Abstract
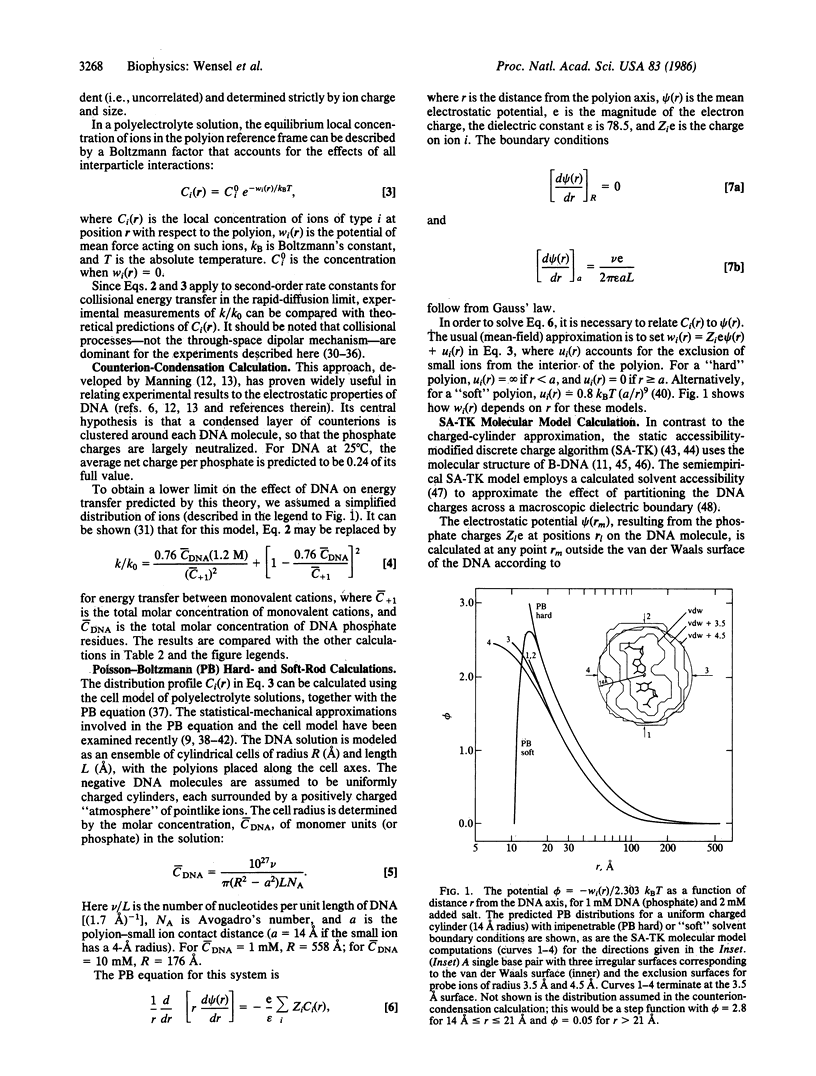
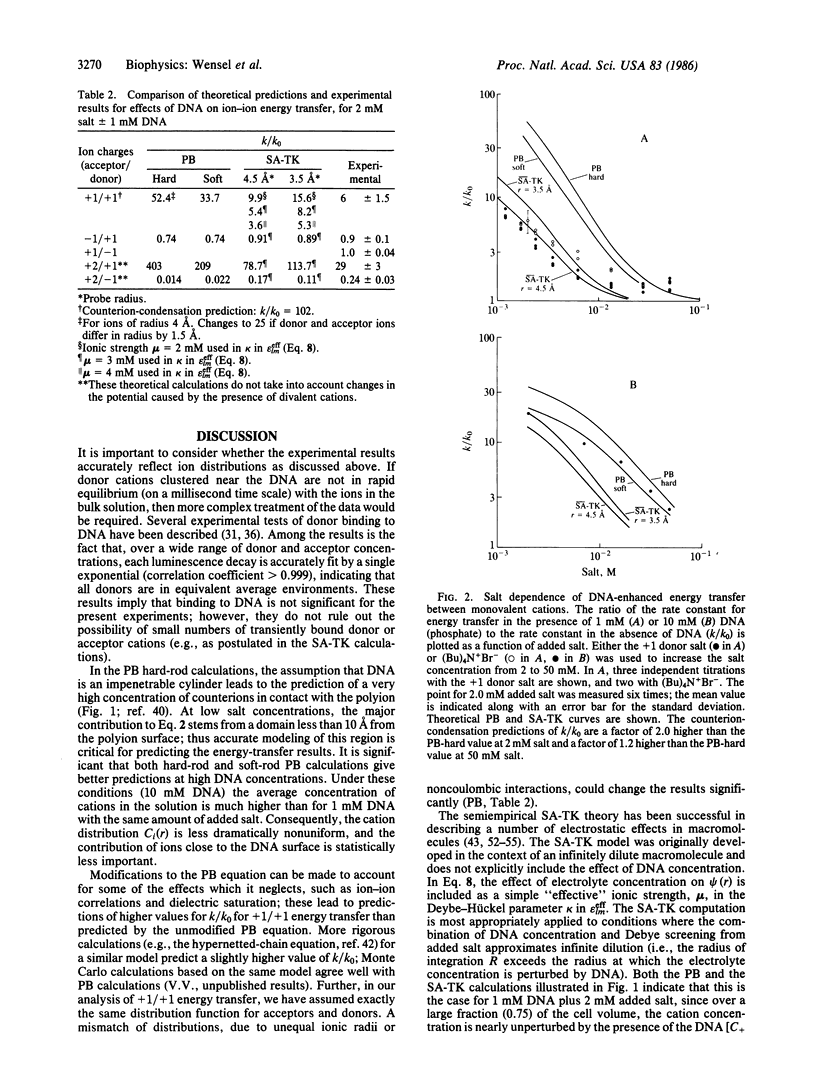
Measurements of the effect of DNA on rates of bimolecular energy transfer between ions provide a direct indication of how cations cluster in regions near DNA and how anions are repelled from the same regions. Energy transfer from luminescent lanthanide ions (in the "rapid-diffusion" limit) probes collision frequencies that are dependent on the equilibrium spatial distributions of ions. The addition of 1 mM DNA (phosphate) to a 2 mM salt solution increases the overall collision frequency between monovalent cations by a factor of 6 +/- 1.5; it increases the divalent-monovalent cation collision frequency by a factor of 29 +/- 3; and it decreases the divalent cation-monovalent anion collision frequency by a factor of 0.24 +/- 0.03. Comparisons are made with the changes in collision frequencies predicted by several different theoretical descriptions of ion distributions. The closest agreement with experimental results for monovalent ions at 1 mM DNA is obtained with a static accessibility-modified discrete charge calculation, based on a detailed molecular model of B-DNA. At high DNA concentration (10 mM), the best results are obtained by numerical solutions of the Poisson-Boltzmann equation for a "soft-rod" model of DNA. Poisson-Boltzmann calculations for a "hard-rod" model greatly overestimate the effects of DNA on collision frequencies, as does a calculation based on counterion-condensation theory.
Full text
PDF


Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr, Hart P. A. Sodium-23 NMR studies of cation-DNA interactions. Biophys Chem. 1978 Jan;7(4):301–316. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(78)85007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson C. F., Record M. T., Jr The relationship between the poisson-boltzmann model and the condensation hypothesis: an analysis based on the low salt form of the Donnan coefficient. Biophys Chem. 1980 Jun;11(3-4):353–360. doi: 10.1016/0301-4622(80)87008-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bleam M. L., Anderson C. F., Record M. T. Relative binding affinities of monovalent cations for double-stranded DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jun;77(6):3085–3089. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.6.3085. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Granot J. Effect of finite ionic size on the solution of the Poisson-Boltzmann equation: application to the binding of divalent metal ions to DNA. Biopolymers. 1983 Jul;22(7):1831–1841. doi: 10.1002/bip.360220715. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klein B. J., Pack G. R. Calculations of the spatial distribution of charge density in the environment of DNA. Biopolymers. 1983 Nov;22(11):2331–2352. doi: 10.1002/bip.360221103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Bret M., Zimm B. H. Monte Carlo determination of the distribution of ions about a cylindrical polyelectrolyte. Biopolymers. 1984 Feb;23(2):271–285. doi: 10.1002/bip.360230208. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lee B., Richards F. M. The interpretation of protein structures: estimation of static accessibility. J Mol Biol. 1971 Feb 14;55(3):379–400. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90324-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Manning G. S. The molecular theory of polyelectrolyte solutions with applications to the electrostatic properties of polynucleotides. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):179–246. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B. Electrostatic effects in proteins. Annu Rev Biophys Biophys Chem. 1985;14:387–417. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.14.060185.002131. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B., Gurd F. R., Garcia-Moreno B., Flanagan M. A., March K. L., Shire S. J. pH-dependent processes in proteins. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1985;18(2):91–197. doi: 10.3109/10409238509085133. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B., Hanania G. I., Gurd F. R. Solvent accessibility calculations for sperm whale ferrimyoglobin based on refined crystallographic data. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1978 Mar 30;81(2):410–415. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(78)91548-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B., Ohlendorf D. H. Electrostatic deformation of DNA by a DNA-binding protein. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 25;260(10):5860–5862. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B., Richards F. M. Anion binding and pH-dependent electrostatic effects in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1982 Sep 28;21(20):4989–4999. doi: 10.1021/bi00263a024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B., Richards F. M. Differential electrostatic stabilization of A-, B-, and Z-forms of DNA. Biopolymers. 1984 Dec;23(12):2743–2759. doi: 10.1002/bip.360231205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Matthew J. B., Weber P. C., Salemme F. R., Richards F. M. Electrostatic orientation during electron transfer between flavodoxin and cytochrome c. Nature. 1983 Jan 13;301(5896):169–171. doi: 10.1038/301169a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meares C. F., Rice L. S. Diffusion-enhanced energy transfer shows accessibility of ribonucleic acid polymerase inhibitor binding sites. Biochemistry. 1981 Feb 3;20(3):610–617. doi: 10.1021/bi00506a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pullman A., Pullman B. Molecular electrostatic potential of the nucleic acids. Q Rev Biophys. 1981 Aug;14(3):289–380. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500002341. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Anderson C. F., Lohman T. M. Thermodynamic analysis of ion effects on the binding and conformational equilibria of proteins and nucleic acids: the roles of ion association or release, screening, and ion effects on water activity. Q Rev Biophys. 1978 May;11(2):103–178. doi: 10.1017/s003358350000202x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Record M. T., Jr, Mazur S. J., Melançon P., Roe J. H., Shaner S. L., Unger L. Double helical DNA: conformations, physical properties, and interactions with ligands. Annu Rev Biochem. 1981;50:997–1024. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.50.070181.005025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reuben J., Shporer M., Gabbay E. J. The Alkali Ion-DNA Interaction as Reflected in the Nuclear Relaxation Rates of Na and Rb. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jan;72(1):245–247. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.1.245. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Riggs A. D., Suzuki H., Bourgeois S. Lac repressor-operator interaction. I. Equilibrium studies. J Mol Biol. 1970 Feb 28;48(1):67–83. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(70)90219-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roe J. H., Burgess R. R., Record M. T., Jr Kinetics and mechanism of the interaction of Escherichia coli RNA polymerase with the lambda PR promoter. J Mol Biol. 1984 Jul 15;176(4):495–522. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(84)90174-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SHACK J., JENKINS R. J., THOMPSETT J. M. The binding of sodium chloride and calf thymus desoxypentose nucleic acid. J Biol Chem. 1952 Sep;198(1):85–92. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Steitz T. A., Weber I. T., Matthew J. B. Catabolite gene activator protein: structure, homology with other proteins, and cyclic AMP and DNA binding. Cold Spring Harb Symp Quant Biol. 1983;47(Pt 1):419–426. doi: 10.1101/sqb.1983.047.01.049. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stryer L., Thomas D. D., Meares C. F. Diffusion-enhanced fluorescence energy transfer. Annu Rev Biophys Bioeng. 1982;11:203–222. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bb.11.060182.001223. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas D. D., Carlsen W. F., Stryer L. Fluorescence energy transfer in the rapid-diffusion limit. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Dec;75(12):5746–5750. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.12.5746. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber P. C., Tollin G. Electrostatic interactions during electron transfer reactions between c-type cytochromes and flavodoxin. J Biol Chem. 1985 May 10;260(9):5568–5573. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wensel T. G., Chang C. H., Meares C. F. Diffusion-enhanced lanthanide energy-transfer study of DNA-bound cobalt(III) bleomycins: comparisons of accessibility and electrostatic potential with DNA complexes of ethidium and acridine orange. Biochemistry. 1985 Jun 4;24(12):3060–3069. doi: 10.1021/bi00333a039. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Winter R. B., Berg O. G., von Hippel P. H. Diffusion-driven mechanisms of protein translocation on nucleic acids. 3. The Escherichia coli lac repressor--operator interaction: kinetic measurements and conclusions. Biochemistry. 1981 Nov 24;20(24):6961–6977. doi: 10.1021/bi00527a030. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- deHaseth P. L., Lohman T. M., Record M. T., Jr Nonspecific interaction of lac repressor with DNA: an association reaction driven by counterion release. Biochemistry. 1977 Nov 1;16(22):4783–4790. doi: 10.1021/bi00641a004. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



