Abstract
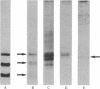
An antiserum generated in rabbits against human seminal alpha-inhibin-52 has been used to develop a sensitive radioimmunoassay for the detection of alpha-inhibins. The alpha-inhibin-52 antiserum reacts with alpha-inhibin-92 and alpha-inhibin-31 with equal avidity. These peptides were found to be present in human pituitary, hypothalamus, and serum. In exclusion chromatography on Sephadex G-100, the immunoreactive material eluted in a large molecular size region. Immunoblot analysis of column-derived fractions of these extracts revealed the presence of alpha-inhibin-92. The mean concentrations of immunoreactive alpha-inhibin were found to be 7.2 ng/ml in normal adult male serum, 70.3 ng/g (wet weight) of pituitary, and 12.9 ng/g (wet weight) of hypothalamus. This communication reports on the evidence for the existence of gonadal peptides in the brain.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Channing C. P., Gordon W. L., Liu W. K., Ward D. N. Physiology and biochemistry of ovarian inhibin. Proc Soc Exp Biol Med. 1985 Mar;178(3):339–361. doi: 10.3181/00379727-178-42017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchimont P., Verstraelen-Proyard J., Hazee-Hagelstein M. T., Renard C., Demoulin A., Bourguignon J. P., Hustin J. Inhibin: from concept to reality. Vitam Horm. 1979;37:243–302. doi: 10.1016/s0083-6729(08)61071-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Li C. H., Hammonds R. G., Jr, Ramasharma K., Chung D. Human seminal alpha inhibins: isolation, characterization, and structure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4041–4044. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4041. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ling N., Ying S. Y., Ueno N., Esch F., Denoroy L., Guillemin R. Isolation and partial characterization of a Mr 32,000 protein with inhibin activity from porcine follicular fluid. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Nov;82(21):7217–7221. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.21.7217. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lumpkin M., Negro-Vilar A., Franchimont P., McCann S. Evidence for a hypothalamic site of action of inhibin to suppress FSH release. Endocrinology. 1981 Mar;108(3):1101–1104. doi: 10.1210/endo-108-3-1101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Main S. J., Davies R. V., Setchell B. P. The evidence that inhibin must exist. J Reprod Fertil Suppl. 1979;(26):3–14. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasharma K., Sairam M. R. Isolation and characterization of inhibin from human seminal plasma. Ann N Y Acad Sci. 1982;383:307–328. doi: 10.1111/j.1749-6632.1982.tb23175.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasharma K., Sairam M. R., Ranganathan M. R. Effect of inhibin like factors on gonadotrophin release by the mouse pituitary in vitro. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 1981 Dec;98(4):496–505. doi: 10.1530/acta.0.0980496. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ramasharma K., Sairam M. R., Seidah N. G., Chrétien M., Manjunath P., Schiller P. W., Yamashiro D., Li C. H. Isolation, structure, and synthesis of a human seminal plasma peptide with inhibin-like activity. Science. 1984 Mar 16;223(4641):1199–1202. doi: 10.1126/science.6422553. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rivier J., Spiess J., McClintock R., Vaughan J., Vale W. Purification and partial characterization of inhibin from porcine follicular fluid. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Nov 27;133(1):120–127. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91849-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbard D., Frazier G. R. Statistical analysis of radioligand assay data. Methods Enzymol. 1975;37:3–22. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(75)37003-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schalch D. S., Reichlin S. Plasma growth hormone concentration in the rat determined by radioimmunoassay: influence of sex, pregnancy, lactation, anesthesia, hypophysectomy and extrasellar pituitary transplants. Endocrinology. 1966 Aug;79(2):275–280. doi: 10.1210/endo-79-2-275. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seidah N. G., Arbatti N. J., Rochemont J., Sheth A. R., Chrétien M. Complete amino acid sequence of human seminal plasma beta-inhibin. Prediction of post Gln-Arg cleavage as a maturation site. FEBS Lett. 1984 Oct 1;175(2):349–355. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(84)80766-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thorell J. I., Johansson B. G. Enzymatic iodination of polypeptides with 125I to high specific activity. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1971 Dec 28;251(3):363–369. doi: 10.1016/0005-2795(71)90123-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Towbin H., Staehelin T., Gordon J. Electrophoretic transfer of proteins from polyacrylamide gels to nitrocellulose sheets: procedure and some applications. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Sep;76(9):4350–4354. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.9.4350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]