Abstract
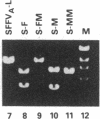
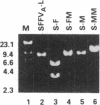
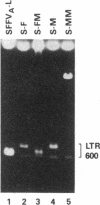
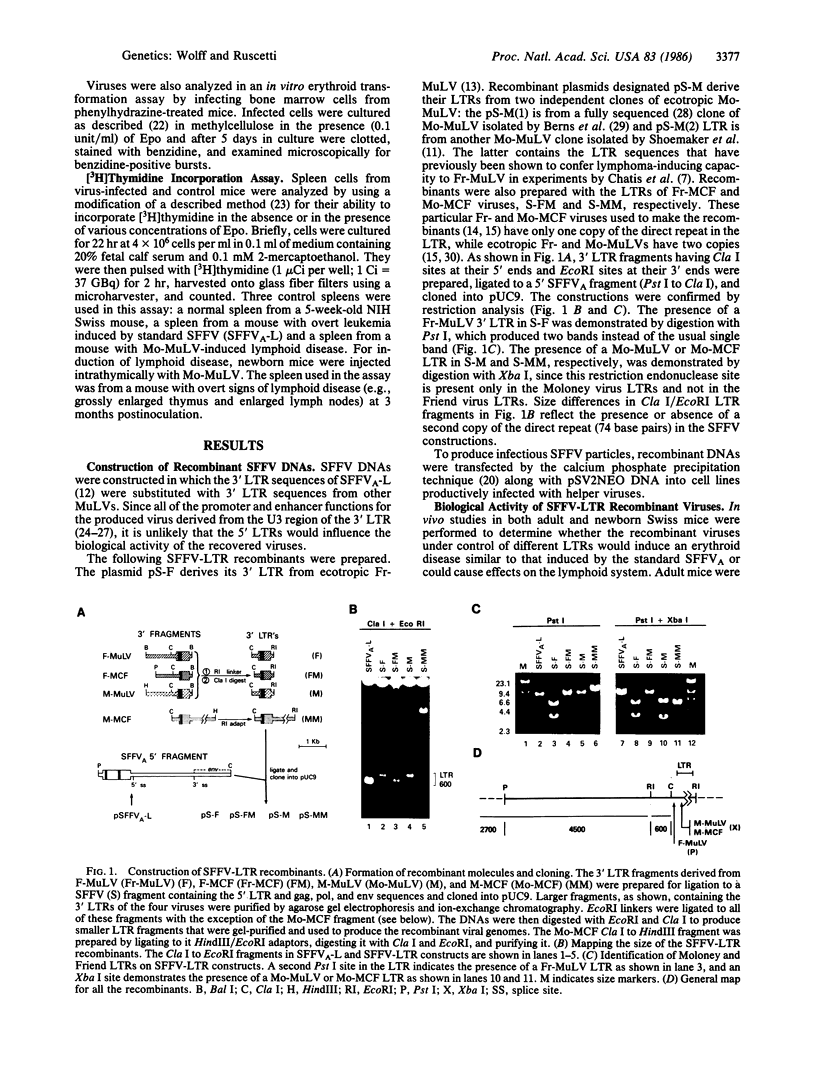
Although it has been previously determined that the long terminal repeat (LTR) sequences of several murine retroviruses specify the major tissue tropism of leukemias they induce, data reported here show that the LTR is not responsible for tissue tropism in the case of all leukemogenic viruses. In an effort to determine whether LTR sequences of the acute erythroleukemia-inducing spleen focus-forming virus (SFFV), like those of the other murine leukemia viruses, are uniquely required to confer tissue specificity to the virus, we prepared recombinant SFFVs in which the LTR region containing promoter and enhancer functions was replaced with analogous LTR regions from Friend and Moloney ecotropic and mink cell focus-inducing viruses. It was found that all of the SFFV constructs, even those with a LTR derived from lymphoma-inducing viruses such as Moloney murine leukemia virus, transformed erythroid cells in vitro and induced exclusively an erythroid disease. These results demonstrate that sequences in SFFV that determine the tissue-specific nature of the disease reside outside the LTR.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Berns A. J., Lai M. H., Bosselman R. A., McKennett M. A., Bacheler L. T., Fan H., Maandag E. C., van der Putten H. V., Verma I. M. Molecular cloning of unintegrated and a portion of integrated moloney murine leukemia viral DNA in bacteriophage lambda. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):254–263. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.254-263.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bestwick R. K., Boswell B. A., Kabat D. Molecular cloning of biologically active Rauscher spleen focus-forming virus and the sequences of its env gene and long terminal repeat. J Virol. 1984 Sep;51(3):695–705. doi: 10.1128/jvi.51.3.695-705.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bosselman R. A., van Straaten F., Van Beveren C., Verma I. M., Vogt M. Analysis of the env gene of a molecularly cloned and biologically active Moloney mink cell focus-forming proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Oct;44(1):19–31. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.1.19-31.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Hartley J. W., Rowe W. P., Hopkins N. Role for the 3' end of the genome in determining disease specificity of Friend and Moloney murine leukemia viruses. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4408–4411. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4408. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chatis P. A., Holland C. A., Silver J. E., Frederickson T. N., Hopkins N., Hartley J. W. A 3' end fragment encompassing the transcriptional enhancers of nondefective Friend virus confers erythroleukemogenicity on Moloney leukemia virus. J Virol. 1984 Oct;52(1):248–254. doi: 10.1128/jvi.52.1.248-254.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. P., Kaufhold R., Chan A., Mak T. W. Comparison of the transcriptional properties of the Friend and Moloney retrovirus long terminal repeats: importance of tandem duplications and of the core enhancer sequence. Virology. 1985 Jul 30;144(2):481–494. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90288-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clark S. P., Mak T. W. Nucleotide sequences of the murine retrovirus Friend SFFVp long terminal repeats: identification of a structure with extensive dyad symmetry 5' to the TATA box. Nucleic Acids Res. 1982 May 25;10(10):3315–3330. doi: 10.1093/nar/10.10.3315. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Even J., Anderson S. J., Hampe A., Galibert F., Lowy D., Khoury G., Sherr C. J. Mutant feline sarcoma proviruses containing the viral oncogene (v-fes) and either feline or murine control elements. J Virol. 1983 Mar;45(3):1004–1016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.45.3.1004-1016.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gilboa E., Mitra S. W., Goff S., Baltimore D. A detailed model of reverse transcription and tests of crucial aspects. Cell. 1979 Sep;18(1):93–100. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(79)90357-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Graham F. L., van der Eb A. J. A new technique for the assay of infectivity of human adenovirus 5 DNA. Virology. 1973 Apr;52(2):456–467. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(73)90341-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hankins W. D., Troxler D. Polycythemia- and anemia-inducing erythroleukemia viruses exhibit differential erythroid transforming effects in vitro. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):693–699. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90545-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ishimoto A., Adachi A., Sakai K., Matsuyama M. Long terminal repeat of Friend-MCF virus contains the sequence responsible for erythroid leukemia. Virology. 1985 Feb;141(1):30–42. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90180-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koch W., Zimmermann W., Oliff A., Friedrich R. Molecular analysis of the envelope gene and long terminal repeat of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: implications for the functions of these sequences. J Virol. 1984 Mar;49(3):828–840. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.3.828-840.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal G. A simple microassay for erythropoietin based on 3H-thymidine incorporation into spleen cells from phenylhydrazine treated mice. Exp Hematol. 1983 Aug;11(7):649–660. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Linemeyer D. L., Menke J. G., Ruscetti S. K., Evans L. H., Scolnick E. M. Envelope gene sequences which encode the gp52 protein of spleen focus-forming virus are required for the induction of erythroid cell proliferation. J Virol. 1982 Jul;43(1):223–233. doi: 10.1128/jvi.43.1.223-233.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller A. D., Verma I. M. Two base changes restore infectivity to a noninfectious molecular clone of Moloney murine leukemia virus (pMLV-1). J Virol. 1984 Jan;49(1):214–222. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.1.214-222.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A. I., Hager G. L., Chang E. H., Scolnick E. M., Chan H. W., Lowy D. R. Transfection of molecularly cloned Friend murine leukemia virus DNA yields a highly leukemogenic helper-independent type C virus. J Virol. 1980 Jan;33(1):475–486. doi: 10.1128/jvi.33.1.475-486.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., Collins L., Mirenda C. Molecular cloning of Friend mink cell focus-inducing virus: identification of mink cell focus-inducing virus-like messages in normal and transformed cells. J Virol. 1983 Nov;48(2):542–546. doi: 10.1128/jvi.48.2.542-546.1983. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Oliff A., Linemeyer D., Ruscetti S., Lowe R., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. Subgenomic fragment of molecular cloned Friend murine leukemia virus DNA contains the gene(s) responsible for Friend murine leukemia virus-induced disease. J Virol. 1980 Sep;35(3):924–936. doi: 10.1128/jvi.35.3.924-936.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosen C. A., Haseltine W. A., Lenz J., Ruprecht R., Cloyd M. W. Tissue selectivity of murine leukemia virus infection is determined by long terminal repeat sequences. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):862–866. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.862-866.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruscetti S., Wolff L. Spleen focus-forming virus: relationship of an altered envelope gene to the development of a rapid erythroleukemia. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1984;112:21–44. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-69677-0_2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shinnick T. M., Lerner R. A., Sutcliffe J. G. Nucleotide sequence of Moloney murine leukaemia virus. Nature. 1981 Oct 15;293(5833):543–548. doi: 10.1038/293543a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker C., Goff S., Gilboa E., Paskind M., Mitra S. W., Baltimore D. Structure of a cloned circular Moloney murine leukemia virus DNA molecule containing an inverted segment: implications for retrovirus integration. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 Jul;77(7):3932–3936. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.7.3932. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Southern P. J., Berg P. Transformation of mammalian cells to antibiotic resistance with a bacterial gene under control of the SV40 early region promoter. J Mol Appl Genet. 1982;1(4):327–341. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stephenson J. R., Axelrad A. A., McLeod D. L., Shreeve M. M. Induction of colonies of hemoglobin-synthesizing cells by erythropoietin in vitro. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1971 Jul;68(7):1542–1546. doi: 10.1073/pnas.68.7.1542. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Temin H. M. Function of the retrovirus long terminal repeat. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):3–5. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90367-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vieira J., Messing J. The pUC plasmids, an M13mp7-derived system for insertion mutagenesis and sequencing with synthetic universal primers. Gene. 1982 Oct;19(3):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(82)90015-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vogt M., Haggblom C., Swift S., Haas M. Envelope gene and long terminal repeat determine the different biological properties of Rauscher, Friend, and Moloney mink cell focus-inducing viruses. J Virol. 1985 Jul;55(1):184–192. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.1.184-192.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L., Kaminchik J., Hankins W. D., Ruscetti S. K. Sequence comparisons of the anemia- and polycythemia-inducing strains of Friend spleen focus-forming virus. J Virol. 1985 Feb;53(2):570–578. doi: 10.1128/jvi.53.2.570-578.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wolff L., Ruscetti S. Malignant transformation of erythroid cells in vivo by introduction of a nonreplicating retrovirus vector. Science. 1985 Jun 28;228(4707):1549–1552. doi: 10.1126/science.2990034. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]