of the attenuated poliovirus Sabin 1 strain genome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):5793–5797. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.5793. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ordahl C. P., Evans G. L., Cooper T. A., Kunz G., Perriard J. C. Complete cDNA-derived amino acid sequence of chick muscle creatine kinase. J Biol Chem. 1984 Dec 25;259(24):15224–15227. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Payvar F., Schimke R. T. Methylmercury hydroxide enhancement of translation and transcription of ovalbumin and conalbumin mRNA's. J Biol Chem. 1979 Aug 25;254(16):7636–7642. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pelletier J., Sonenberg N. Insertion mutagenesis to increase secondary structure within the 5' noncoding region of a eukaryotic mRNA reduces translational efficiency. Cell. 1985 Mar;40(3):515–526. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90200-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perdue M. L., Borchelt D., Resnick R. J. Participation of 5'-terminal leader sequences in in vitro translation of Rous sarcoma virus RNA. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jun 10;257(11):6551–6555. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Privalsky M. L., Bishop J. M. Proteins specified by avian erythroblastosis virus: coding region localization and identification of a previously undetected erb-B polypeptide. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Jul;79(13):3958–3962. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.13.3958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rogers J. C. Two barley alpha-amylase gene families are regulated differently in aleurone cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 25;260(6):3731–3738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito H., Hayday A. C., Wiman K., Hayward W. S., Tonegawa S. Activation of the c-myc gene by translocation: a model for translational control. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Dec;80(24):7476–7480. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.24.7476. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Soeda E., Arrand J. R., Griffin B. E. Polyoma virus DNA: complete nucleotide sequence of the gene which codes for polyoma virus capsid protein VP1 and overlaps the VP2/VP3 genes. J Virol. 1980 Feb;33(2):619–630. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.2.619-630.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spena A., Krause E., Dobberstein B. Translation efficiency of zein mRNA is reduced by hybrid formation between the 5'- and 3'-untranslated region. EMBO J. 1985 Sep;4(9):2153–2158. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03909.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeishi K., Kaneda S., Ayusawa D., Shimizu K., Gotoh O., Seno T. Nucleotide sequence of a functional cDNA for human thymidylate synthase. Nucleic Acids Res. 1985 Mar 25;13(6):2035–2043. doi: 10.1093/nar/13.6.2035. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tinoco I., Jr, Borer P. N., Dengler B., Levin M. D., Uhlenbeck O. C., Crothers D. M., Bralla J. Improved estimation of secondary structure in ribonucleic acids. Nat New Biol. 1973 Nov 14;246(150):40–41. doi: 10.1038/newbio246040a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willis D., Foglesong D., Granoff A. Nucleotide sequence of an immediate-early frog virus 3 gene. J Virol. 1984 Dec;52(3):905–912. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.3.905-912.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yates J. R., Nuss D. L. Resistance to inhibitors of mammalian cell protein synthesis induced by preincubation in hypertonic growth medium. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 25;257(24):15030–15034. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]