Abstract
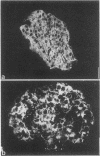
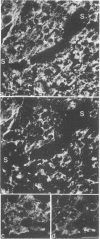
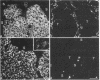
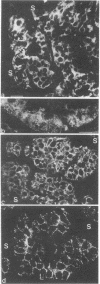
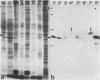
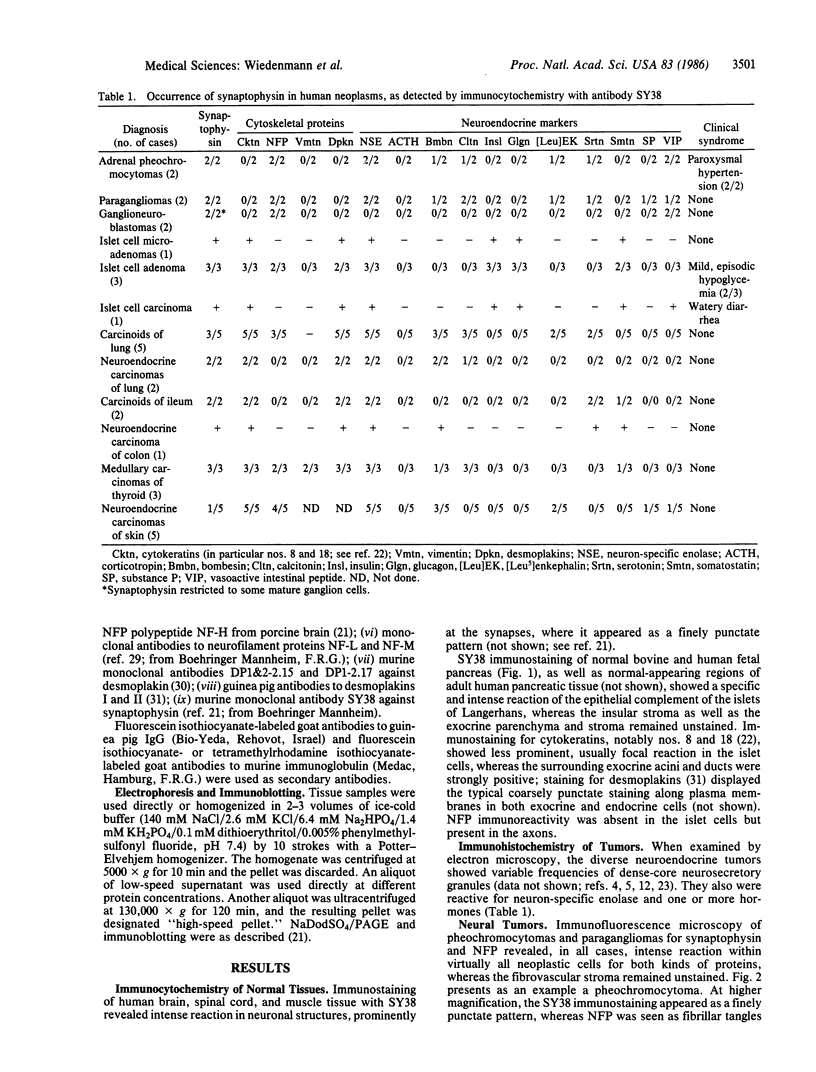
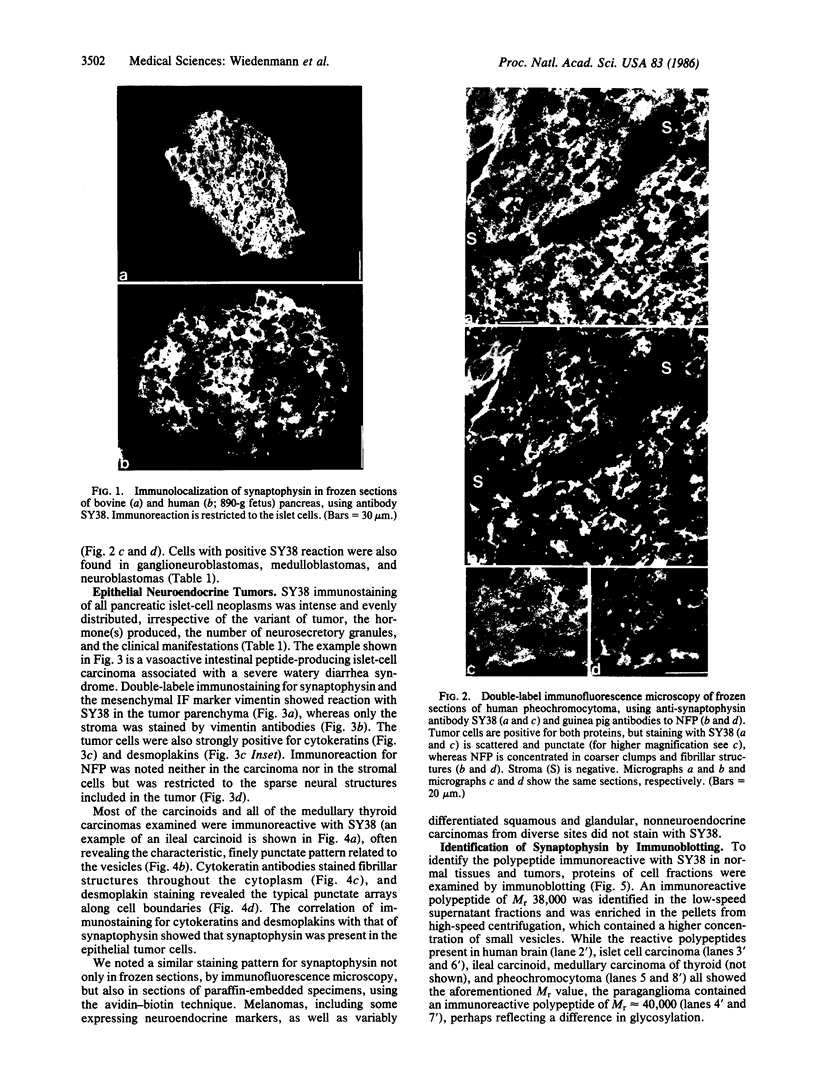
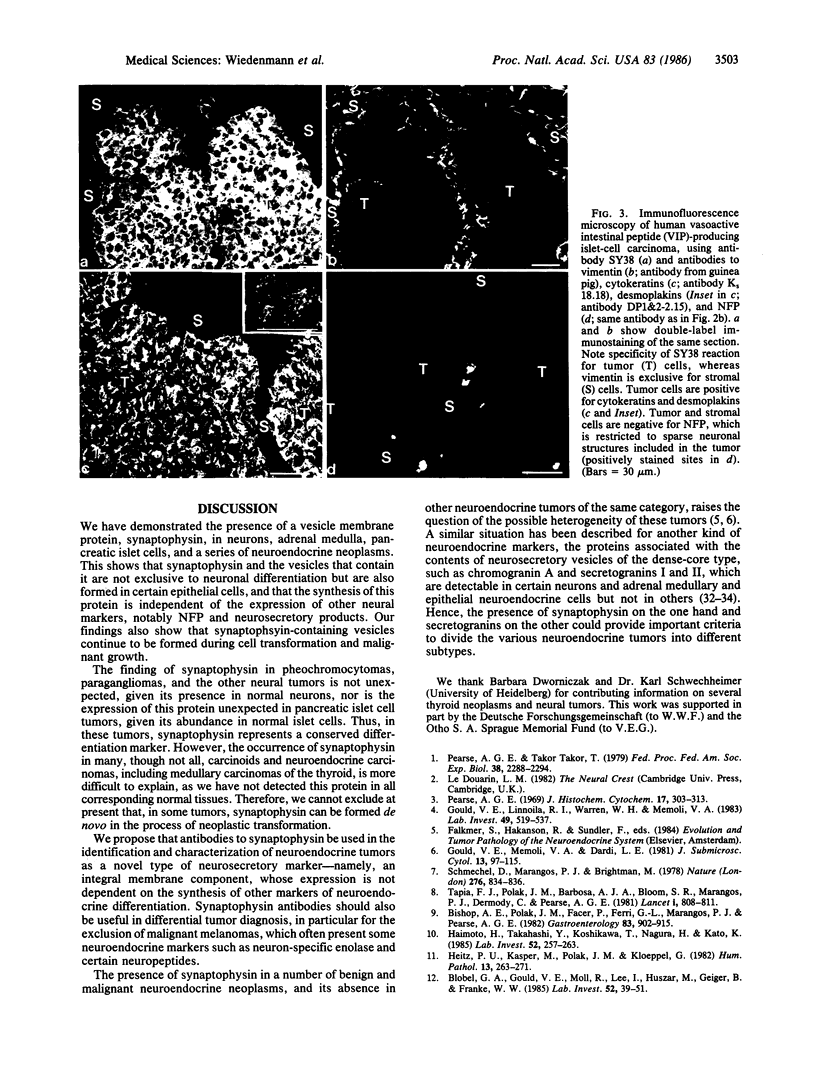
Synaptophysin is an integral membrane glycoprotein (Mr 38,000) that occurs in presynaptic vesicles of neurons and in similar vesicles of the adrenal medulla. By using a monoclonal antibody to this protein (SY38), we have found, by immunohistochemistry and immunoblotting, that an identical or similar protein is also expressed in neuroendocrine tumors of neural type, such as pheochromocytomas and paragangliomas. In addition, this protein occurs in certain neuroendocrine epithelial cells, such as pancreatic islet cells; in a variety of neuroendocrine epithelial tumors, including isletcell adenomas and carcinomas and several carcinoids and neuroendocrine carcinomas of the gastrointestinal and the bronchial tracts; and in medullary carcinomas of the thyroid. Our results show that synaptophysin, and the vesicles that contain it, can occur in normal and neoplastic neuroendocrine cells of neural type, as demonstrated by colocalization with neurofilaments, as well as in those of epithelial type, as shown by colocalization with cytokeratin filaments and desmoplakins. We conclude that synaptophysin is expressed independently of other neuronal differentiation markers and propose that it be used as a differentiation marker in tumor diagnosis.
Full text
PDF
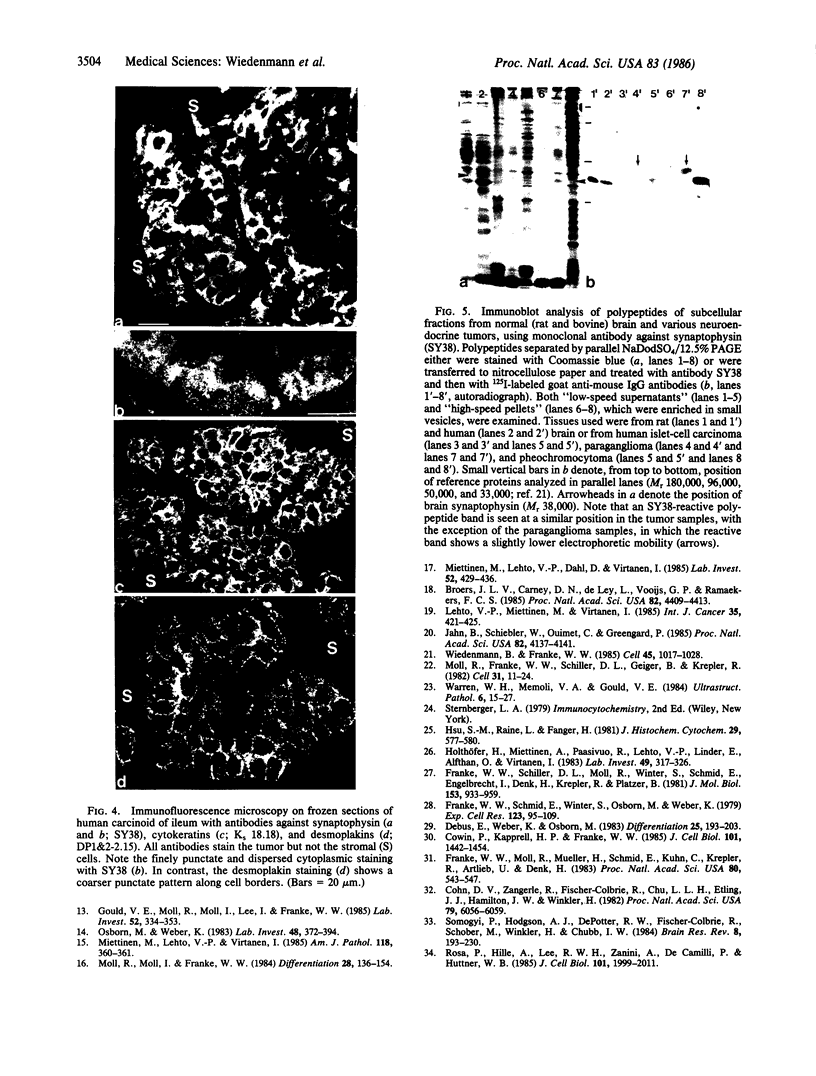
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop A. E., Polak J. M., Facer P., Ferri G. L., Marangos P. J., Pearse A. G. Neuron specific enolase: a common marker for the endocrine cells and innervation of the gut and pancreas. Gastroenterology. 1982 Oct;83(4):902–915. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blobel G. A., Gould V. E., Moll R., Lee I., Huszar M., Geiger B., Franke W. W. Coexpression of neuroendocrine markers and epithelial cytoskeletal proteins in bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine neoplasms. Lab Invest. 1985 Jan;52(1):39–51. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Broers J. L., Carney D. N., de Ley L., Vooijs G. P., Ramaekers F. C. Differential expression of intermediate filament proteins distinguishes classic from variant small-cell lung cancer cell lines. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jul;82(13):4409–4413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.13.4409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cohn D. V., Zangerle R., Fischer-Colbrie R., Chu L. L., Elting J. J., Hamilton J. W., Winkler H. Similarity of secretory protein I from parathyroid gland to chromogranin A from adrenal medulla. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6056–6059. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6056. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cowin P., Kapprell H. P., Franke W. W. The complement of desmosomal plaque proteins in different cell types. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1442–1454. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1442. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Debus E., Weber K., Osborn M. Monoclonal antibodies specific for glial fibrillary acidic (GFA) protein and for each of the neurofilament triplet polypeptides. Differentiation. 1983;25(2):193–203. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb01355.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Moll R., Mueller H., Schmid E., Kuhn C., Krepler R., Artlieb U., Denk H. Immunocytochemical identification of epithelium-derived human tumors with antibodies to desmosomal plaque proteins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):543–547. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.543. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Moll R., Winter S., Schmid E., Engelbrecht I., Denk H., Krepler R., Platzer B. Diversity of cytokeratins. Differentiation specific expression of cytokeratin polypeptides in epithelial cells and tissues. J Mol Biol. 1981 Dec 25;153(4):933–959. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90460-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould V. E., Linnoila R. I., Memoli V. A., Warren W. H. Neuroendocrine components of the bronchopulmonary tract: hyperplasias, dysplasias, and neoplasms. Lab Invest. 1983 Nov;49(5):519–537. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gould V. E., Moll R., Moll I., Lee I., Franke W. W. Neuroendocrine (Merkel) cells of the skin: hyperplasias, dysplasias, and neoplasms. Lab Invest. 1985 Apr;52(4):334–353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haimoto H., Takahashi Y., Koshikawa T., Nagura H., Kato K. Immunohistochemical localization of gamma-enolase in normal human tissues other than nervous and neuroendocrine tissues. Lab Invest. 1985 Mar;52(3):257–263. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Heitz P. U., Kasper M., Polak J. M., Klöppel G. Pancreatic endocrine tumors. Hum Pathol. 1982 Mar;13(3):263–271. doi: 10.1016/s0046-8177(82)80183-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holthöfer H., Miettinen A., Paasivuo R., Lehto V. P., Linder E., Alfthan O., Virtanen I. Cellular origin and differentiation of renal carcinomas. A fluorescence microscopic study with kidney-specific antibodies, antiintermediate filament antibodies, and lectins. Lab Invest. 1983 Sep;49(3):317–326. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hsu S. M., Raine L., Fanger H. Use of avidin-biotin-peroxidase complex (ABC) in immunoperoxidase techniques: a comparison between ABC and unlabeled antibody (PAP) procedures. J Histochem Cytochem. 1981 Apr;29(4):577–580. doi: 10.1177/29.4.6166661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jahn R., Schiebler W., Ouimet C., Greengard P. A 38,000-dalton membrane protein (p38) present in synaptic vesicles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4137–4141. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4137. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lehto V. P., Miettinen M., Virtanen I. A dual expression of cytokeratin and neurofilaments in bronchial carcinoid cells. Int J Cancer. 1985 Apr 15;35(4):421–425. doi: 10.1002/ijc.2910350402. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Lehto V. P., Dahl D., Virtanen I. Varying expression of cytokeratin and neurofilaments in neuroendocrine tumors of human gastrointestinal tract. Lab Invest. 1985 Apr;52(4):429–436. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miettinen M., Lehto V. P., Virtanen I. Immunofluorescence microscopic evaluation of the intermediate filament expression of the adrenal cortex and medulla and their tumors. Am J Pathol. 1985 Mar;118(3):360–366. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Franke W. W., Schiller D. L., Geiger B., Krepler R. The catalog of human cytokeratins: patterns of expression in normal epithelia, tumors and cultured cells. Cell. 1982 Nov;31(1):11–24. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90400-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moll R., Moll I., Franke W. W. Identification of Merkel cells in human skin by specific cytokeratin antibodies: changes of cell density and distribution in fetal and adult plantar epidermis. Differentiation. 1984;28(2):136–154. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-0436.1984.tb00277.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moss P. S., Honeycutt N., Pawson T., Martin G. S. Viral transformation of chick myogenic cells. The relationship between differentiation and the expression of the SRC gene. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Oct 1;123(1):95–105. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90425-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osborn M., Weber K. Tumor diagnosis by intermediate filament typing: a novel tool for surgical pathology. Lab Invest. 1983 Apr;48(4):372–394. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G., Takor T. Embryology of the diffuse neuroendocrine system and its relationship to the common peptides. Fed Proc. 1979 Aug;38(9):2288–2294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pearse A. G. The cytochemistry and ultrastructure of polypeptide hormone-producing cells of the APUD series and the embryologic, physiologic and pathologic implications of the concept. J Histochem Cytochem. 1969 May;17(5):303–313. doi: 10.1177/17.5.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rosa P., Hille A., Lee R. W., Zanini A., De Camilli P., Huttner W. B. Secretogranins I and II: two tyrosine-sulfated secretory proteins common to a variety of cells secreting peptides by the regulated pathway. J Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;101(5 Pt 1):1999–2011. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.5.1999. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmechel D., Marangos P. J., Brightman M. Neurone-specific enolase is a molecular marker for peripheral and central neuroendocrine cells. Nature. 1978 Dec 21;276(5690):834–836. doi: 10.1038/276834a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Somogyi P., Hodgson A. J., DePotter R. W., Fischer-Colbrie R., Schober M., Winkler H., Chubb I. W. Chromogranin immunoreactivity in the central nervous system. Immunochemical characterisation, distribution and relationship to catecholamine and enkephalin pathways. Brain Res. 1984 Dec;320(2-3):193–230. doi: 10.1016/0165-0173(84)90007-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tapia F. J., Polak J. M., Barbosa A. J., Bloom S. R., Marangos P. J., Dermody C., Pearse A. G. Neuron-specific enolase is produced by neuroendocrine tumours. Lancet. 1981 Apr 11;1(8224):808–811. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)92682-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warren W. H., Memoli V. A., Gould V. E. Immunohistochemical and ultrastructural analysis of bronchopulmonary neuroendocrine neoplasms. I. Carcinoids. Ultrastruct Pathol. 1984;6(1):15–27. doi: 10.3109/01913128409016661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wiedenmann B., Franke W. W. Identification and localization of synaptophysin, an integral membrane glycoprotein of Mr 38,000 characteristic of presynaptic vesicles. Cell. 1985 Jul;41(3):1017–1028. doi: 10.1016/s0092-8674(85)80082-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]