Abstract
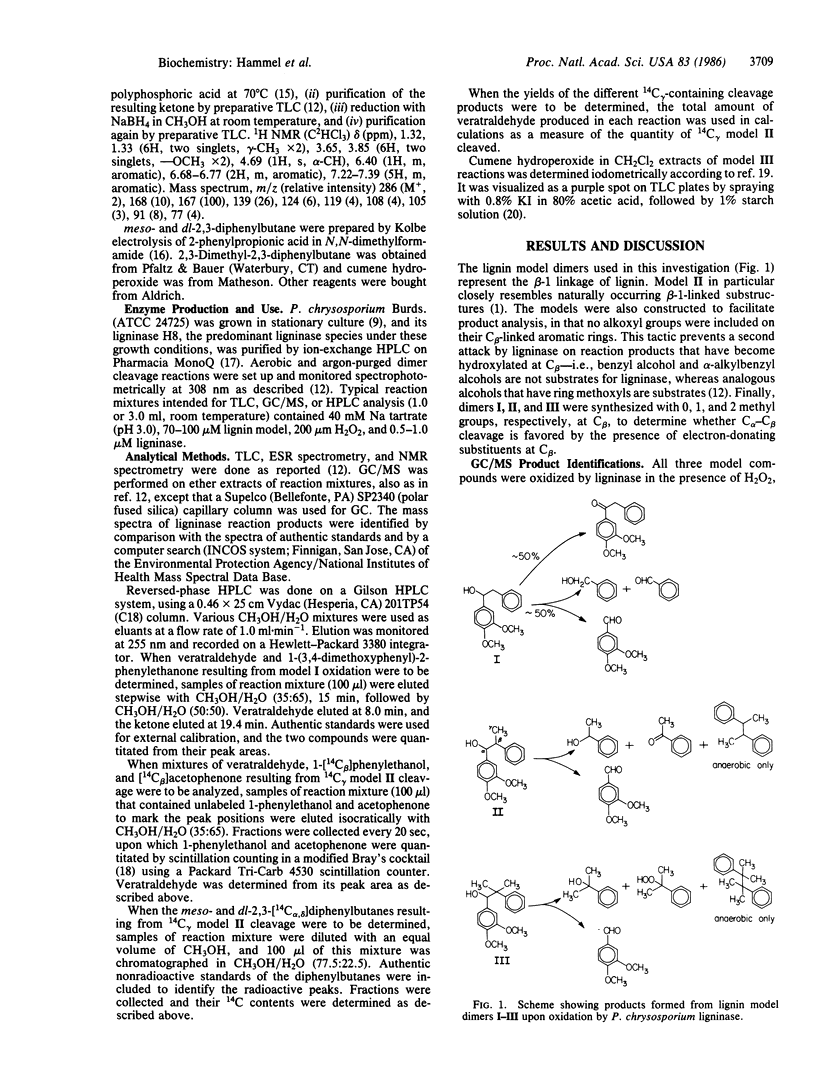
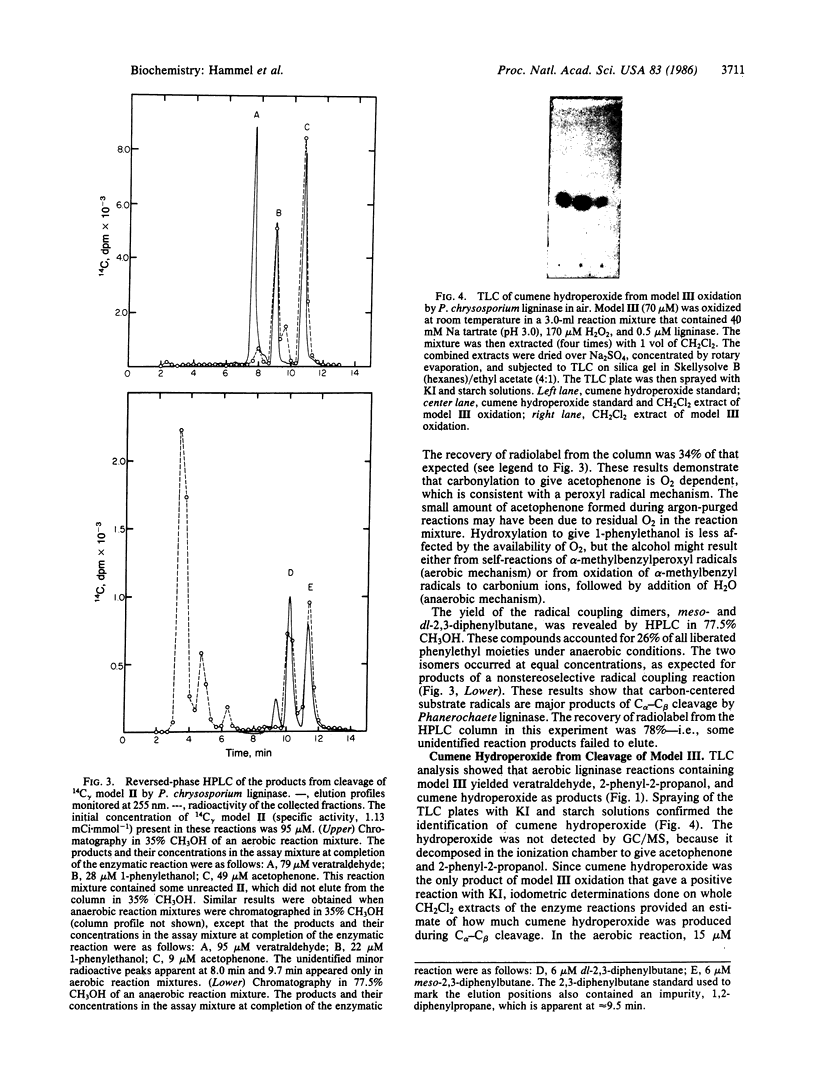
The H2O2-requiring ligninase of the basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium oxidatively cleaves both lignin and lignin model compounds between C alpha and C beta (C-1 and C-2) of their aliphatic side chains. Previous work has demonstrated a reaction mechanism by which ligninase oxidizes aromatic substrates to their cation radicals, which then undergo side chain cleavage to yield carbon-centered free radicals. These carbon-centered radicals add O2 to give substrate peroxyl radicals that react further to yield the hydroxylated and carbonylated end products usually seen in experiments with ligninase. To investigate this radical mechanism, we have now designed three dimeric lignin models: 1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-phenylethanol (I), 1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-phenylpropanol (II), and 1-(3,4-dimethoxyphenyl)-2-methyl-2-phenylpropanol (III). The following results were obtained when these models were oxidized by ligninase: methyl groups at C beta of the substrate favored C alpha-C beta cleavage versus C alpha oxidation to the ketone. GC/MS and HPLC analysis showed that II gave a radical coupling dimer, 2,3-diphenylbutane, as a major (26% yield) reaction product under anaerobic conditions. The anaerobic oxidation of III yielded 2,3-dimethyl-2,3-diphenylbutane. Spin-trapping experiments with nitrosobenzene showed that model II oxidation produced alpha-methylbenzyl radicals, whereas model III oxidation gave alpha, alpha-dimethylbenzyl radicals. TLC and iodometric determinations showed that III gave cumene hydroperoxide as a major (21% yield) reaction product in air. These findings demonstrate that carbon-centered and peroxyl radicals at C beta are major products of C alpha-C beta cleavage by ligninase.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buege J. A., Aust S. D. Microsomal lipid peroxidation. Methods Enzymol. 1978;52:302–310. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(78)52032-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Floyd R. A., Soong L. M. Spin trapping in biological systems. Oxidation of the spin trap 5,5-dimethyl-1-pyrroline-1-oxide by a hydroperoxide-hematin-system. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1977 Jan 10;74(1):79–84. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(77)91377-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Garssen G. J., Vliegenthart J. F., Boldingh J. The origin and structures of dimeric fatty acids from the anaerobic reaction between soya-bean lipoxygenase, linoleic acid and its hydroperoxide. Biochem J. 1972 Nov;130(2):435–442. doi: 10.1042/bj1300435. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glenn J. K., Morgan M. A., Mayfield M. B., Kuwahara M., Gold M. H. An extracellular H2O2-requiring enzyme preparation involved in lignin biodegradation by the white rot basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1983 Aug 12;114(3):1077–1083. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(83)90672-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gold M. H., Kuwahara M., Chiu A. A., Glenn J. K. Purification and characterization of an extracellular H2O2-requiring diarylpropane oxygenase from the white rot basidiomycete, Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1984 Nov 1;234(2):353–362. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(84)90280-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hammel K. E., Tien M., Kalyanaraman B., Kirk T. K. Mechanism of oxidative C alpha-C beta cleavage of a lignin model dimer by Phanerochaete chrysosporium ligninase. Stoichiometry and involvement of free radicals. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 15;260(14):8348–8353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Janzen E. G. Spin trapping. Methods Enzymol. 1984;105:188–198. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(84)05025-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kellogg E. W., 3rd, Fridovich I. Superoxide, hydrogen peroxide, and singlet oxygen in lipid peroxidation by a xanthine oxidase system. J Biol Chem. 1975 Nov 25;250(22):8812–8817. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kersten P. J., Tien M., Kalyanaraman B., Kirk T. K. The ligninase of Phanerochaete chrysosporium generates cation radicals from methoxybenzenes. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2609–2612. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kirk T. K., Connors W. J., Bleam R. D., Hackett W. F., Zeikus J. G. Preparation and microbial decomposition of synthetic [14C]ligins. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 Jul;72(7):2515–2519. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.7.2515. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K., Bull C., Fee J. A. Steady-state and transient-state kinetic studies on the oxidation of 3,4-dimethoxybenzyl alcohol catalyzed by the ligninase of Phanerocheate chrysosporium Burds. J Biol Chem. 1986 Feb 5;261(4):1687–1693. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K. Lignin-Degrading Enzyme from the Hymenomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium Burds. Science. 1983 Aug 12;221(4611):661–663. doi: 10.1126/science.221.4611.661. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tien M., Kirk T. K. Lignin-degrading enzyme from Phanerochaete chrysosporium: Purification, characterization, and catalytic properties of a unique H(2)O(2)-requiring oxygenase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(8):2280–2284. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.8.2280. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- de Groot J. J., Veldink G. A., Vliegenthart J. F., Boldingh J., Wever R., van Gelder B. F. Demonstration by EPR spectroscopy of the functional role of iron in soybean lipoxygenase-1. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1975 Jan 23;377(1):71–79. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(75)90287-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]