Abstract
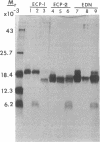
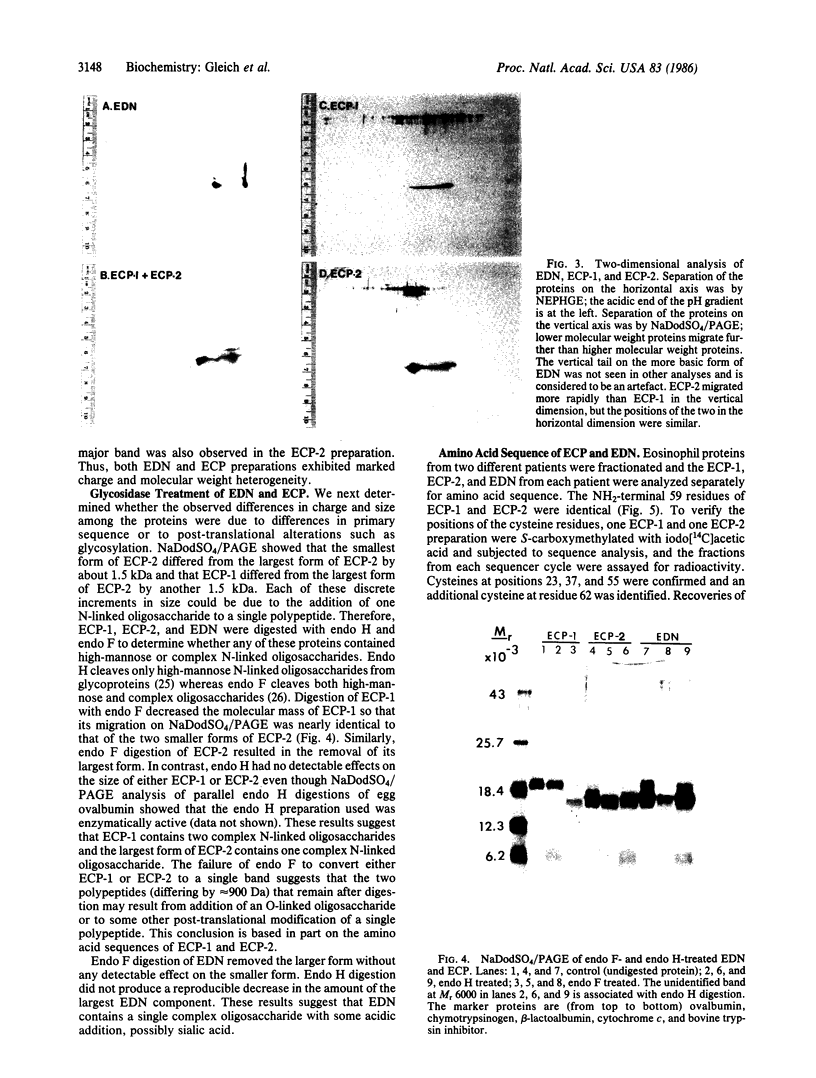
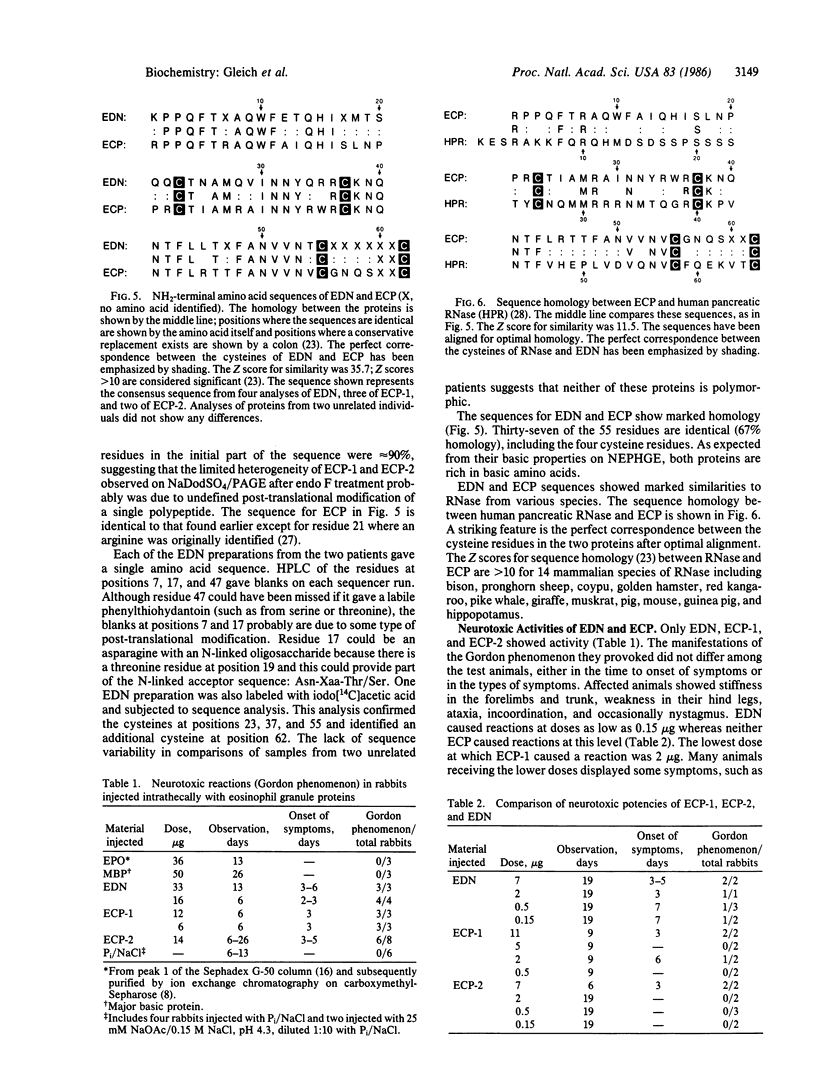
Eosinophil-derived neurotoxin (EDN) and eosinophil cationic protein (ECP) were isolated from lysates of human eosinophil granules by gel filtration and ion exchange chromatography on heparin-Sepharose. Radioimmunoassay, using monoclonal antibodies, of fractions from the heparin-Sepharose chromatography showed one peak of EDN activity and two peaks of ECP activity (termed ECP-1 and ECP-2). EDN, ECP-1, and ECP-2 each exhibited heterogeneity in charge and molecular weight when analyzed by two-dimensional nonequilibrium pH gradient electrophoresis and NaDodSO4/PAGE. Digestion of EDN with endoglycosidase F (endo F) decreased its molecular weight and charge heterogeneity. Thus, END likely contains a single complex oligosaccharide. Endo F digestion of ECP-1 and ECP-2 decreased the molecular weight of both polypeptides, indicating that both likely contain at least one complex oligosaccharide. Amino acid sequence analyses showed that ECP-1 and ECP-2 are identical from residue 1 through residue 59 and that the sequences of EDN and ECP are highly homologous (37 of 55 residues identical). Both EDN and ECP NH2-terminal sequences showed significant homology to RNase, especially in regions of the RNase molecule involved in ligand binding. EDN, ECP-1, and ECP-2 had neurotoxic activity, causing the Gordon phenomenon at doses down to 0.15 micrograms when injected into the cisterna magna; the proteins were comparable in their activities. These results indicate that EDN and ECP are related proteins and suggest that they derived from genes associated with the RNase family.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackerman S. J., Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., Richardson B. A., Butterworth A. E. Comparative toxicity of purified human eosinophil granule cationic proteins for schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 1985 Jul;34(4):735–745. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.1985.34.735. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ackerman S. J., Loegering D. A., Venge P., Olsson I., Harley J. B., Fauci A. S., Gleich G. J. Distinctive cationic proteins of the human eosinophil granule: major basic protein, eosinophil cationic protein, and eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2977–2982. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beintema J. J., Wietzes P., Weickmann J. L., Glitz D. G. The amino acid sequence of human pancreatic ribonuclease. Anal Biochem. 1984 Jan;136(1):48–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(84)90306-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Borst J., Alexander S., Elder J., Terhorst C. The T3 complex on human T lymphocytes involves four structurally distinct glycoproteins. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 25;258(8):5135–5141. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Butterworth A. E., Wassom D. L., Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., David J. R. Damage to schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni induced directly by eosinophil major basic protein. J Immunol. 1979 Jan;122(1):221–229. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Carlson M. G., Peterson C. G., Venge P. Human eosinophil peroxidase: purification and characterization. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1875–1879. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Ackerman S. J., Loegering D. A., Gleich G. J. Purification of human eosinophil-derived neurotoxin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Aug;78(8):5165–5169. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.8.5165. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durack D. T., Sumi S. M., Klebanoff S. J. Neurotoxicity of human eosinophils. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1443–1447. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1443. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elder J. H., Alexander S. endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase F: endoglycosidase from Flavobacterium meningosepticum that cleaves both high-mannose and complex glycoproteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Aug;79(15):4540–4544. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.15.4540. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fairbanks G., Steck T. L., Wallach D. F. Electrophoretic analysis of the major polypeptides of the human erythrocyte membrane. Biochemistry. 1971 Jun 22;10(13):2606–2617. doi: 10.1021/bi00789a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fredens K., Dahl R., Venge P. The Gordon phenomenon induced by the eosinophil cationic protein and eosinophil protein X. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1982 Nov;70(5):361–366. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(82)90025-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Frigas E., Loegering D. A., Wassom D. L., Steinmuller D. Cytotoxic properties of the eosinophil major basic protein. J Immunol. 1979 Dec;123(6):2925–2927. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., Kueppers F., Bajaj S. P., Mann K. G. Physiochemical and biological properties of the major basic protein from guinea pig eosinophil granules. J Exp Med. 1974 Aug 1;140(2):313–332. doi: 10.1084/jem.140.2.313. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., Maldonado J. E. Identification of a major basic protein in guinea pig eosinophil granules. J Exp Med. 1973 Jun 1;137(6):1459–1471. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.6.1459. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gleich G. J., Loegering D. A., Mann K. G., Maldonado J. E. Comparative properties of the Charcot-Leyden crystal protein and the major basic protein from human eosinophils. J Clin Invest. 1976 Mar;57(3):633–640. doi: 10.1172/JCI108319. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HIRS C. H. Dinitrophenyiribonucleases. Brookhaven Symp Biol. 1962 Dec;15:154–183. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koshland D. E., Jr, Neet K. E. The catalytic and regulatory properties of enzymes. Annu Rev Biochem. 1968;37:359–410. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.37.070168.002043. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lipman D. J., Pearson W. R. Rapid and sensitive protein similarity searches. Science. 1985 Mar 22;227(4693):1435–1441. doi: 10.1126/science.2983426. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McLaren D. J., McKean J. R., Olsson I., Venges P., Kay A. B. Morphological studies on the killing of schistosomula of Schistosoma mansoni by human eosinophil and neutrophil cationic proteins in vitro. Parasite Immunol. 1981 Winter;3(4):359–373. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-3024.1981.tb00414.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moosic J. P., Sung E., Nilson A., Jones P. P., McKean D. J. The selective solubilization of different murine splenocyte membrane fractions with lubrol WX and triton X-100 distinguishes two forms of Ia antigens. A cell surface (alpha, beta) and an intracellular (alpha, Ii, beta). J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 25;257(16):9684–9691. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Persson A. M., Winqvist I. Biochemical properties of the eosinophil cationic protein and demonstration of its biosynthesis in vitro in marrow cells from patients with an eosinophilia. Blood. 1986 Feb;67(2):498–503. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Venge P. Cationic proteins of human granulocytes. II. Separation of the cationic proteins of the granules of leukemic myeloid cells. Blood. 1974 Aug;44(2):235–246. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olsson I., Venge P., Spitznagel J. K., Lehrer R. I. Arginine-rich cationic proteins of human eosinophil granules: comparison of the constituents of eosinophilic and neutrophilic leukocytes. Lab Invest. 1977 May;36(5):493–500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson C. G., Venge P. Purification and characterization of a new cationic protein--eosinophil protein-X (EPX)--from granules of human eosinophils. Immunology. 1983 Sep;50(1):19–26. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J., Fett J. W., Lobb R. R., Alderman E. M., Bethune J. L., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Amino acid sequence of human tumor derived angiogenin. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5486–5494. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr G. E., Beecher J. F., Bell M., McKean D. J. Polyquarternary amines prevent peptide loss from sequenators. Anal Biochem. 1978 Feb;84(2):622–7?0=ENG. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(78)90086-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tarr G. E. Rapid separation of amino acid phenylthiohydantoins by isocratic high-performance liquid chromatography. Anal Biochem. 1981 Feb;111(1):27–32. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90223-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Varki A., Kornfeld S. The spectrum of anionic oligosaccharides released by endo-beta-N-acetylglucosaminidase H from glycoproteins. Structural studies and interactions with the phosphomannosyl receptor. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2808–2818. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]