Abstract
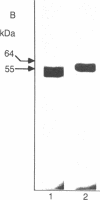
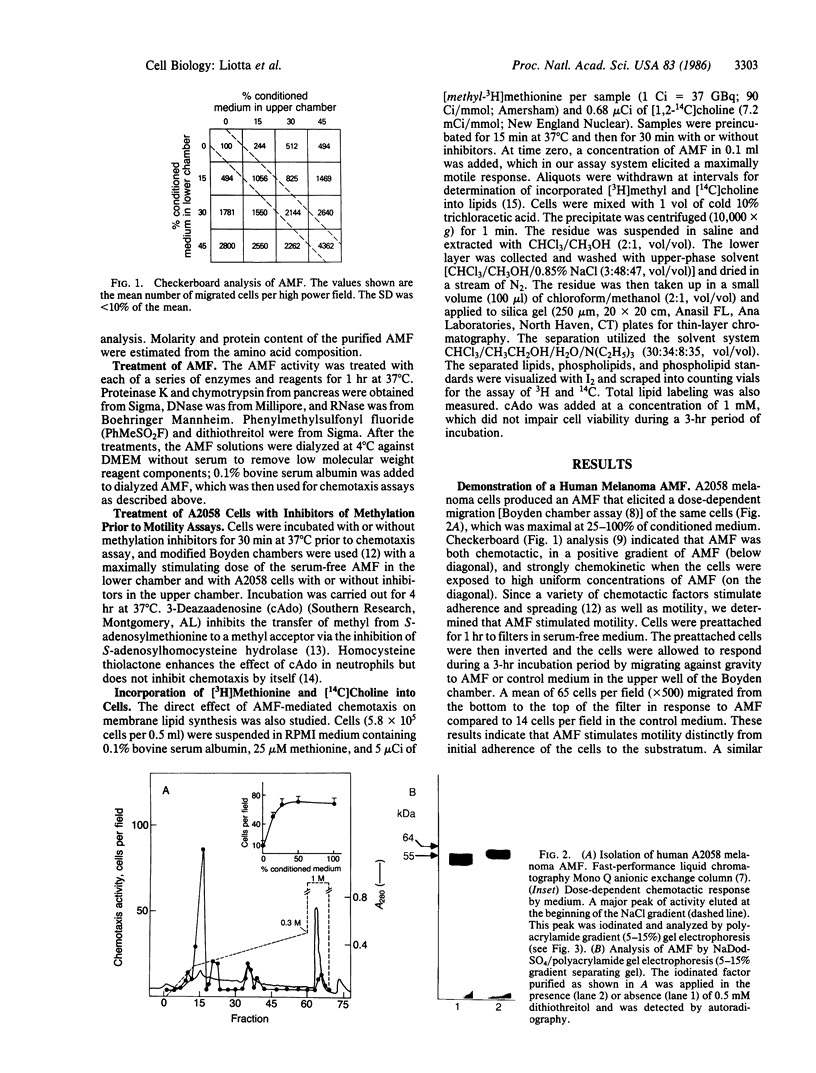
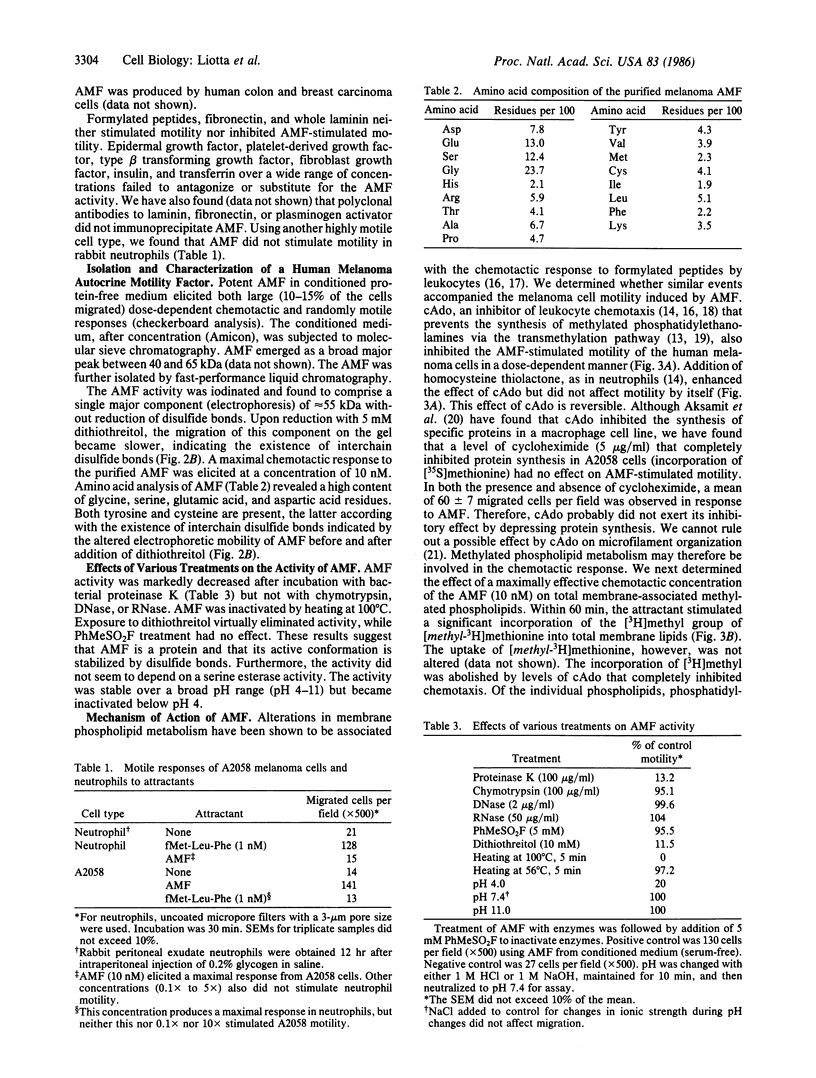
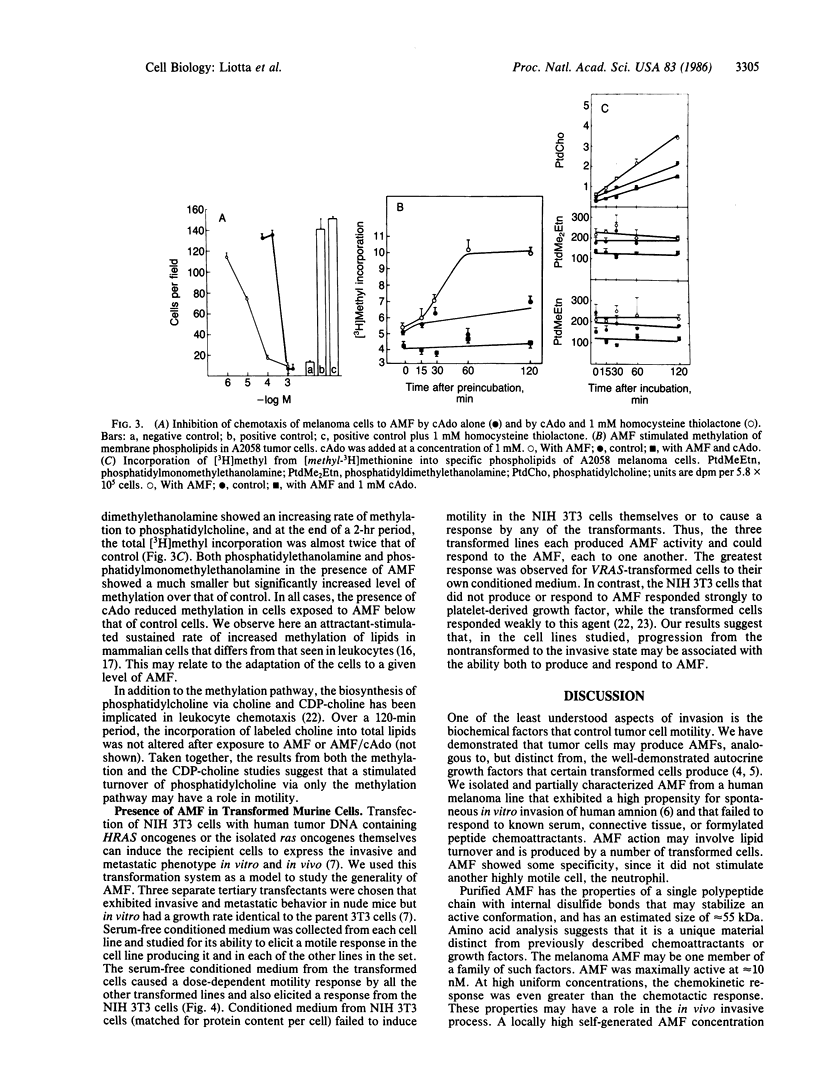
A cell motility-stimulating factor has been isolated, purified, and partially characterized from the serum-free conditioned medium of human A2058 melanoma cells. We term this activity "autocrine motility factor" (AMF). AMF has the properties of a protein with an estimated size of 55 kDa. At concentrations of 10 nM or less, AMF stimulated the random or directed motility of the producer cells. However, AMF is not an attractant for neutrophils. Amino acid analysis of the purified AMF protein revealed a high content of serine, glycine, glutamic acid, and aspartic acid residues. The activity of AMF was not replaced or blocked by known growth factors such as epidermal growth factor or type beta transforming growth factor. Mechanistic studies showed that AMF stimulated the incorporation of [3H]methyl into cell membrane phospholipids after incubation with [methyl-3H]methionine with a sustained increase in the methylation of phosphatidyldimethylethanolamine to phosphatidylcholine. In contrast, AMF did not affect the incorporation of [1,2-14C]choline into phosphatidylcholine. AMF was produced in large amounts by three different clones of ras oncogene-transfected metastatic NIH 3T3 cells but not by the nontransformed parental cells. AMF may play a major role in the local invasive behavior of tumor cells and may also facilitate the concerted invasion by groups of tumor cells.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Aksamit R. R., Backlund P. S., Jr, Cantoni G. L. Chemotaxis and the synthesis of specific proteins are inhibited by 3-deazaadenosine and other adenosine analogs in a mouse macrophage cell line. J Biol Chem. 1983 Jan 10;258(1):20–23. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Albini A., Allavena G., Parodi S., Santi L. Comparison of the chemotactic response to conditioned medium of BALB/c3T3 fibroblasts and their SV 40 transformants. Tumori. 1985 Apr 30;71(2):97–100. doi: 10.1177/030089168507100202. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anzano M. A., Roberts A. B., Smith J. M., Sporn M. B., De Larco J. E. Sarcoma growth factor from conditioned medium of virally transformed cells is composed of both type alpha and type beta transforming growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Oct;80(20):6264–6268. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.20.6264. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Backlund P. S., Jr, Meade B. D., Manclark C. R., Cantoni G. L., Aksamit R. R. Pertussis toxin inhibition of chemotaxis and the ADP-ribosylation of a membrane protein in a human-mouse hybrid cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2637–2641. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2637. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bareis D. L., Hirata F., Schiffmann E., Axelrod J. Phospholipid metabolism, calcium flux, and the receptor-mediated induction of chemotaxis in rabbit neutrophils. J Cell Biol. 1982 Jun;93(3):690–697. doi: 10.1083/jcb.93.3.690. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bokoch G. M., Gilman A. G. Inhibition of receptor-mediated release of arachidonic acid by pertussis toxin. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):301–308. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90008-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Castaño J. G., Alemany S., Nieto A., Mato J. M. Activation of phospholipid methyltransferase by glucagon in rat hepatocytes. J Biol Chem. 1980 Oct 10;255(19):9041–9043. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garcia-Castro I., Mato J. M., Vasanthakumar G., Wiesmann W. P., Schiffmann E., Chiang P. K. Paradoxical effects of adenosine on neutrophil chemotaxis. J Biol Chem. 1983 Apr 10;258(7):4345–4349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilman A. G. G proteins and dual control of adenylate cyclase. Cell. 1984 Mar;36(3):577–579. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90336-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grotendorst G. R. Alteration of the chemotactic response of NIH/3T3 cells to PDGF by growth factors, transformation, and tumor promoters. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):279–285. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90221-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guranowski A., Montgomery J. A., Cantoni G. L., Chiang P. K. Adenosine analogues as substrates and inhibitors of S-adenosylhomocysteine hydrolase. Biochemistry. 1981 Jan 6;20(1):110–115. doi: 10.1021/bi00504a019. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hirata F., Schiffmann E., Venkatasubramanian K., Salomon D., Axelrod J. A phospholipase A2 inhibitory protein in rabbit neutrophils induced by glucocorticoids. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2533–2536. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K. L., Kiechle F. L., Jarett L. Insulin stimulation of phospholipid methylation in isolated rat adipocyte plasma membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Feb;81(4):1089–1092. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.4.1089. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koop D. R., Morgan E. T., Tarr G. E., Coon M. J. Purification and characterization of a unique isozyme of cytochrome P-450 from liver microsomes of ethanol-treated rabbits. J Biol Chem. 1982 Jul 25;257(14):8472–8480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kort E. N., Goy M. F., Larsen S. H., Adler J. Methylation of a membrane protein involved in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Oct;72(10):3939–3943. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.10.3939. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lam W. C., Delikatny E. J., Orr F. W., Wass J., Varani J., Ward P. A. The chemotactic response of tumor cells. A model for cancer metastasis. Am J Pathol. 1981 Jul;104(1):69–76. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Marín-Cao D. Protein and phospholipid methylation during chemotaxis in Dictyostelium discoideum and its relationship to calcium movements. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Dec;76(12):6106–6109. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.12.6106. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mato J. M., Pencev D., Vasanthakumar G., Schiffmann E., Pastan I. Inhibitors of endocytosis perturb phospholipid metabolism in rabbit neutrophils and other cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(7):1929–1932. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.7.1929. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McCarthy J. B., Basara M. L., Palm S. L., Sas D. F., Furcht L. T. The role of cell adhesion proteins--laminin and fibronectin--in the movement of malignant and metastatic cells. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1985;4(2):125–152. doi: 10.1007/BF00050692. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Molski T. F., Naccache P. H., Marsh M. L., Kermode J., Becker E. L., Sha'afi R. I. Pertussis toxin inhibits the rise in the intracellular concentration of free calcium that is induced by chemotactic factors in rabbit neutrophils: possible role of the "G proteins" in calcium mobilization. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 30;124(2):644–650. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)91603-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Okajima F., Ui M. ADP-ribosylation of the specific membrane protein by islet-activating protein, pertussis toxin, associated with inhibition of a chemotactic peptide-induced arachidonate release in neutrophils. A possible role of the toxin substrate in Ca2+-mobilizing biosignaling. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):13863–13871. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pike M. C., Kredich N. M., Snyderman R. Phospholipid methylation in macrophages is inhibited by chemotactic factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2922–2926. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2922. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Postlethwaite A. E., Snyderman R., Kang A. H. The chemotactic attraction of human fibroblasts to a lymphocyte-derived factor. J Exp Med. 1976 Nov 2;144(5):1188–1203. doi: 10.1084/jem.144.5.1188. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russo R. G., Foltz C. M., Liotta L. A. New invasion assay using endothelial cells grown on native human basement membrane. Clin Exp Metastasis. 1983 Apr-Jun;1(2):115–127. doi: 10.1007/BF00121491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schiffmann E., Gallin J. I. Biochemistry of phagocyte chemotaxis. Curr Top Cell Regul. 1979;15:203–261. doi: 10.1016/b978-0-12-152815-7.50010-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Springer W. R., Koshland D. E., Jr Identification of a protein methyltransferase as the cheR gene product in the bacterial sensing system. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Feb;74(2):533–537. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.2.533. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stock J., Borczuk A., Chiou F., Burchenal J. E. Compensatory mutations in receptor function: a reevaluation of the role of methylation in bacterial chemotaxis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8364–8368. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8364. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stopford C. R., Wolberg G., Prus K. L., Reynolds-Vaughn R., Zimmerman T. P. 3-Deazaadenosine-induced disorganization of macrophage microfilaments. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4060–4064. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4060. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorgeirsson U. P., Turpeenniemi-Hujanen T., Williams J. E., Westin E. H., Heilman C. A., Talmadge J. E., Liotta L. A. NIH/3T3 cells transfected with human tumor DNA containing activated ras oncogenes express the metastatic phenotype in nude mice. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):259–262. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.259. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Todaro G. J., Fryling C., De Larco J. E. Transforming growth factors produced by certain human tumor cells: polypeptides that interact with epidermal growth factor receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Sep;77(9):5258–5262. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.9.5258. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tomono T., Ikeda H., Tokunaga E. High-performance ion-exchange chromatography of plasma proteins. J Chromatogr. 1983 Aug 26;266:39–47. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)90877-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiesmann W. P., Johnson J. P., Miura G. A., Chaing P. K. Aldosterone-stimulated transmethylations are linked to sodium transport. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 2):F43–F47. doi: 10.1152/ajprenal.1985.248.1.F43. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yoshida K., Ozaki T., Ushijima K., Hayashi H. Studies on the mechanisms of invasion in cancer. I. Isolation and purification of a factor chemotactic for cancer cells. Int J Cancer. 1970 Jul 15;6(1):123–132. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910060116. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zigmond S. H., Hirsch J. G. Leukocyte locomotion and chemotaxis. New methods for evaluation, and demonstration of a cell-derived chemotactic factor. J Exp Med. 1973 Feb 1;137(2):387–410. doi: 10.1084/jem.137.2.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]