Abstract
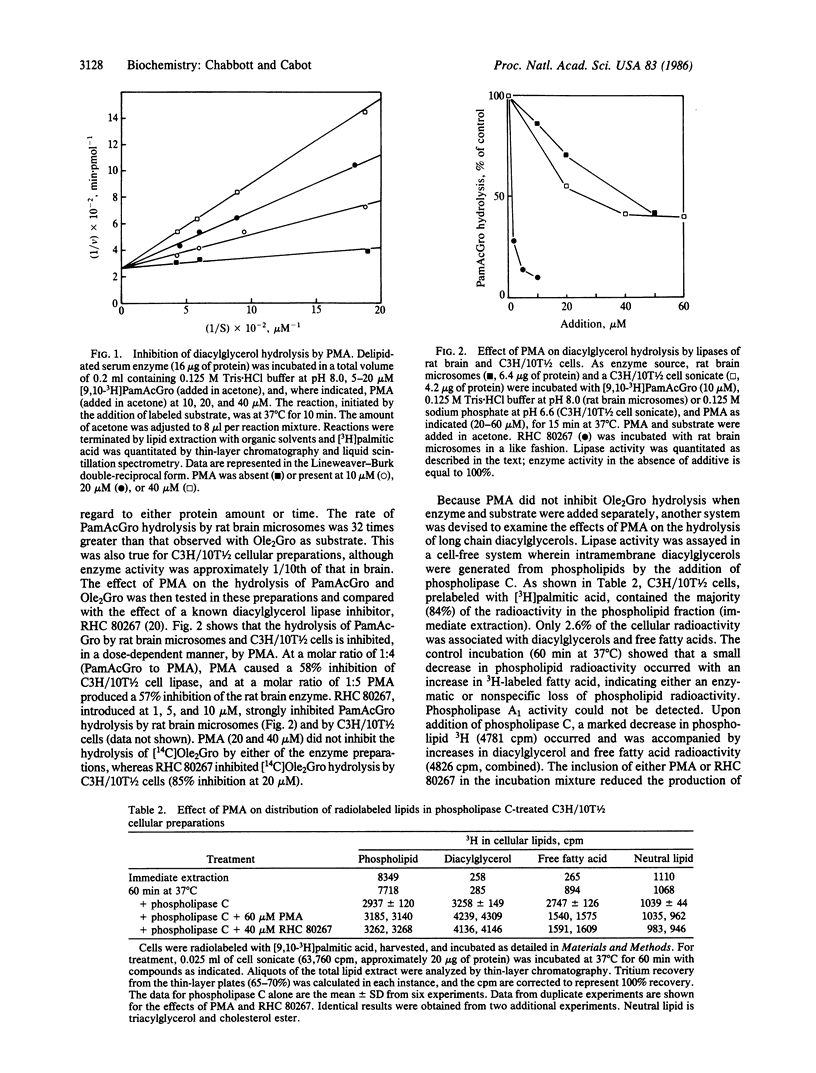
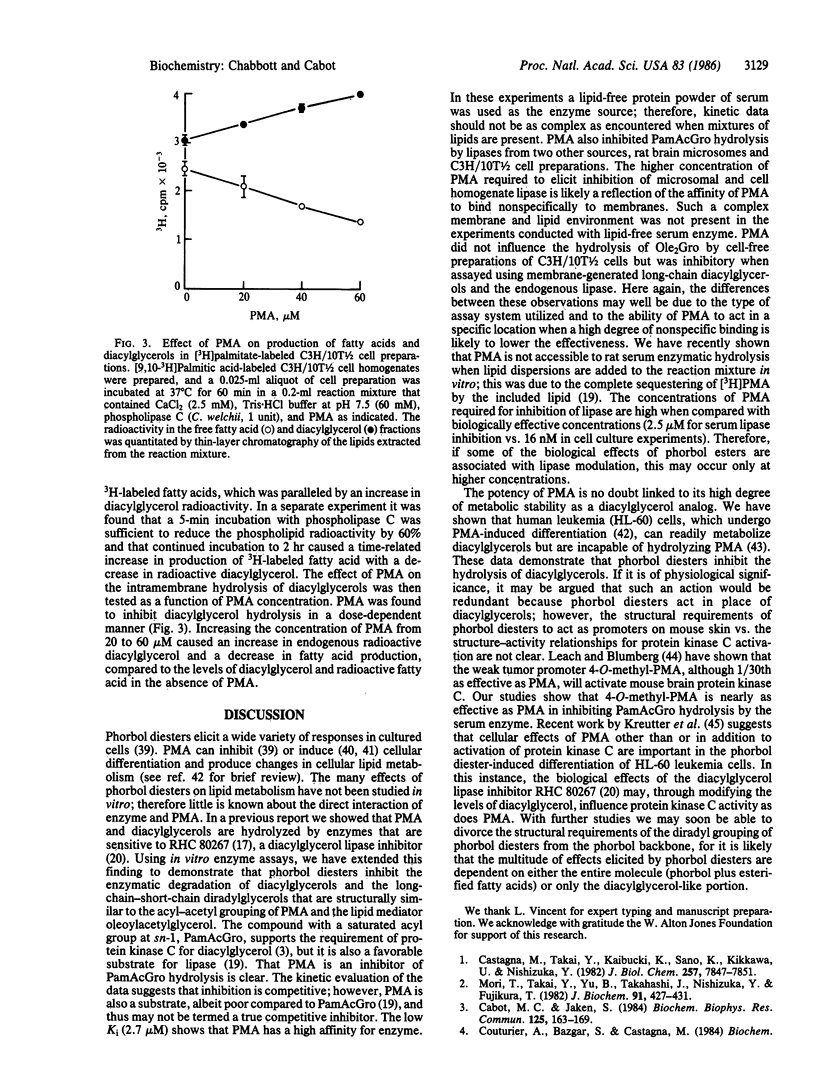
The effect of phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate (PMA) on diacylglycerol lipase activity was examined in rat serum, tissue, and cellular preparations by using di[14C]oleoylglycerol, [3H]palmitoylacetylglycerol, and membrane-resident phospholipase C-generated diacylglycerols as substrates. These experiments were conducted to address whether phorbol esters can mimic diacylglycerols in interacting with enzymes other than protein kinase C. Serum hydrolysis of palmitoylacetylglycerol, assayed by the formation of [3H]palmitic acid, was inhibited by PMA, 4-O-methyl-PMA, or phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate (in order of decreasing potency). The hydrolysis of palmitoylacetylglycerol was inhibited more than 40% by the addition of PMA at a 1:1 molar ratio with substrate. The inhibition resembled the competitive type, with a Ki of approximately 2.7 microM. PMA in the 10-60 microM range also inhibited hydrolysis of palmitoylacetylglycerol by lipases from rat brain microsomes and by homogenates of C3H/10T1/2 mouse fibroblasts. PMA was likewise inhibitory when assayed in an intramembrane enzyme-substrate milieu in which diacylglycerols were generated, in situ, by treatment of [3H]palmitate-labeled cell homogenates with phospholipase C. Collectively, these data demonstrate that PMA, which is now thought to act by mimicry of diacylglycerols, can inhibit the action of diacylglycerol lipase. It is possible that such a mechanism is linked to the multiplicity of responses elicited by phorbol diesters and that other agents may function by means of enzyme interactions (post-phospholipase C) to influence the levels of the cellular diacylglycerol mediators.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- BLIGH E. G., DYER W. J. A rapid method of total lipid extraction and purification. Can J Biochem Physiol. 1959 Aug;37(8):911–917. doi: 10.1139/o59-099. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barrett J. C., Brown M. T., Sisskin E. E. Deacylation of 12-O-[3H]tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate and [3H]phorbol-12,13-didecanoate in hamster skin and hamster cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1982 Aug;42(8):3098–3101. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J. Phosphatidylinositol hydrolysis: a multifunctional transducing mechanism. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 1981 Nov;24(2):115–140. doi: 10.1016/0303-7207(81)90055-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berry D. L., Bracken W. M., Fischer S. M., Viaje A., Slaga T. J. Metabolic conversion of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate in adult and newborn mouse skin and mouse liver microsomes. Cancer Res. 1978 Aug;38(8):2301–2306. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Breitman T. R., Collins S. J., Keene B. R. Replacement of serum by insulin and transferrin supports growth and differentiation of the human promyelocytic cell line, HL-60. Exp Cell Res. 1980 Apr;126(2):494–498. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(80)90296-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabot M. C., Gatt S. Lipases of rat brain microsomes. Adv Exp Med Biol. 1978;101:101–111. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4615-9071-2_10. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabot M. C. Hydrolysis of novel diacylglycerol analogs and phorbol diesters by serum lipase. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1985 Feb 8;833(2):330–335. doi: 10.1016/0005-2760(85)90206-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabot M. C., Jaken S. Structural and chemical specificity of diacylglycerols for protein kinase C activation. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Nov 30;125(1):163–169. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80349-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabot M. C. Tumor promoting phorbol diesters: substrates for diacylglycerol lipase. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Aug 30;123(1):170–177. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90395-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabot M. C., Welsh C. J., Callaham M. F., Huberman E. Alterations in lipid metabolism induced by 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate in differentiating human myeloid leukemia cells. Cancer Res. 1980 Oct;40(10):3674–3679. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cabot M. C., Welsh C. J. Ether lipid studies in mouse C3H/10T1/2 cells and a 3-methylcholanthrene-transformed clone. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1981 Oct 1;211(1):240–244. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(81)90450-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castagna M., Takai Y., Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Kikkawa U., Nishizuka Y. Direct activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase by tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 10;257(13):7847–7851. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Collins S. J., Gallo R. C., Gallagher R. E. Continuous growth and differentiation of human myeloid leukaemic cells in suspension culture. Nature. 1977 Nov 24;270(5635):347–349. doi: 10.1038/270347a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Diamond L., O'Brien T. G., Rovera G. Tumor promoters: effects on proliferation and differentiation of cells in culture. Life Sci. 1978 Nov 13;23(20):1979–1988. doi: 10.1016/0024-3205(78)90229-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ebeling J. G., Vandenbark G. R., Kuhn L. J., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M., Niedel J. E. Diacylglycerols mimic phorbol diester induction of leukemic cell differentiation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):815–819. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.815. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Huberman E., Callaham M. F. Induction of terminal differentiation in human promyelocytic leukemia cells by tumor-promoting agents. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1293–1297. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1293. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jetten A. M., Ganong B. R., Vandenbark G. R., Shirley J. E., Bell R. M. Role of protein kinase C in diacylglycerol-mediated induction of ornithine decarboxylase and reduction of epidermal growth factor binding. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(7):1941–1945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.7.1941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaibuchi K., Sano K., Hoshijima M., Takai Y., Nishizuka Y. Phosphatidylinositol turnover in platelet activation; calcium mobilization and protein phosphorylation. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):323–335. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90020-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kikkawa U., Takai Y., Tanaka Y., Miyake R., Nishizuka Y. Protein kinase C as a possible receptor protein of tumor-promoting phorbol esters. J Biol Chem. 1983 Oct 10;258(19):11442–11445. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kreutter D., Caldwell A. B., Morin M. J. Dissociation of protein kinase C activation from phorbol ester-induced maturation of HL-60 leukemia cells. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5979–5984. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lackey R. J., Cabot M. C. Serum lipase active in the hydrolysis of the tumor promoter, 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Cancer Lett. 1983 Jun;19(2):165–172. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(83)90150-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lapetina E. G., Reep B., Ganong B. R., Bell R. M. Exogenous sn-1,2-diacylglycerols containing saturated fatty acids function as bioregulators of protein kinase C in human platelets. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1358–1361. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leach K. L., Blumberg P. M. Modulation of protein kinase C activity and [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate binding by various tumor promoters in mouse brain cytosol. Cancer Res. 1985 May;45(5):1958–1963. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCaffrey P. G., Friedman B., Rosner M. R. Diacylglycerol modulates binding and phosphorylation of the epidermal growth factor receptor. J Biol Chem. 1984 Oct 25;259(20):12502–12507. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McNamara M. J., Schmitt J. D., Wykle R. L., Daniel L. W. 1-0-Hexadecyl-2-acetyl-sn-glycerol stimulates differentiation of HL-60 human promyelocytic leukemia cells to macrophage-like cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Jul 31;122(2):824–830. doi: 10.1016/s0006-291x(84)80108-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michell R. H. Inositol lipid metabolism in dividing and differentiating cells. Cell Calcium. 1982 Oct;3(4-5):429–440. doi: 10.1016/0143-4160(82)90028-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mori T., Takai Y., Yu B., Takahashi J., Nishizuka Y., Fujikura T. Specificity of the fatty acyl moieties of diacylglycerol for the activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase. J Biochem. 1982 Feb;91(2):427–431. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a133714. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Niedel J. E., Kuhn L. J., Vandenbark G. R. Phorbol diester receptor copurifies with protein kinase C. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(1):36–40. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.1.36. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Brien T. G., Diamond L. Metabolism of tritium-labeled 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate by cells in culture. Cancer Res. 1978 Aug;38(8):2562–2566. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff C. A., Bertram J. S., Brankow D. W., Heidelberger C. Quantitative and qualitative studies of chemical transformation of cloned C3H mouse embryo cells sensitive to postconfluence inhibition of cell division. Cancer Res. 1973 Dec;33(12):3239–3249. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reznikoff C. A., Brankow D. W., Heidelberger C. Establishment and characterization of a cloned line of C3H mouse embryo cells sensitive to postconfluence inhibition of division. Cancer Res. 1973 Dec;33(12):3231–3238. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rovera G., Santoli D., Damsky C. Human promyelocytic leukemia cells in culture differentiate into macrophage-like cells when treated with a phorbol diester. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2779–2783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saito M., Egawa K. Isolation and characterization of a murine serum esterase which hydrolyzes a tumor promoter, 12-O-tetradecanoyl phorbol 13-acetate. J Biol Chem. 1984 May 10;259(9):5821–5826. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sasakawa N., Ishii K., Yamamoto S., Kato R. Induction of ornithine decarboxylase activity by 1-oleoyl-2-acetyl-glycerol in isolated mouse epidermal cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Apr 30;128(2):913–920. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)90133-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoyab M., Warren T. C., Todaro G. J. Isolation and characterization of an ester hydrolase active on phorbol diesters from murine liver. J Biol Chem. 1981 Dec 10;256(23):12529–12534. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sutherland C. A., Amin D. Relative activities of rat and dog platelet phospholipase A2 and diglyceride lipase. Selective inhibition of diglyceride lipase by RHC 80267. J Biol Chem. 1982 Dec 10;257(23):14006–14010. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takai Y., Kishimoto A., Kikkawa U., Mori T., Nishizuka Y. Unsaturated diacylglycerol as a possible messenger for the activation of calcium-activated, phospholipid-dependent protein kinase system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1979 Dec 28;91(4):1218–1224. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(79)91197-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welsh C. J., Sayer A. M., Littlefield L. G., Cabot M. C. Modification of lipid acyl groups by serum deprivation does not affect phorbol ester-induced differentiation of human leukemia cells. Cancer Lett. 1982 Jul-Aug;16(2):145–154. doi: 10.1016/0304-3835(82)90055-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood R., Harlow R. D. Structural analyses of rat liver phosphoglycerides. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1969 Dec;135(1):272–281. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(69)90540-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


