Abstract
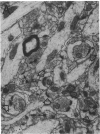
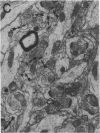
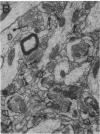
Most, but not all, aged rats exhibit a profound deficit in spatial memory when tested in a radial maze--a task known to depend on the integrity of the hippocampal formation. In this study, animals were divided into three groups based on their spatial memory capacity: young adult rats with good memory, aged rats with impaired memory, and aged rats with good memory. Memory-impaired aged animals showed a loss of perforated axospinous synapses in the dentate gyrus of the hippocampal formation in comparison with either young adults or aged rats with good memory. This finding suggests that the loss of perforated axospinous synapses in the hippocampal formation underlies the age-related deficit in spatial memory.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barnes C. A. Memory deficits associated with senescence: a neurophysiological and behavioral study in the rat. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1979 Feb;93(1):74–104. doi: 10.1037/h0077579. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohen R. S., Siekevitz P. Form of the postsynaptic density. A serial section study. J Cell Biol. 1978 Jul;78(1):36–46. doi: 10.1083/jcb.78.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cotman C. W., Scheff S. W. Compensatory synapse growth in aged animals after neuronal death. Mech Ageing Dev. 1979 Jan;9(1-2):103–117. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(79)90124-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cruz Orive L. M. On the estimation of particle number. J Microsc. 1980 Sep;120(Pt 1):15–27. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2818.1980.tb04116.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curcio C. A., Hinds J. W. Stability of synaptic density and spine volume in dentate gyrus of aged rats. Neurobiol Aging. 1983 Spring;4(1):77–87. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(83)90058-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Desmond N. L., Levy W. B. Synaptic correlates of associative potentiation/depression: an ultrastructural study in the hippocampus. Brain Res. 1983 Apr 11;265(1):21–30. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(83)91329-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geinisman Y., Bondareff W., Dodge J. T. Dendritic atrophy in the dentate gyrus of the senescent rat. Am J Anat. 1978 Jul;152(3):321–329. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001520305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geinisman Y., Bondareff W., Dodge J. T. Hypertrophy of astroglial processes in the dentate gyrus of the senescent rat. Am J Anat. 1978 Dec;153(4):537–543. doi: 10.1002/aja.1001530405. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geinisman Y., Bondareff W., Dodge J. T. Partial deafferentation of neurons in the dentate gyrus of the senescent rat. Brain Res. 1977 Oct 14;134(3):541–545. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(77)90828-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Geinisman Y. Loss of axon terminals contacting neuronal somata in the dentate gyrus of aged rats. Brain Res. 1981 May 11;212(1):136–139. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90040-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Genisman Y., Bondareff W. Decrease in the number of synapses in the senescent brain: a quantitative electron microscopic analysis of the dentate gyrus molecular layer in the rat. Mech Ageing Dev. 1976 Jan-Feb;5(1):11–23. doi: 10.1016/0047-6374(76)90003-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenough W. T., West R. W., DeVoogd T. J. Subsynaptic plate perforations: changes with age and experience in the rat. Science. 1978 Dec 8;202(4372):1096–1098. doi: 10.1126/science.715459. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hoff S. F., Scheff S. W., Benardo L. S., Cotman C. W. Lesion-induced synaptogenesis in the dentate gyrus of aged rats: I. Loss and reacquisition of normal synaptic density. J Comp Neurol. 1982 Mar 1;205(3):246–252. doi: 10.1002/cne.902050304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hyman B. T., Van Hoesen G. W., Damasio A. R., Barnes C. L. Alzheimer's disease: cell-specific pathology isolates the hippocampal formation. Science. 1984 Sep 14;225(4667):1168–1170. doi: 10.1126/science.6474172. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landfield P. W., McGaugh J. L., Lynch G. Impaired synaptic potentiation processes in the hippocampus of aged, memory-deficient rats. Brain Res. 1978 Jul 7;150(1):85–101. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90655-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Landfield P. W., Pitler T. A. Prolonged Ca2+-dependent afterhyperpolarizations in hippocampal neurons of aged rats. Science. 1984 Nov 30;226(4678):1089–1092. doi: 10.1126/science.6494926. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lippa A. S., Critchett D. J., Ehlert F., Yamamura H. I., Enna S. J., Bartus R. T. Age-related alterations in neurotransmitter receptors: an electrophysiological and biochemical analysis. Neurobiol Aging. 1981 Spring;2(1):3–8. doi: 10.1016/0197-4580(81)90052-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olton D. S., Walker J. A., Gage F. H. Hippocampal connections and spatial discrimination. Brain Res. 1978 Jan 13;139(2):295–308. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(78)90930-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olton D. S., Walker J. A., Wolf W. A. A disconnection analysis of hippocampal function. Brain Res. 1982 Feb 11;233(2):241–253. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(82)91200-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters A., Kaiserman-Abramof I. R. The small pyramidal neuron of the rat cerebral cortex. The synapses upon dendritic spines. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1969 Sep 22;100(4):487–506. doi: 10.1007/BF00344370. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SCOVILLE W. B., MILNER B. Loss of recent memory after bilateral hippocampal lesions. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1957 Feb;20(1):11–21. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.20.1.11. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Verwer R. W., De Groot D. M. The effect of shape assumptions on the estimation of the numerical density of synapses from thin sections. Prog Brain Res. 1982;55:195–203. doi: 10.1016/S0079-6123(08)64198-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vrensen G., Cardozo J. N. Changes in size and shape of synaptic connections after visual training: an ultrastructural approach of synaptic plasticity. Brain Res. 1981 Aug 10;218(1-2):79–97. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(81)90990-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winocur G. Radial-arm-maze behavior by rats with dorsal hippocampal lesions: effect of cuing. J Comp Physiol Psychol. 1982 Apr;96(2):155–169. doi: 10.1037/h0077882. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woods B. T., Schoene W., Kneisley L. Are hippocampal lesions sufficient to cause lasting amnesia? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 1982 Mar;45(3):243–247. doi: 10.1136/jnnp.45.3.243. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Toledo-Morrell L., Morrell F. Electrophysiological markers of aging and memory loss in rats. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1985;444:296–311. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1985.tb37598.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Toledo-Morrell L., Morrell F., Fleming S. Age-dependent deficits in spatial memory are related to impaired hippocampal kindling. Behav Neurosci. 1984 Oct;98(5):902–907. doi: 10.1037//0735-7044.98.5.902. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]