Abstract
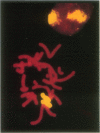
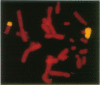
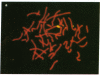
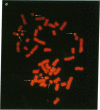
This report describes the use of fluorescence in situ hybridization for chromosome classification and detection of chromosome aberrations. Biotin-labeled DNA was hybridized to target chromosomes and subsequently rendered fluorescent by successive treatments with fluorescein-labeled avidin and biotinylated anti-avidin antibody. Human chromosomes in human-hamster hybrid cell lines were intensely and uniformly stained in metaphase spreads and interphase nuclei when human genomic DNA was used as a probe. Interspecies translocations were detected easily at metaphase. The human-specific fluorescence intensity from cell nuclei and chromosomes was proportional to the amount of target human DNA. Human Y chromosomes were fluorescently stained in metaphase and interphase nuclei by using a 0.8-kilobase DNA probe specific for the Y chromosome. Cells from males were 40 times brighter than those from females. Both Y chromosomal domains were visible in most interphase nuclei of XYY amniocytes. Human 28S ribosomal RNA genes on metaphase chromosomes were distinctly stained by using a 1.5-kilobase DNA probe.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Albertson D. G. Mapping muscle protein genes by in situ hybridization using biotin-labeled probes. EMBO J. 1985 Oct;4(10):2493–2498. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03961.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bauman J. G., Wiegant J., Borst P., van Duijn P. A new method for fluorescence microscopical localization of specific DNA sequences by in situ hybridization of fluorochromelabelled RNA. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Aug;128(2):485–490. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90087-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burgerhout W. Identification of interspecific translocation chromosomes in human-Chinese hamster hybrid cells. Humangenetik. 1975 Sep 23;29(3):229–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00297628. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Burns J., Chan V. T., Jonasson J. A., Fleming K. A., Taylor S., McGee J. O. Sensitive system for visualising biotinylated DNA probes hybridised in situ: rapid sex determination of intact cells. J Clin Pathol. 1985 Oct;38(10):1085–1092. doi: 10.1136/jcp.38.10.1085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caspersson T., Farber S., Foley G. E., Kudynowski J., Modest E. J., Simonsson E., Wagh U., Zech L. Chemical differentiation along metaphase chromosomes. Exp Cell Res. 1968 Jan;49(1):219–222. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(68)90538-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooke H. J., Schmidtke J., Gosden J. R. Characterisation of a human Y chromosome repeated sequence and related sequences in higher primates. Chromosoma. 1982;87(5):491–502. doi: 10.1007/BF00333470. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies K. E., Young B. D., Elles R. G., Hill M. E., Williamson R. Cloning of a representative genomic library of the human X chromosome after sorting by flow cytometry. Nature. 1981 Oct 1;293(5831):374–376. doi: 10.1038/293374a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devine E. A., Nolin S. L., Houck G. E., Jr, Jenkins E. C., Brown W. T. Chromosomal localization of several families of repetitive sequences by in situ hybridization. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 Jan;37(1):114–123. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Disteche C. M., Kunkel L. M., Lojewski A., Orkin S. H., Eisenhard M., Sahar E., Travis B., Latt S. A. Isolation of mouse x-chromosome specific DNA from an x-enriched lambda phage library derived from flow sorted chromosomes. Cytometry. 1982 Mar;2(5):282–286. doi: 10.1002/cyto.990020503. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duhamel R. C., Johnson D. A. Use of nonfat dry milk to block nonspecific nuclear and membrane staining by avidin conjugates. J Histochem Cytochem. 1985 Jul;33(7):711–714. doi: 10.1177/33.7.2409130. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durnam D. M., Gelinas R. E., Myerson D. Detection of species specific chromosomes in somatic cell hybrids. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Nov;11(6):571–577. doi: 10.1007/BF01534722. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Erickson J. M., Rushford C. L., Dorney D. J., Wilson G. N., Schmickel R. D. Structure and variation of human ribosomal DNA: molecular analysis of cloned fragments. Gene. 1981 Dec;16(1-3):1–9. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(81)90055-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham G. J., Hall T. J., Cummings M. R. Isolation of repetitive DNA sequences from human chromosome 21. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Jan;36(1):25–35. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gray J. W., Langlois R. G. Chromosome classification and purification using flow cytometry and sorting. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1986;15:195–235. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.15.060186.001211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Keys C., VarsanyiBreiner A., Kao F. T., Jones C., Puck T. T., Housman D. Isolation and localization of DNA segments from specific human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gusella J. F., Keys C., VarsanyiBreiner A., Kao F. T., Jones C., Puck T. T., Housman D. Isolation and localization of DNA segments from specific human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2829–2833. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2829. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harper M. E., Ullrich A., Saunders G. F. Localization of the human insulin gene to the distal end of the short arm of chromosome 11. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jul;78(7):4458–4460. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.7.4458. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jabs E. W., Wolf S. F., Migeon B. R. Characterization of a cloned DNA sequence that is present at centromeres of all human autosomes and the X chromosome and shows polymorphic variation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(15):4884–4888. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.15.4884. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. D., Nogueira Araujo G. M. A simple method of reducing the fading of immunofluorescence during microscopy. J Immunol Methods. 1981;43(3):349–350. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(81)90183-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krumlauf R., Jeanpierre M., Young B. D. Construction and characterization of genomic libraries from specific human chromosomes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2971–2975. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2971. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lalande M., Dryja T. P., Schreck R. R., Shipley J., Flint A., Latt S. A. Isolation of human chromosome 13-specific DNA sequences cloned from flow sorted chromosomes and potentially linked to the retinoblastoma locus. Cancer Genet Cytogenet. 1984 Dec;13(4):283–295. doi: 10.1016/0165-4608(84)90073-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landegent J. E., Jansen in de Wal N., van Ommen G. J., Baas F., de Vijlder J. J., van Duijn P., Van der Ploeg M. Chromosomal localization of a unique gene by non-autoradiographic in situ hybridization. Nature. 1985 Sep 12;317(6033):175–177. doi: 10.1038/317175a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landegent J. E., Jasen in de Wal N., Baan R. A., Hoeijmakers J. H., Van der Ploeg M. 2-Acetylaminofluorene-modified probes for the indirect hybridocytochemical detection of specific nucleic acid sequences. Exp Cell Res. 1984 Jul;153(1):61–72. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(84)90448-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Langer P. R., Waldrop A. A., Ward D. C. Enzymatic synthesis of biotin-labeled polynucleotides: novel nucleic acid affinity probes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Nov;78(11):6633–6637. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.11.6633. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Schonberg S. A male-specific DNA probe detects heterochromatin sequences in a familial Yq- chromosome. Am J Hum Genet. 1984 Nov;36(6):1394–1396. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lau Y. F., Ying K. L., Donnell G. N. Identification of a case of Y:18 translocation using a Y-specific repetitive DNA probe. Hum Genet. 1985;69(2):102–105. doi: 10.1007/BF00293276. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L. Different central nervous system cell types display distinct and nonrandom arrangements of satellite DNA sequences. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 May;81(10):3123–3127. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.10.3123. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manuelidis L., Ward D. C. Chromosomal and nuclear distribution of the HindIII 1.9-kb human DNA repeat segment. Chromosoma. 1984;91(1):28–38. doi: 10.1007/BF00286482. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mathog D., Hochstrasser M., Gruenbaum Y., Saumweber H., Sedat J. Characteristic folding pattern of polytene chromosomes in Drosophila salivary gland nuclei. 1984 Mar 29-Apr 4Nature. 308(5958):414–421. doi: 10.1038/308414a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mendelsohn M. L., Mayall B. H., Bogart E., Moore D. H., 2nd, Perry B. H. DNA content and DNA-based centromeric index of the 24 human chromosomes. Science. 1973 Mar 16;179(4078):1126–1129. doi: 10.1126/science.179.4078.1126. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller C. R., Davies K. E., Cremer C., Rappold G., Gray J. W., Ropers H. H. Cloning of genomic sequences from the human Y chromosome after purification by dual beam flow sorting. Hum Genet. 1983;64(2):110–115. doi: 10.1007/BF00327104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nilsson B. A bibliography of literature concerning chromosome identification--with special reference to fluorescence Giemsa staining techniques. Hereditas. 1973;73(2):259–270. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-5223.1973.tb01088.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rappold G. A., Cremer T., Hager H. D., Davies K. E., Müller C. R., Yang T. Sex chromosome positions in human interphase nuclei as studied by in situ hybridization with chromosome specific DNA probes. Hum Genet. 1984;67(3):317–325. doi: 10.1007/BF00291361. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schardin M., Cremer T., Hager H. D., Lang M. Specific staining of human chromosomes in Chinese hamster x man hybrid cell lines demonstrates interphase chromosome territories. Hum Genet. 1985;71(4):281–287. doi: 10.1007/BF00388452. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmickel R. D. Quantitation of human ribosomal DNA: hybridization of human DNA with ribosomal RNA for quantitation and fractionation. Pediatr Res. 1973 Jan;7(1):5–12. doi: 10.1203/00006450-197301000-00002. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson L. H., Mooney C. L., Burkhart-Schultz K., Carrano A. V., Siciliano M. J. Correction of a nucleotide-excision-repair mutation by human chromosome 19 in hamster-human hybrid cells. Somat Cell Mol Genet. 1985 Jan;11(1):87–92. doi: 10.1007/BF01534738. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trask B., van den Engh G., Landegent J., in de Wal N. J., van der Ploeg M. Detection of DNA sequences in nuclei in suspension by in situ hybridization and dual beam flow cytometry. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1401–1403. doi: 10.1126/science.2416058. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Van Prooijen-Knegt A. C., Van Hoek J. F., Bauman J. G., Van Duijn P., Wool I. G., Van der Ploeg M. In situ hybridization of DNA sequences in human metaphase chromosomes visualized by an indirect fluorescent immunocytochemical procedure. Exp Cell Res. 1982 Oct;141(2):397–407. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(82)90228-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Willard H. F. Chromosome-specific organization of human alpha satellite DNA. Am J Hum Genet. 1985 May;37(3):524–532. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang T. P., Hansen S. K., Oishi K. K., Ryder O. A., Hamkalo B. A. Characterization of a cloned repetitive DNA sequence concentrated on the human X chromosome. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Nov;79(21):6593–6597. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.21.6593. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zorn C., Cremer C., Cremer T., Zimmer J. Unscheduled DNA synthesis after partial UV irradiation of the cell nucleus. Distribution in interphase and metaphase. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Nov;124(1):111–119. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90261-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]