Abstract
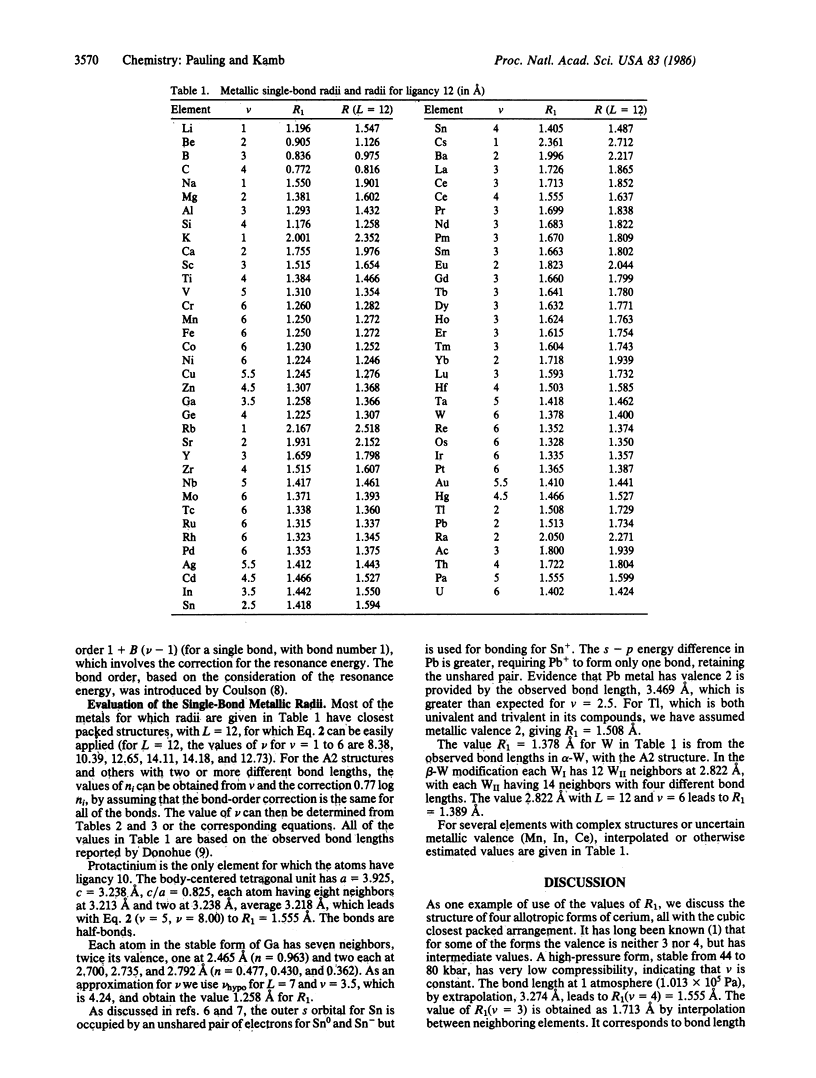
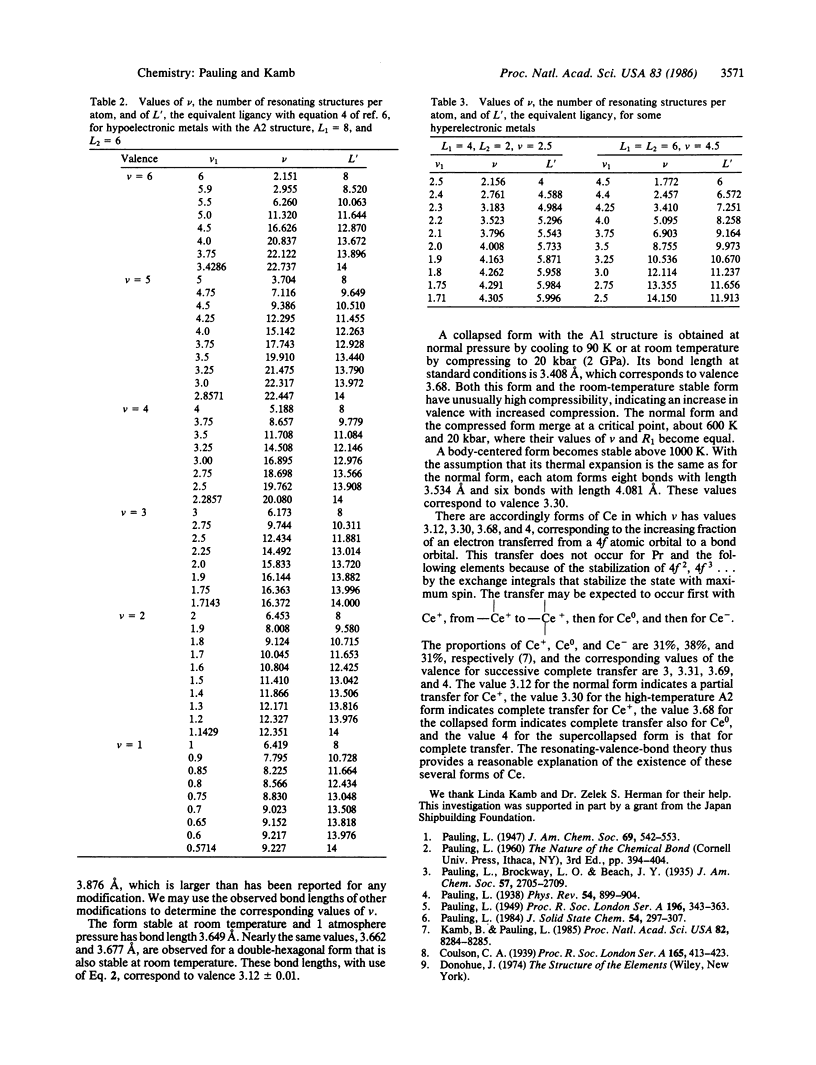
An earlier discussion [Pauling, L. (1947) J. Am. Chem. Soc. 69, 542] of observed bond lengths in elemental metals with correction for bond number and resonance energy led to a set of single-bond metallic radii with values usually somewhat less than the corresponding values obtained from molecules and complex ions. A theory of resonating covalent bonds has now been developed that permits calculation of the number of resonance structures per atom and of the effective resonance energy per bond. With this refined method of correcting the observed bond lengths for the effect of resonance energy, a new set of single-bond covalent radii, in better agreement with values from molecules and complex ions, has been constructed.
Keywords: statistical theory of resonance of covalent bonds
Full text
PDF
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Kamb B., Pauling L. Extension of the statistical theory of resonating valence bonds to hyperelectronic metals. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Dec;82(24):8284–8285. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.24.8284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pauling L., Sheehan W. F. The Dissociation Energy of Carbon Monoxide and the Heat of Sublimation of Graphite. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1949 Jul;35(7):359–363. doi: 10.1073/pnas.35.7.359. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



