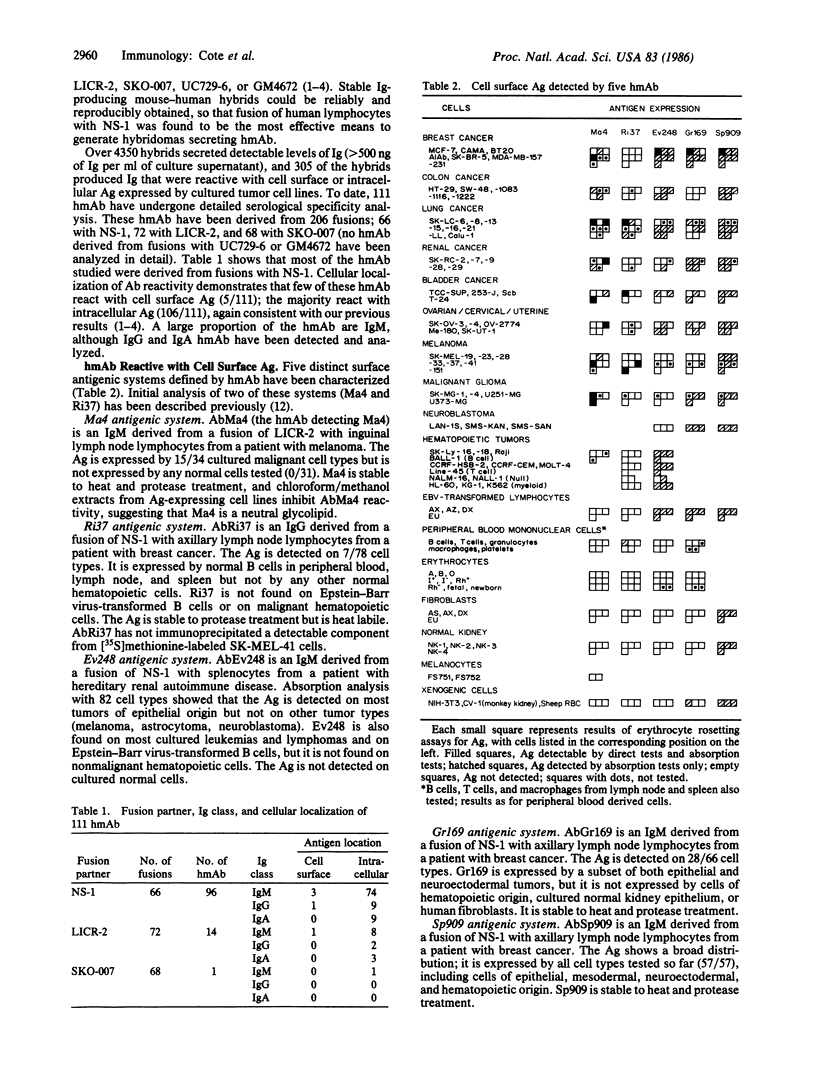
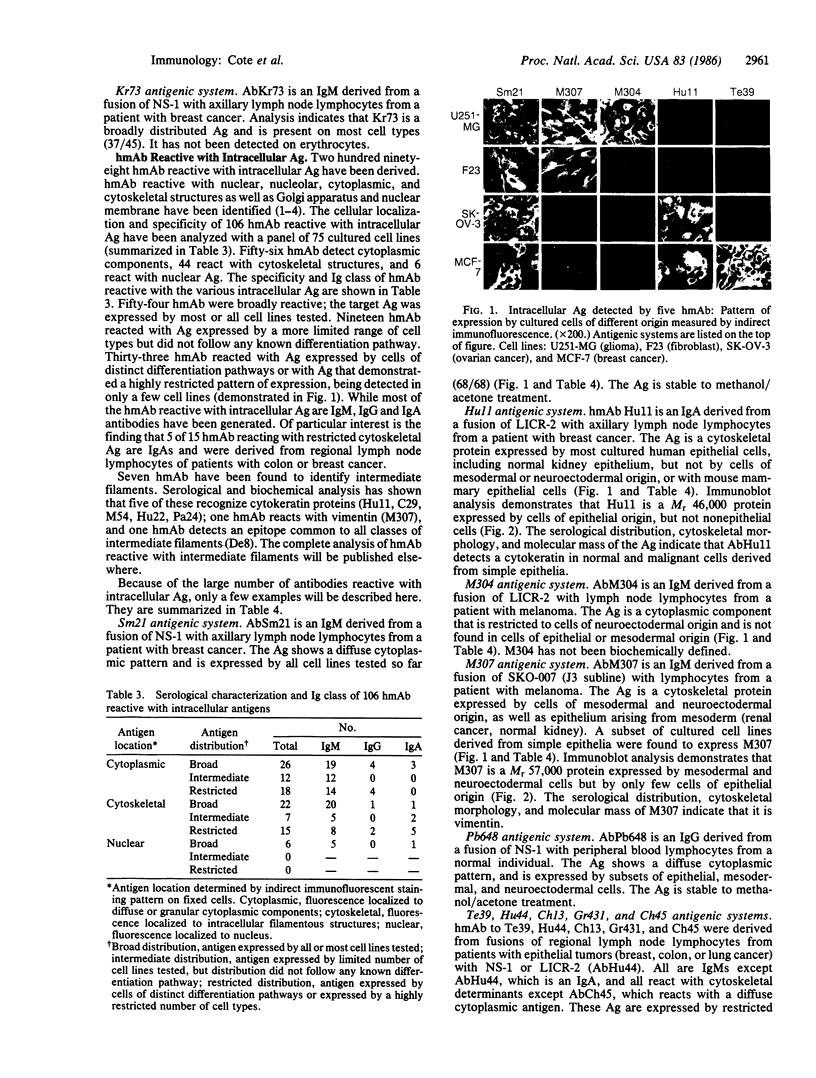
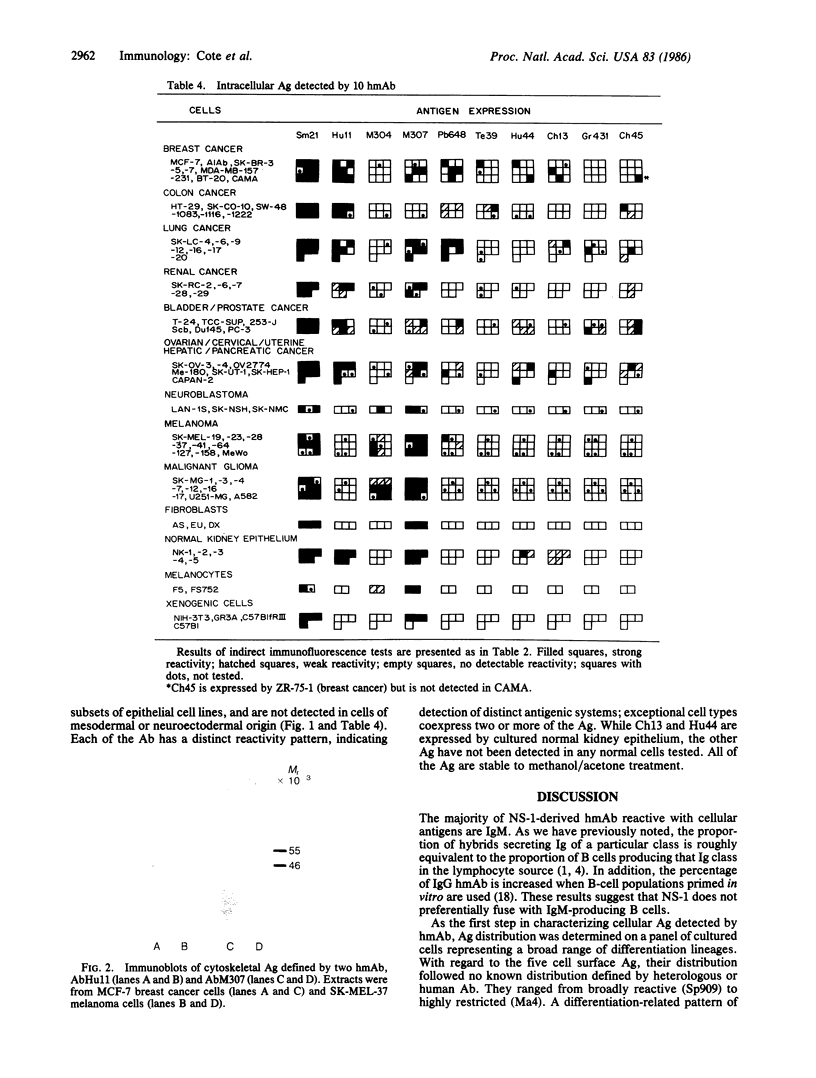
Abstract
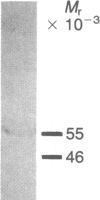
Over 4350 human Ig-secreting hybrids have been generated through the fusion of human lymphocytes with NS-1 (mouse), LICR-2, SKO-007, GM4672, or UC729-6 (human) myeloma and lymphoblastoid cell lines. NS-1 proved to be the most satisfactory fusion partner, and 83% of the stable Ig-secreting clones were derived from NS-1 fusions. Three hundred five hybrids produced human monoclonal antibodies (hmAb) reactive with cell surface or intracellular antigens expressed by cultured human tumor cell lines, and 111 of these have undergone detailed serological specificity analysis. Several general points have emerged from our study of hmAb: A significant proportion of the human B-cell clones produce antibody reactive with cellular antigens. The majority of these antigens have an intracellular location and are broadly distributed. Intracellular and cell surface differentiation antigens and other antigens with restricted distribution have been defined by hmAb, including two cell surface antigens not detected on normal cells. The relationship of these findings to cancer is unclear, as hmAb reactive with antigens showing distinctive distribution have been generated from the lymphocytes of normal individuals as well as tumor-bearing patients.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Cote R. J., Morrissey D. M., Houghton A. N., Beattie E. J., Jr, Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Generation of human monoclonal antibodies reactive with cellular antigens. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):2026–2030. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.2026. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cote R. J., Morrissey D. M., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Analysis of human monoclonal antibodies derived from lymphocytes of patients with cancer. Fed Proc. 1984 Jun;43(9):2465–2469. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Croce C. M., Linnenbach A., Hall W., Steplewski Z., Koprowski H. Production of human hybridomas secreting antibodies to measles virus. Nature. 1980 Dec 4;288(5790):488–489. doi: 10.1038/288488a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edwards P. A., Smith C. M., Neville A. M., O'Hare M. J. A human-hybridoma system based on a fast-growing mutant of the ARH-77 plasma cell leukemia-derived line. Eur J Immunol. 1982 Aug;12(8):641–648. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830120804. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Moll R., Winter S., Schmid E., Engelbrecht I., Denk H., Krepler R., Platzer B. Diversity of cytokeratins. Differentiation specific expression of cytokeratin polypeptides in epithelial cells and tissues. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 25;153(4):933–959. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glassy M. C., Handley H. H., Hagiwara H., Royston I. UC 729-6, a human lymphoblastoid B-cell line useful for generating antibody-secreting human-human hybridomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6327–6331. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6327. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haspel M. V., McCabe R. P., Pomato N., Janesch N. J., Knowlton J. V., Peters L. C., Hoover H. C., Jr, Hanna M. G., Jr Generation of tumor cell-reactive human monoclonal antibodies using peripheral blood lymphocytes from actively immunized colorectal carcinoma patients. Cancer Res. 1985 Aug;45(8):3951–3961. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Houghton A. N., Brooks H., Cote R. J., Taormina M. C., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. Detection of cell surface and intracellular antigens by human monoclonal antibodies. Hybrid cell lines derived from lymphocytes of patients with malignant melanoma. J Exp Med. 1983 Jul 1;158(1):53–65. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.1.53. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Imam A., Drushella M. M., Taylor C. R., Tökés Z. A. Generation and immunohistological characterization of human monoclonal antibodies to mammary carcinoma cells. Cancer Res. 1985 Jan;45(1):263–271. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Köhler G., Milstein C. Derivation of specific antibody-producing tissue culture and tumor lines by cell fusion. Eur J Immunol. 1976 Jul;6(7):511–519. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830060713. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Farrell P. H. High resolution two-dimensional electrophoresis of proteins. J Biol Chem. 1975 May 25;250(10):4007–4021. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Old L. J. Cancer immunology: the search for specificity--G. H. A. Clowes Memorial lecture. Cancer Res. 1981 Feb;41(2):361–375. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson L., Kaplan H. S. Human-human hybridomas producing monoclonal antibodies of predefined antigenic specificity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5429–5431. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5429. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Intermediate filaments: cell-type-specific markers in differentiation and pathology. Cell. 1982 Dec;31(2 Pt 1):303–306. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90122-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pfreundschuh M. G., Ueda R., Rauterberg E. W., Dörken B. H., Shiku H. Comparison of multiple rosetting assays for detecting antibody reactivity of different immunoglobulin classes against surface antigens of benign and malignant tissue culture cells. J Immunol Methods. 1980;37(1):71–81. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(80)90182-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pukel C. S., Lloyd K. O., Travassos L. R., Dippold W. G., Oettgen H. F., Old L. J. GD3, a prominent ganglioside of human melanoma. Detection and characterisation by mouse monoclonal antibody. J Exp Med. 1982 Apr 1;155(4):1133–1147. doi: 10.1084/jem.155.4.1133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]