Abstract
In recent experiments the spontaneous formation of hollow bilayer vesicles with polyhedral symmetry has been observed. On the basis of the experimental phenomenology it was suggested that the mechanism for the formation of bilayer polyhedra is minimization of elastic bending energy. Motivated by these experiments, we study the elastic bending energy of polyhedral bilayer vesicles. In agreement with experiments, and provided that excess amphiphiles exhibiting spontaneous curvature are present in sufficient quantity, we find that polyhedral bilayer vesicles can indeed be energetically favorable compared to spherical bilayer vesicles. Consistent with experimental observations we also find that the bending energy associated with the vertices of bilayer polyhedra can be locally reduced through the formation of pores. However, the stabilization of polyhedral bilayer vesicles over spherical bilayer vesicles relies crucially on molecular segregation of excess amphiphiles along the ridges rather than the vertices of bilayer polyhedra. Furthermore, our analysis implies that, contrary to what has been suggested on the basis of experiments, the icosahedron does not minimize elastic bending energy among arbitrary polyhedral shapes and sizes. Instead, we find that, for large polyhedron sizes, the snub dodecahedron and the snub cube both have lower total bending energies than the icosahedron.
I. INTRODUCTION
The self-assembly of complex two-dimensional objects from simple constituent units plays an important role throughout condensed matter physics, materials science, and molecular biology. Of particular importance for biology is the self-assembly of amphiphilic molecules into flexible bilayers [1-3] which provide the structural basis for cell membranes. The physical properties of amphiphile bilayers are often studied using artificial bilayer vesicles [1-4] of controlled molecular composition. In many settings [1-5] the shape of such bilayer vesicles is characterized by a constant or smoothly varying curvature and minimizes the elastic energy of the vesicle. In experiment as well as theory [2,4,5], characteristic sequences of distinct vesicle shapes are obtained as a function of geometric parameters, such as the vesicle surface area at fixed vesicle volume, and elastic parameters, such as the bilayer spontaneous curvature. This has led to a general framework for the description and prediction of smooth vesicle shapes [2,4] in which elasticity theory is combined with variational and perturbative methods for energy minimization.
In recent experiments [6-10], however, faceted bilayer vesicles with shapes reminiscent of polyhedra have been observed. Polyhedra are characterized by flat faces connected by ridges and vertices with high local curvature, and are generally not regarded as being energetically favorable shapes of bilayer vesicles. In these experiments, two types of oppositely charged, single-tailed amphiphiles were used [6,7], with a slight excess of one amphiphile species over the other. Consistent with the classic view of bilayer vesicles [1-4], the amphiphiles were found to self-organize into spherical bilayer vesicles at high temperatures. However, provided that the number of excess, unpaired amphiphiles was tuned to some optimal range [6-10], cooling the system below the chain melting temperature yielded the spontaneous formation of polyhedral bilayer vesicles. The bilayer polyhedra were reported to be stable over weeks and to be consistently reproduced upon thermal cycling. Furthermore, it was suggested [6,7] that the observed polyhedral shapes had icosahedral symmetry, although some uncertainty regarding the polyhedral symmetry remained. Finally, the vertices of polyhedral bilayer vesicles were found to exhibit pores [6-8], which was put forward [6] as a mechanism for avoiding the large elastic bending energy associated with closed vertices of bilayer polyhedra.
On the basis of the experimental phenomenology it was suggested [6,7] that minimization of elastic bending energy determines the shape of bilayer polyhedra. In a previous article [11] we took these intriguing experimental observations as our starting point and investigated the minimal bending energies of bilayer polyhedra. We found that, while polyhedral vesicles can be energetically favorable compared to spherical vesicles for the bilayer composition used in the aforementioned experiments [6-10], the snub dodecahedron and the snub cube generally have lower elastic bending energies than the icosahedron. The purpose of the present article is to provide a more comprehensive discussion of the bending energies of bilayer polyhedra for various experimental scenarios and allowing for different models of the elastic contributions to the free energy of bilayer polyhedra. Our overall aim is thereby to provide basic estimates of the relative bending energies associated with different polyhedral symmetries and to contrast these polyhedral bending energies with the elastic bending energy of spherical bilayer vesicles. The disagreement between experiment and theory concerning the most favorable polyhedral symmetry suggests that either the mechanism governing the shape of bilayer polyhedra is not solely minimization of elastic bending energy or the dominant shape of the faceted bilayer vesicles observed in experiments does not correspond to the icosahedron.
To predict polyhedral shapes with minimal energy, a number of methodologies based on computer simulations have been developed over recent years [12-16]. Here we use a complementary method, in which we first derive general expressions for the contributions to the elastic bending energy of bilayer polyhedra due to the ridges, closed vertices, and vertex pores observed experimentally [6-8]. Particularly simple expressions of ridge, vertex, and pore energies are obtained from the Helfrich-Canham-Evans free energy of bending [17-19]. We assess the validity of these phenomenological expressions, which only involve a few parameters, by making comparisons to solutions of the two-dimensional equations of elasticity obtained previously for the ridges and vertices of polyhedra in certain limiting cases [20-25]. On this basis we then survey total polyhedral bending energies for a variety of different symmetry classes of polyhedra [26-28], which are characterized by distinct values of the geometric parameters entering our expressions of ridge, vertex, and pore energies.
The organization of this article is as follows. Section II provides a brief review of the experimental phenomenology of bilayer polyhedra and of the contributions to their free energy. In Sec. III we derive general expressions for the elastic bending energies associated with ridges, closed vertices, and vertex pores from the Helfrich-Canham-Evans free energy of bending. Comparisons to the corresponding solutions obtained previously in limiting cases of the equations of elasticity are made in Sec. IV. Section V analyzes the elastic bending energy associated with pores of bilayer polyhedra. In Sec. VI we calculate total bending energies of bilayer polyhedra for various polyhedral symmetry classes. A discussion of our results is provided in Sec. VII, and a summary and conclusions can be found in Sec. VIII.
II. EXPERIMENTAL PHENOMENOLOGY OF BILAYER POLYHEDRA
The bilayer polyhedra observed in experiments [6-10] were composed of two different types of amphiphiles: myristic acid and cetyltrimethylammonium hydroxide (CTAOH). Myristic acid carries a single negative charge while CTAOH is positively charged, and the hydrophobic parts of both amphiphile species consist of a single hydrocarbon chain. In a salt-free aqueous solution dilute in amphiphiles, the two amphiphile species were observed to self-assemble into bilayers [29]. The bilayers had a thickness of approximately 4 nm, and the interamphiphile spacing was found [6,29] to be around 0.4–0.6 nm. While above the chain melting temperature the bending rigidity of the bilayers formed by myristic acid and CTAOH falls within the range 1–10 kBT, cooling the system to room temperature yielded very stiff bilayers with rigidities greater than 100 kBT [7]. In small-angle neutron scattering experiments it was indeed found [29] that bilayers were nearly flat over a spatial length scale of more than 1 μm.
In earlier work, a mesoscopic model [30] was used to further investigate the intriguing mechanical properties of catanionic bilayers summarized above. In this model, electrostatic interactions are described by a standard Ising Hamiltonian, while a spring network accounts for the formation of hydrogen bonds between amphiphiles. The behavior of bilayers obtained with this model is consistent with a simple picture [6,7,29] of catanionic bilayers in which oppositely charged amphiphiles pair up to form zwitterionic amphiphiles with zero net charge and two hydrophobic tails, thereby expelling excess amphiphiles from flat bilayers. Due to their molecular shape, such unpaired excess amphiphiles are expected to exhibit spontaneous curvature. It was estimated [7] from the monolayer chain length of myristic acid that the induced spontaneous curvature of excess anionic amphiphiles is equal to around 0.3 nm−1.
At high temperatures, mixtures of myristic acid and CTAOH were found to self-assemble into spherical bilayer vesicles [7]. As the system is cooled below the chain melting temperature, the behavior of these vesicles can be characterized [6-10,29] by the fraction of the anionic amphiphile component over total amphiphile content, which we denote by rI. Using electron and light microscopy it was found that, if rI ≠ 0.5, spherical bilayer vesicles may facet to form polyhedral shapes or break up to form flat bilayer disks. Both of these aggregate shapes may coexist with spherical bilayer vesicles. While the diameter of bilayer disks was observed [29] to vary from 30 nm to 3 μm, the diameters of bilayer polyhedra were reported [6-10] to fall within a characteristic range of 1–2 μm. Bilayer polyhedra are estimated [6] to contain around 107 catanionic pairs and an excess of myristic acid corresponding to around 106 single amphiphiles.
Electron and fluorescence microscopy studies have suggested [6-10] that bilayer polyhedra exhibit pores at their vertices. By bleaching fluorescent molecules inside bilayer polyhedra and measuring fluorescence recovery after photo-bleaching, the pore diameter was estimated [8] to be equal to around 40 nm. However, in the same set of experiments it was also found that some of the observed polyhedral vertices were, in fact, closed. Finally, on the basis of electron and confocal microscopy a classification of the symmetry of bilayer polyhedra was attempted. Some features of the observed polyhedral shapes, including their hexagonal cross section and fivefold vertex geometry, were found to be consistent with an icosahedral symmetry, but there was also considerable heterogeneity in the observed polyhedral shapes [6-10].
Following Ref. [7], we distinguish between three basic types of contributions to the free energy of bilayer polyhedra. First, there are elastic contributions to the free energy associated with the energy required to bend amphiphile bilayers along the ridges and closed vertices of polyhedra, and to bend amphiphile monolayers along the edges of polyhedral pores. For a given polyhedral symmetry and size, the total energetic cost associated with these terms depends on the elastic parameters characterizing the bilayer and on the geometric parameters defining the polyhedral shape. The total elastic energy of bilayer polyhedra is to be compared with the elastic energy associated with bilayer vesicles exhibiting a constant or smoothly varying curvature. In particular, if no constraints on the vesicle surface area or the vesicle volume are imposed, and the bilayer composition is homogeneous, the classic framework for the description of smooth vesicle shapes implies [4] that spherical bilayer vesicles minimize bending energy.
A second class of contributions to the free energy of bilayer polyhedra arises from the entropic cost of segregating excess amphiphiles along polyhedral ridges and vertices. These entropic terms make the formation of bilayer polyhedra with defined amphiphile domains unfavorable compared to homogeneous bilayer vesicles. However, considering the experimental observation [7] of segregated domains of excess amphiphiles along polyhedral ridges and vertices, entropic contributions do not seem to be dominant. Indeed, the picture of heterogeneous bilayers presented in Refs. [6,7,29,30] suggests that excess amphiphiles are segregated during the cooling down process, leading to the separation of amphiphile bilayers into distinct domains which do not mix at low temperatures. Here we are not concerned with the precise mechanism leading to the segregation of amphiphile domains and assume that bilayers formed by myristic acid and CTAOH do indeed spontaneously expel excess amphiphiles during the cooling down process.
Third, we need to consider electrostatic contributions to the free energy of bilayer polyhedra. On the one hand, segregated excess amphiphiles carry charges of equal sign and, hence, repel each other. Thus, in addition to entropic effects, the mechanism leading to amphiphile segregation must overcome electrostatic repulsion between excess amphiphiles. On the other hand, the finite surface charge density observed along the ridges and vertices of bilayer polyhedra [7] induces screening clouds in the surrounding solution. Different membrane shapes lead to different shapes of the screening clouds which, as discussed further in Sec. VI C, can affect the energetic cost associated with polyhedral ridges and pores. However, electrostatic contributions to the bending rigidity of amphiphile bilayers are expected [31-34] to be of the order of 1–10 kBT and, hence, at least one order of magnitude smaller than the experimental values [7] of the bending rigidity of bilayer polyhedra. This suggests [30] that the electrostatic energies associated with deformations of the screening cloud are small compared to the membrane bending energy. Thus, we follow here Ref. [7] and assume that the shape of bilayer polyhedra is governed by minimization of elastic bending energy.
III. BENDING ENERGIES OF BILAYER POLYHEDRA
In this section we derive simple phenomenological expressions for the bending energies associated with the ridges, closed vertices, and vertex pores of bilayer polyhedra. Our starting point is the Helfrich-Canham-Evans free energy of bending [1-4,17-19], namely,
| (1) |
where Kb is the bilayer bending rigidity, R1 and R2 are the two principal radii of curvature, and H0 is the bilayer spontaneous curvature. In situations where we consider amphiphile monolayers instead of amphiphile bilayers, Kb in Eq. (1) is replaced by the monolayer bending rigidity , and H0 is replaced by the monolayer spontaneous curvature .
A. Ridge energy
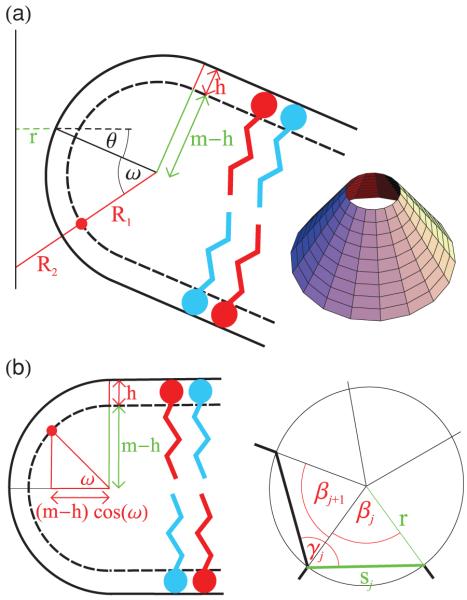
Figures 1(a) and 1(b) show two models of an amphiphile bilayer bending along the ridge of a polyhedron with dihedral angle αi. For simplicity we take R2 → ∞ in Eq. (1) for both models. The elastic energy of ridges which do not necessarily satisfy this assumption is discussed in Sec. IV. Moreover, we focus here on the most straightforward case of symmetric bilayer leaflets and take H0 = 0 nm−1 in Eq. (1). The richer case in which there is segregation of excess amphiphiles, and hence, the possibility of an inhomogeneous composition of the membrane leaflets, is considered in Sec. III D.
FIG. 1.
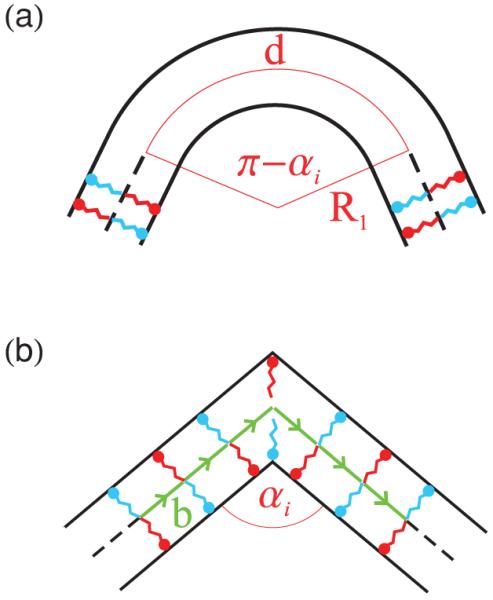
(Color online) Side view of a ridge with dihedral angle αi bending (a) over an arc length d of a cylinder with radius R1 and (b) over an arc length comparable to the small-scale cutoff b. The red and blue amphiphile species represent myristic acid and CTAOH, which are negatively and positively charged, respectively. The arrows in panel (b) denote bond vectors connecting adjacent amphiphiles.
Our first model in Fig. 1(a) is inspired by the electron micrographs of bilayer polyhedra in Refs. [6-8]. We assume that, along a ridge, a bilayer bends over an angle π − αi around a cylinder of radius R1, where the index i denotes the particular polyhedral ridge under consideration. From Eq. (1) one then finds the ridge energy
| (2) |
where li is the ridge length and d = R1(π − αi) is the arc length subtended by the ridge.
Our second model, illustrated in Fig. 1(b), allows bilayers to bend sharply along ridges and thereby provides a more faithful representation of the polyhedral geometry. We discretize the system [35] using an interamphiphile spacing b and note that, for a curve embedded in two-dimensional space, the bond vector connecting adjacent amphiphiles is t̂ = (cos φ, sin φ), where φ = φ(u) is the angle between t̂ and the abscissa at some segment u along the curve. Using the relation
| (3) |
one then obtains from Eq. (1) a simple expression of the ridge energy,
| (4) |
If the ridge bends “sharply,” we take
| (5) |
where the factor of two in the argument of the Dirac δ function arises because we assume that the ridge in Fig. 1(b) bends over a length 2b so that a single amphiphile is located at the tip of the ridge, thereby reducing the density in Eq. (4). The ridge energy in Eq. (3) then becomes
| (6) |
Setting d = 2b, Eqs. (2) and (6) both yield
| (7) |
where the rescaled bilayer bending rigidity K̄b = Kb/(2b) and the superscript (h) indicates that this expression of the ridge energy applies to homogeneous membranes. An expression similar [36] to Eq. (7) was used in Ref. [7] to describe the elastic bending energy associated with polyhedral ridges. The scale of the ridge energy in Eq. (7) is set by our assumption d = 2b which, on the basis of the scattering measurements in Refs. [6,29], gives d ≈ 1 nm. The choice d = 2b ≈ 1 nm for the arc length, and the resulting estimates of the energy density, are confirmed in Sec. IV by comparing Eq. (7) to an expression of the ridge energy which allows for both principal radii of curvature to be finite.
B. Vertex energy
A phenomenological but straightforward expression for the elastic bending energy associated with closed bilayer vertices is obtained following similar steps as in Sec. III A. As indicated in Fig. 2, one can regard vertices as points at which the bond vectors parallel to ridges change direction to become parallel to neighboring ridges, which is complementary to the model of ridges illustrated in Fig. 1(b). We decompose the total vertex energy Gv into a sum of q terms with j = 1, …,q, where q denotes the number of ridges meeting at a vertex. Retracing the steps leading to the ridge energy in Eq. (7) one finds
| (8) |
where βj denotes the face angle subtended at a given vertex by two neighboring ridges, and, similarly as in Sec. III A, we took the ridge length across a vertex to be equal to 2b and set
| (9) |
The total vertex energy is then given by
| (10) |
where the superscript (h) again indicates that this expression applies to homogeneous membranes.
FIG. 2.
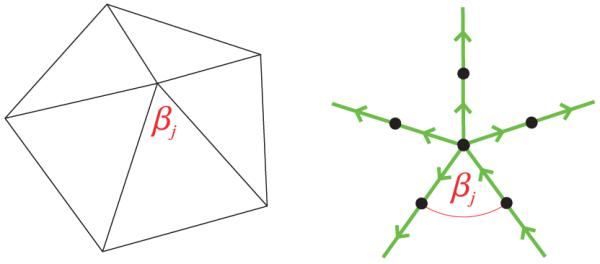
(Color online) Illustration of a polyhedral vertex with face angle βj. As in Fig. 1(b), the arrows represent bond vectors connecting adjacent amphiphiles, but now with the bond vectors being parallel rather than perpendicular to ridges.
C. Pore energy
Calculations of the elastic bending energy associated with toroidal pores in planar bilayers can be found in Refs. [7,8,37], and a generalization to arbitrary pore shapes is provided in Ref. [38]. Based on this previous work, we devised two complementary models of vertex pores. Our first model [see Fig. 3(a)] is again inspired by the experimental images in Refs. [6-8], which suggest that the vertices of bilayer polyhedra locally resemble cones. Accordingly, we approximate the vertex of a given polyhedron by a cone with apex angle π − 2θ, where θ = π/2 − arccos(1 − Ω/2π) for a solid angle Ω subtended by the polyhedron vertex. We then use the Helfrich-Canham-Evans free energy of bending in Eq. (1) with the monolayer bending rigidity and spontaneous curvature to calculate the bending energy of a pore around the tip of a cone, leading to an approximate expression for the bending energy of polyhedral pores.
FIG. 3.
(Color online) Schematic illustrations of two models of vertex pores for an amphiphile monolayer thickness m and an amphiphile headgroup thickness h. (a) Cross section of half of a pore around the tip of a cone (inset) with apex angle π − 2θ and radius r. (b) Side view (left panel) and top-down view (right panel) of a pore with radius r composed of straight edges of length sj along each face which bend through an angle γj from one face to a neighboring face.
From Fig. 3(a) we read off the principal radii of curvature, R1 and R2, and the area element, dS, of a conical pore with semicircular cross section:
| (11) |
| (12) |
| (13) |
for 0 ≤ ω ≤ π/2 and −π/2 ≤ ω ≤ 0, respectively, where m denotes the monolayer thickness, h the thickness of the amphiphile headgroup, and r is the pore radius. Note from Fig. 3(a) that only pore radii r ≥ rm, where rm = m(1 − cos θ) is defined as the value of r for which the separation between opposite sides of the pore is equal to zero, have physical significance. For bilayer polyhedra, we have [7] the representative values m ≈ 2 nm and h ≈ 0.5 nm.
Following the steps outlined in Appendix A, one finds that Eqs. (11)–(13) together with Eq. (1), give
| (14) |
where we have defined
| (15) |
and
| (16) |
| (17) |
The superscript (c) in Eq. (14) indicates that this expression of the pore energy applies to conical pores. For θ = 0, the above result for the bending energy of a conical pore reduces to the corresponding expression obtained previously for planar bilayers [7,8,37].
Our second model of vertex pores [see Fig. 3(b)] allows for a more faithful representation of the polyhedral geometry. We assume that, along each face, the vertex pore consists of a straight edge with a semicircular cross section [see Fig. 3(b), left panel], which bends through an angle γj across a ridge from one face to a neighboring face [see Fig. 3(b), right panel]. Accordingly, we split the energy cost associated with such a polygonal pore into a term corresponding to the elastic bending energy of a straight edge along a polyhedral face, and a term corresponding to the energy cost of bending the edge of the pore from one face to a neighboring face. For a straight edge of length sj, the version of Eq. (1) appropriate for a monolayer gives
| (18) |
where from Fig. 3(b) we have that .
The contribution stems from bending the pore about the vertical axis in the left panel of Fig. 3(b) by some angle γj. According to the right panel of Fig. 3(b) we have
| (19) |
Retracing the steps which led to the ridge energy in Eq. (7), but now for the horizontal amphiphile component as indicated in the left panel of Fig. 3(b), one finds
| (20) |
where the rescaled monolayer bending rigidity and the dimensionless spontaneous curvature . The total pore energy is then given by
| (21) |
where the superscript (p) signifies that Eq. (21) applies to polygonal pores. Our expressions of conical and polygonal pore energies in Eqs. (14) and (21) are discussed further in Sec. V.
D. Segregation of excess amphiphiles
The experimental phenomenology of polyhedral bilayer vesicles suggests [6,7] that the two amphiphile species constituting bilayer polyhedra pair up to form flat bilayers and thereby expel excess (unpaired) amphiphiles from polyhedral faces. As already noted in Sec. II, segregated excess amphiphiles exhibit a spontaneous curvature [7], thus favoring a curved membrane shape. It has indeed been observed [6-8] that excess amphiphiles seed pores into bilayers and localize along the ridges of bilayer polyhedra. As far as the effect of excess amphiphiles on pore energies is concerned, we therefore follow Ref. [7] and assume that vertex pores are composed of excess amphiphiles, leading to a finite value of in Eqs. (14) and (21) if sufficiently many excess amphiphiles are present.
How does segregation of excess amphiphiles modify the ridge energy in Eq. (7) and the vertex energy in Eq. (10)? To address this question, we consider a particularly favorable scenario for the formation of polyhedral ridges and vertices in heterogeneous bilayers and thereby obtain a lower bound on the elastic energies associated with ridges and pores in the presence of molecular segregation. Assuming perfect segregation, excess amphiphiles are concentrated along the outer membrane leaflets along ridges and closed vertices so as to induce an anisotropic spontaneous curvature commensurate with the dihedral and vertex angles associated with a given polyhedral geometry. As illustrated in Fig. 4 for a ridge with dihedral angle αi, this leaves us with the inner membrane leaflet which, in the absence of some additional amphiphile species with “inverted-wedge shape” [1-3], must be bent in order to cover the hydrophobic tails of the excess amphiphiles localized in the outer membrane leaflet along ridges and closed bilayer vertices.
FIG. 4.
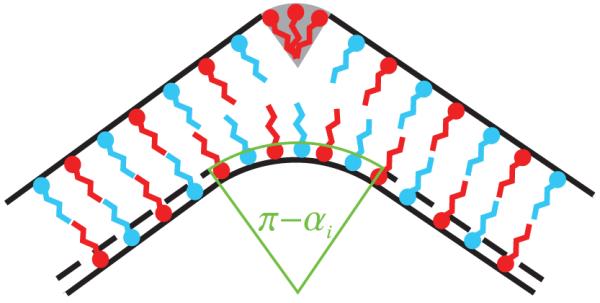
(Color online) Side view of a ridge with dihedral angle αi and perfect segregation of excess amphiphiles in the outer bilayer leaflet. Note that, compared to Fig. 1, the neutral plane of bending is shifted from the mid-plane of the bilayer to the amphiphile head-tail interface of the inner membrane leaflet.
For perfectly segregated ridges and vertices, we describe the bending of the inner membrane leaflet in a similar way as in the case of the bilayer ridges and vertices considered in Secs. III A and III B, but with the neutral plane of bending shifted from the midplane of the bilayer to the amphiphile head-tail interface of the inner amphiphile leaflet (see Fig. 4). Thus, following analogous steps as in Secs. III A and III B, we obtain the modified ridge and vertex energies
| (22) |
| (23) |
where the superscript (s) indicates that in these expressions we assume perfect segregation of excess amphiphiles. Thus, provided that the optimal amount of excess amphiphiles is present [6,7], the ridge and vertex energies are lowered by a factor . Experiments [6,7] and simulations [30] suggest that . Since the segregation of excess amphiphiles, and their fit to dihedral and vertex angles, will generally be less than perfect, we regard the simple phenomenological expressions in Eqs. (22) and (23) as lower bounds on the ridge and vertex energies in heterogeneous bilayers.
The heuristic picture of amphiphile segregation developed above allows us to estimate the amount of excess amphiphiles present for a given polyhedral shape and size. In particular, we define the fraction of anionic amphiphile content, which is the amphiphile species in excess for bilayer polyhedra [6-10], over total amphiphile content as
| (24) |
where NR denotes the total number of excess amphiphiles segregated along ridges, NP denotes the total number of excess amphiphiles segregated at vertex pores, NT denotes the total number of amphiphiles contained in the polyhedron shell, and, consistent with the estimates in Sec. II, we have taken NR + NP ⪡ NT. In agreement with typical experimental observations [6-8], Eq. (24) assumes that bilayer polyhedra exhibit pores at their vertices.
In order to estimate NR we need to determine how many excess amphiphiles must be segregated at a given polyhedral ridge so that the bilayer is bent by an appropriate dihedral angle. Assuming perfect segregation of excess amphiphiles in the outer leaflet, we estimate that excess amphiphiles must be segregated per interamphiphile spacing along the ridge in order to induce an angle π − αi in the outer membrane leaflet. Thus,
| (25) |
where the sum is to be taken over all the ridges of a given polyhedral shape.
A particularly simple estimate of NP is obtained by assuming that pores have a (flat) toroidal shape and radius r, which gives a pore surface area of 2π2m(m + r) nm2. One therefore finds that
| (26) |
where V denotes the number of vertices of a given polyhedral shape and b2 is the surface area per amphiphile. Similarly, a rough estimate of the total number of amphiphiles contained in the polyhedron shell is given by
| (27) |
in which we have implicitly defined [21] the polyhedron radius Rp so that the polyhedron area is equal to for a given edge length and polyhedral symmetry. Combining Eqs. (25)–(27) we can evaluate the ideal value of rI in Eq. (24) obtained from our simple description of amphiphile segregation and make comparisons to the corresponding experimental estimates, a point to which we return in Sec. VI.
IV. ASYMPTOTIC EXPRESSIONS OF VERTEX AND RIDGE ENERGIES
The solution of the two-dimensional equations of elasticity [39] is a formidable challenge, and has only been achieved for the ridges and vertices of polyhedra in certain limiting cases [20-25] corresponding to a diverging Föppl-von Kármán number. The Föppl-von Kármán number is a dimensionless quantity characterizing the competition between bending and stretching deformations and, for spherical shells, is defined as [21]
| (28) |
where Y is the two-dimensional Young’s modulus. In the following we use the available asymptotic solutions of the equations of elasticity for polyhedral ridges and vertices to assess the validity of the phenomenological expressions of ridge and vertex energies obtained in Secs. III A and III B.
A. Vertex energy
In a series of papers [20-22,40,41], the energetic cost of introducing fivefold disclinations in hexagonal lattices has been investigated. It was found [20] that for a flat, circular sheet of radius R, the stretching energy diverges linearly with the area of the sheet: E(R) = A0Y R2, where A0 is a constant. However, if the sheet is allowed to buckle out of the plane, it is, for large enough system sizes, energetically favorable to form a cone with a central region which is “flattened out,” thus avoiding the curvature singularity at the tip of the cone. The bending energy associated with the cone section is found to be E(R) = B0Kb log(R/Rb), where B0 is a constant and Rb is the buckling radius at which it becomes energetically favorable for the lattice to bend out of the plane.
The above results have been used to estimate [21,22] the elastic energy of icosahedral vertices by noting that spherical shells can be discretized using an icosadeltahedral triangulation, which consists of a hexagonal lattice exhibiting 12 fivefold disclinations. Regarding the 12 disclination sites as independent, the vertex energy of icosadeltahedral triangulations of the sphere is found to be given by
| (29) |
for each disclination [21,22], where is the critical Föppl-von Kármán number for buckling to occur, we have neglected constant contributions due to the spherical background curvature, and the parameter A0 has been eliminated by energy minimization with respect to Rb. Good fits [21,22] to the results of simulations are obtained with B0 ≈ 1.30 and Γb ≈ 130.
The energy in Eq. (29) corresponds, for large enough Γ, to the elastic energy associated with the vertex of the icosahedron and can, in this limit, be compared to the more general but heuristic vertex energy in Eq. (10) with values of the geometric parameters appropriate for icosahedral vertices. To this end, we note that the lowest energy states of icosadeltahedral triangulations of the sphere are found to resemble icosahedra for [21,22], which corresponds to a vertex energy greater than 8Kb with, for instance, a value 12Kb for Γ = 1010. As shown in Table I, this estimate compares quite favorably with the value Gv ≈ 11Kb implied by Eq. (10) for the icosahedron. In the estimates obtained from Eq. (29), the contribution due to stretching, which is not considered in Eq. (10), is approximately equal to 0.65Kb. Thus, the energetic cost associated with bending deformations is seen to dominate over the energetic cost associated with stretching deformations in this regime of Γ. For comparison, we note that for bilayer polyhedra it has been estimated [7] that Γ ≈ 106, which, according to Eq. (29), would leave us with a vertex energy of approximately 6.5Kb.
TABLE I.
Vertex energy in Eq. (10) for homogeneousbilayers, vertex energy in Eq. (23) for perfectly segregated bilayers, conical pore energy in Eq. (14) for the minimum pore radius r = rm, and polygonal pore energy in Eq. (21) for r = 0 in units of monolayer bending modulus for the five Platonic solids with m = 2 nm and h = 0.5 nm [7]. The ranges of and are obtained with and , respectively.
| Platonic solid | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Tetrahedron | 6.6 | 10–15 | 4.9–8.2 | |
| Cube | 3.7 | 8.9–11 | 11–16 | |
| Octahedron | 8.8 | 9.1–12 | 6.6–11 | |
| Dodecahedron | 2.4 | 7.6–8.3 | 16–21 | |
| Icosahedron | 11 | 7.9–8.9 | 8.2–14 |
Note from Table I that the bending energies associated with (closed) conical and polygonal pores take similar values for all Platonic solids, with the competition between pores and closed, homogeneous bilayer vertices governed by the ratio . Using the estimate suggested by experiments [6,7] and simulations [30], we find that closed bilayer vertices will be unstable to the formation of pores for homogeneous amphiphile bilayers. However, Table I also implies that the vertex energy obtained for perfectly segregated bilayers is comparable to the bending energy associated with pores, suggesting that, if the optimal amount of excess amphiphiles is present at polyhedral vertices, closed bilayer vertices may be metastable.
B. Ridge energy
According to computer simulations [21,22], the total energy of icosadeltahedral triangulations of the sphere is dominated by vertex energies for , and only in the regime of very large Γ, where the overall shape becomes increasingly icosahedral, do the contributions of ridges to the overall elastic energy become significant. It was shown by Lobkovsky and Witten [21-24] that, for Γ → ∞, the ridge energy is given by
| (30) |
Allowing the broad ranges and for bilayer polyhedra [42], this implies
| (31) |
which should be compared to Eq. (7). The ridge energies in Eqs. (7) and (31) yield similar results for a unit ridge length, thus confirming the assumption d = 2b made in Sec. III A. However, the estimate of the ridge energy due to Lobkovsky and Witten has a stronger dependence on the dihedral angle, but increases more slowly with Rp. In addition to the ridge energy in Eq. (7), we therefore also consider Eq. (31) when calculating the total elastic energy of bilayer polyhedra in Sec. VI.
V. ANALYSIS OF PORE ENERGIES
In Sec. III C we obtained Eqs. (14) and (21) as the elastic bending energies associated with conical and polygonal pores. The purpose of the present section is to discuss how these pore energies vary with the elastic and geometric parameters characterizing polyhedral bilayer vesicles.
A. Conical pores
Figures 5(a) and 5(b) show plots of the conical pore energy in Eq. (14) as a function of the pore radius for θ = 0 and θ = 0.4π, respectively. The angle θ = 0 corresponds to a flat bilayer, while θ = 0.4π roughly corresponds to the vertex geometry of the tetrahedron. A notable feature of the curves in Fig. 5 is that exhibits a minimum as a function of r. This optimal pore radius arises due to the competition between the standard edge tension of a straight bilayer edge [2] acting along the rim of the pore, which leads to an energy cost increasing linearly with r, and the bending energy associated with closing the pore, which is expected to be large for small pore radii. We can see this more clearly by returning to the Helfrich-Canham-Evans free energy of bending in Eq. (1). For simplicity we set , in which case the “rim contribution” corresponds to the integral over 1/R1 and is given by
| (32) |
with ξ ∝ r, where the principal radii of curvature R1 and R2 are defined in Eqs. (11) and (12), respectively. Similarly, the “loop contribution” is associated with the integral over 1/R2 and evaluates to
| (33) |
Neglecting terms which are constant in r, the sum of and is equal to in Eq. (14) for .
FIG. 5.
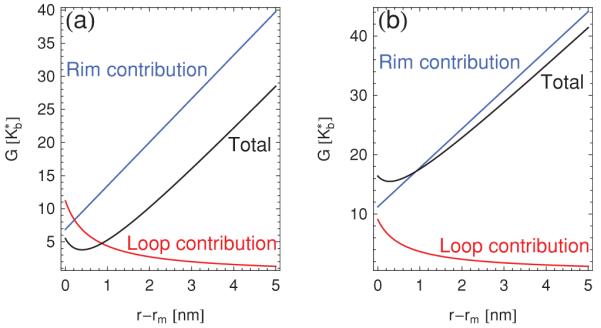
(Color online) Total bending energy of a conical pore in Eq. (14), rim contribution in Eq. (32), and loop contribution in Eq. (33) versus pore radius r for [7] m = 2 nm, h = 0.5 nm, and , with (a) θ = 0 and (b) θ = 0.4π.
Figure 5(a) shows that, in the case θ = 0, the rim and pore contributions to do indeed behave as expected, with increasing linearly with the pore circumference 2πr, and decreasing with increasing r. The sum of and exhibits a minimum as a function of r. As illustrated in Fig. 5(b), these characteristic features persist for θ > 0, with the small r regime () dominated by the nonlinear behavior of the loop contribution to the bending energy, and the large r regime () dominated by the linear behavior of the rim contribution. Considering that the optimal pore radius typically found from Eq. (14) is of the order of 1 nm, which is close to the smallest length scales down to which a description of bilayer pores in terms of continuum elasticity theory can be expected to apply [43], it is questionable [44] whether the optimal pore radius exhibited by conical pores is of physical significance.
Figure 6 compares the pore energies obtained with θ = 0 and θ > 0 for a number of different values of . For the range of spontaneous curvatures considered [7], the pore energy is seen to decrease with increasing monolayer spontaneous curvature. However, for values of the spontaneous curvature much larger () than those in Fig. 6, the rim curvature no longer suffices to relax the spontaneous curvature and the pore energy rises again with increasing . Moreover, from Figs. 5 and 6 we observe the general trend that the conical pore energy is increased relative to the pore energy of a planar bilayer, by up to approximately for the parameter values used in Figs. 5 and 6, with a larger increase in the pore energy corresponding to a smaller apex angle.
FIG. 6.
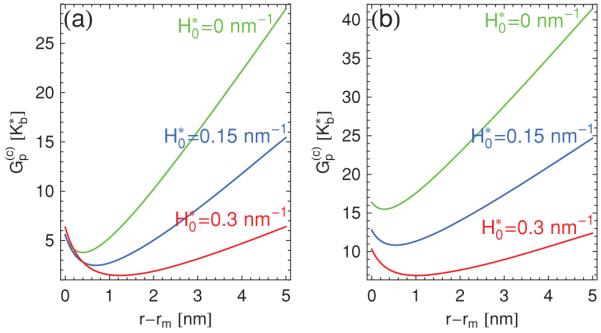
(Color online) Bending energy of a conical pore in Eq. (14) versus pore radius r for [7] m = 2 nm, h = 0.5 nm, and (a) θ = 0 and (b) θ = 0.4π for the indicated values of the monolayer spontaneous curvature .
What is the physical origin of the increase in for θ > 0? Comparing panels (a) and (b) in Figs. 5 and 6 we note that the fractional difference between the pore energies for θ > 0 and θ = 0 is large for small pore radii, but decreases as the pore radius increases. Indeed, the ratio approaches one as r tends to infinity. In order to understand this behavior on a qualitative level, note that rm = 0 for θ = 0, but rm > 0 for θ > 0. In the latter case, if r = rm, the inner sections of the pore “almost” touch, and the loop contribution to the bending energy is large. For θ = 0, however, there is still a pore of finite diameter at r = rm, leading to a correspondingly smaller loop contribution to the bending energy. As r becomes large, and are both increasingly dominated by the rim contribution to the bending energy, and, thus, their ratio as a function of the pore radius approaches one.
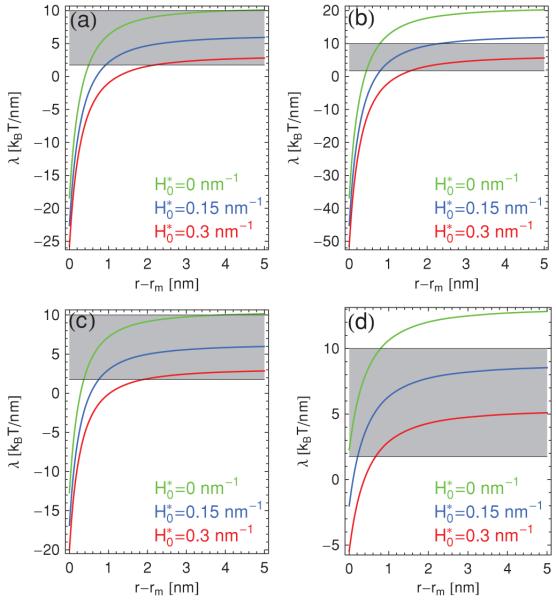
Finally, we use our expression of the pore energy in Eq. (14) to evaluate the edge tension, λ, associated with a conical pore:
| (34) |
Figure 7 shows plots of the edge tension in Eq. (34) as a function of the pore radius and compares the calculated estimates to representative values of λ measured in experiments [2]. Experimental estimates of the edge tension typically rely [2] on measurement of the maximum disk size formed by lipid bilayers, or on measurement of the pore radius in bilayers under tension. Our theoretical estimates of the edge tension vary depending on the choice for the numerical values of and , but are found to be in broad agreement with experimental measurements. A notable discrepancy between theoretical and experimental results is that the edge tension in Eq. (34) depends on r and can even become negative due to the nonmonotonic behavior of the calculated pore energy, while experiments typically report a single (positive) value of the edge tension. This value could be viewed as the asymptotic edge tension obtained in the limit of large r, where the pore energy increases linearly with r and the edge tension is therefore constant. Moreover, we find that the edge tension varies only little with θ [see Figs. 7(a) and 7(c)]. This suggests that a nonzero θ has the primary effect of shifting up the curve for the pore energy, and only marginally distorts the variation of with r, which is also apparent from Figs. 5 and 6. However, changing the (relative) values of m and h does have a pronounced effect on the numerical values of the pore energy as well as on the edge tension [see Figs. 7(a) and 7(d)].
FIG. 7.
(Color online) Edge tension λ in Eq. (34) for a conical pore versus pore radius r for m = 2 nm and (a) θ = 0 and h = 0.5 nm with , (b) θ = 0 and h = 0.5 nm with , (c) θ = 0.4π and h = 0.5 nm with , and (d) θ = 0 and h = 0.8 nm with using for the green (upper) curves, for the blue (middle) curves, and for the red (lower) curves in each panel. The shaded regions of the plots correspond to typical measured values [2] of the edge tension of amphiphile bilayers.
B. Polygonal pores
Figure 8 shows plots of the polygonal pore energy in Eq. (21) as a function of the pore radius r for the vertex geometry of the icosahedron. A notable discrepancy between the polygonal pore energy and the conical pore energy in Eq. (14) is that always increases linearly with r and, hence, does not lead to an optimal pore radius for which the bending energy takes a minimal value. However, Eq. (21) gives a similar range of the pore energy as the corresponding expression for the bending energy of a conical pore. In particular, the asymptotic value of the ratio is equal to the ratio of the pore circumferences in the two models, as indicated in the inset of Fig. 8. Finally, we note from Fig. 8 and Eqs. (18) and (20) that for small pore radii nm the contribution to the polygonal pore energy dominates over the contribution , and vice versa. As a result, for the parameter values in Fig. 8, the polygonal pore energy increases with increasing spontaneous curvature for small pore radii, but decreases with increasing spontaneous curvature for large pore radii.
FIG. 8.
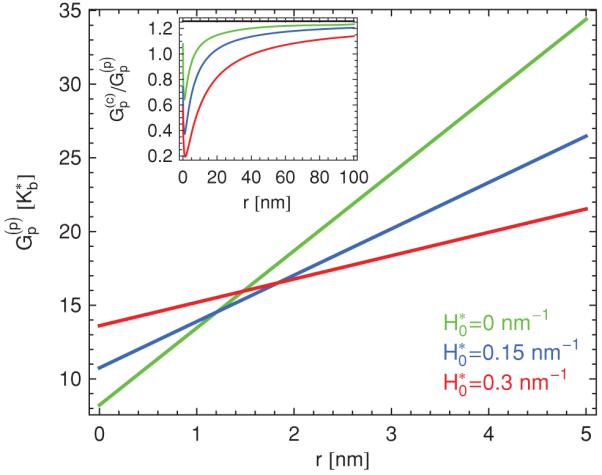
(Color online) Elastic bending energy of a polygonal pore in Eq. (21) versus pore radius r for the icosahedron, and ratio of conical and polygonal pore energies (inset), for [7] m = 2 nm and h = 0.5 nm, using for the green curves (upper curves in the large-r regime), for the blue curves (middle curves in the large-r regime), and for the red curves (lower curves in the large-r regime). The polygonal pore energy is calculated by noting that, for the icosahedron, five ridges meet at each vertex with the face angle βj = π/3. The corresponding conical pore energy is obtained using the vertex angle Ω = 2π − 5 arcsin(2/3) ≈ 2.6 for the icosahedron, which gives θ ≈ 0.2π. The horizontal black line in the inset denotes the ratio of the circumference of conical and polygonal pores, which is equal to for the icosahedron.
VI. POLYHEDRAL BENDING ENERGIES
In this section we evaluate the total bending energies of bilayer polyhedra as a function of the polyhedron radius Rp. As in Secs. III and IV, the polyhedron radius is defined [21] through , where A is the polyhedron area, which is, in turn, proportional to the polyhedron ridge length with a proportionality constant characteristic of the polyhedral geometry. The total bending energies associated with different polyhedral shapes are compared for a fixed area rather than a fixed volume since, as discussed from a theoretical perspective in Sec. IV A and also observed in experiments [6-8], closed bilayer vertices are expected to break up to form pores, thus allowing adjustment of the polyhedron volume for a given number of amphiphiles or fixed surface area. Following Secs. III and IV, polyhedral bending energies involve contributions due to ridges and vertices. The vertex part of the polyhedron bending energy is independent of the polyhedron size and will generally favor bilayer polyhedra which only involve a few vertices. The ridge part of the polyhedron bending energy, however, increases with the polyhedron ridge length and, hence, with the polyhedron radius.
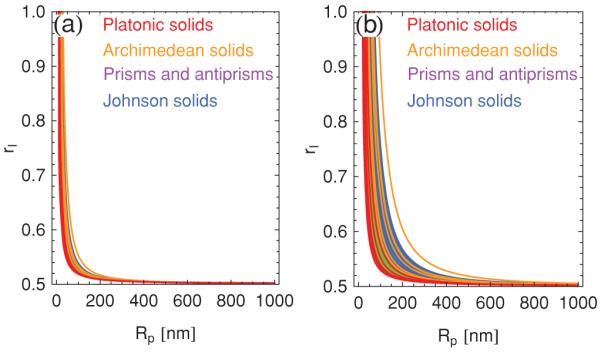
Since ridges impose an energetic cost one expects that, for a fixed area and dihedral angle, the faces of bilayer polyhedra relax to form regular polygons. While there are infinitely many regular convex polygons, there are only five regular convex polyhedra—the Platonic solids, which are vertex-transitive, edge-transitive, and face-transitive [26-28]. Thus, all vertices, ridges, and faces of any given Platonic solid share the same geometric properties relating, for instance, to the values of face and dihedral angles. A natural generalization of the Platonic solids are the semiregular polyhedra, which are vertex-transitive and have regular (but not necessarily congruent) polygons as faces. Apart from the Platonic solids, the semiregular convex polyhedra encompass the 13 Archimedean solids and the two (infinitely large) families of prisms and antiprisms. Relaxing the constraint of vertex transitivity, one obtains the class of convex polyhedra with regular polygons as faces. In addition to the Platonic solids, Archimedean solids, prisms, and antiprisms, this class includes the 92 Johnson solids. It has been shown [45,46] that this list exhausts all convex polyhedra with regular faces.
Thus, counting prisms and antiprisms as one solid each, there are exactly 112 convex polyhedra with regular polygons as faces, and we focus here on this set of polyhedra. As representative examples of convex polyhedra with nonregular polygons as faces we, however, also consider the bending energies of the Catalan solids, which are the duals of the Archimedean solids and, as such, are also highly symmetric. Figure 9 shows examples of polyhedra belonging to the different symmetry classes [26-28,47] we are concerned with here. In particular, Sec. VI A presents results pertaining to the bending energies of homogeneous bilayer polyhedra, and Sec. VI B focuses on the bending energies of bilayer polyhedra exhibiting segregation of excess amphiphiles. Finally, Sec. VI C discusses to what extent our results regarding the minimal bending energies of bilayer polyhedra can be expected to be valid for ridge, vertex, and pore energies which deviate from the elastic models developed in Secs. III and IV.
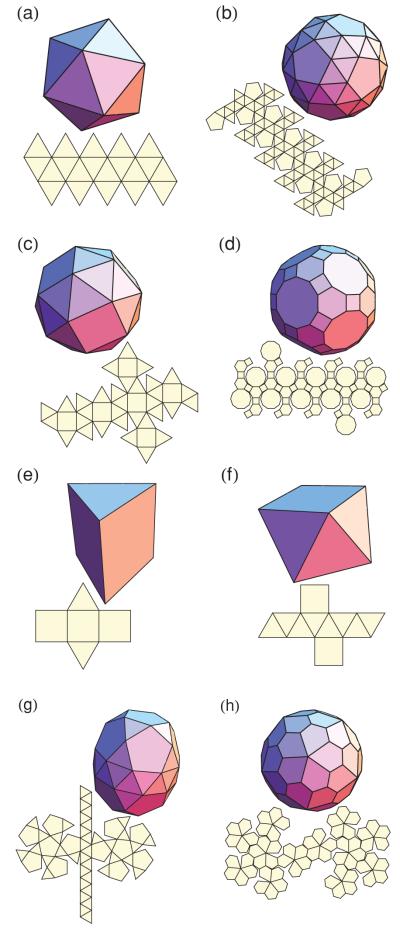
FIG. 9.
(Color online) Image and net representations of (a) the icosahedron, (b) the snub dodecahedron, (c) the snub cube, (d) the great rhombicosidodecahedron, (e) the triangular prism, (f) the square antiprism, (g) the gyroelongated pentagonal birotunda, and (h) the pentagonal hexecontahedron. Polyhedron (a) is a Platonic solid, polyhedra (b), (c), and (d) are Archimedean solids, polyhedron (e) is a prism, polyhedron (f) an antiprism, polyhedron (g) a Johnson solid, and polyhedron (h) a Catalan solid. The Catalan solid in (h) is the dual of the Archimedean solid in (b), and the polyhedra in (b), (c), (g), and (h) are chiral.
A. Homogeneous polyhedra
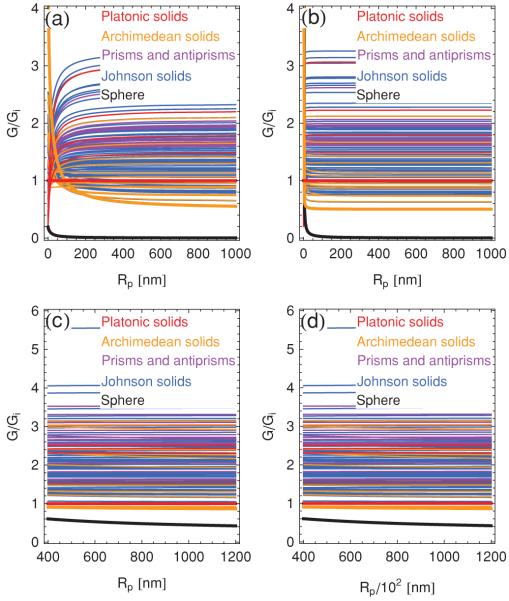
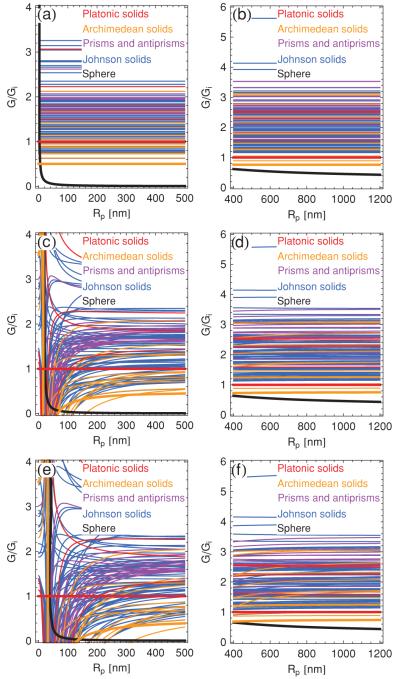
Figure 10 shows the bending energies of the convex polyhedra with regular faces as a function of the polyhedron radius Rp. To begin, consider homogeneous polyhedra with closed bilayer vertices [see Fig. 10(a)]. We calculate the relevant bending energies using the expression in Eq. (7) for the ridge energy and in Eq. (10) for the vertex energy, together with the geometric parameters characterizing the convex polyhedra with regular polygons as faces [26-28,47]. From Fig. 10(a) one finds that spherical bilayer vesicles have a lower bending energy than any of the polyhedral symmetries considered. Moreover, in agreement with a previous study [7], we find that the icosahedron [see Fig. 9(a)] minimizes bending energy among the Platonic solids. However, as shown in Fig. 10(a), the icosahedron does not minimize bending energy if one allows for more general polyhedral symmetries.
FIG. 10.
(Color online) Total bending energies of the convex polyhedra with regular faces, normalized by the bending energy of the icosahedron, Gi, for homogeneous bilayers with (a) the vertex energy in Eq. (10) and the ridge energy in Eq. (7), (b) the polygonal pore energy in Eq. (21) with r = 0 and the ridge energy in Eq. (7), (c) the polygonal pore energy in Eq. (21) with r = 0 and the upper bound Y/Kb = 10 nm−2 on the ridge energy in Eq. (31), and (d) the polygonal pore energy in Eq. (21) with r = 0 and the lower bound Y/Kb = 10−3 nm−2 on the ridge energy in Eq. (31). We use the parameter values [6,7,30] m = 2 nm, h = 0.5 nm, , and . The bold black curve denotes the bending energy of the sphere, and the colored (gray) curves denote the bending energies of bilayer polyhedra, where the bold curve minimizing polyhedral bending energy in the large-Rp regime corresponds to the snub dodecahedron.
As noted above, closed bilayer vertices may break up to form (closed) pores, and the relevant energy curves are displayed in Fig. 10(b). These curves are again obtained with the ridge energy in Eq. (7), but now this expression is combined with the polygonal pore energy in Eq. (21) for r = 0. Although the details of the results in Fig. 10(b) are quantitatively different from those in Fig. 10(a), we again find that in general the sphere is energetically favorable over the convex polyhedra with regular faces, and that the icosahedron does not minimize elastic bending energy among arbitrary polyhedral shapes. Increasing the pore radius does not change these conclusions.
In Figs. 10(c) and 10(d) we plot polyhedral bending energy as a function of Rp using the ridge energy in Eq. (31) and the pore energy in Eq. (21) with r = 0. As mentioned above, simulations suggest [21,22] that, at least for the icosahedron, gives a good description of the ridge energy for . Using the somewhat less stringent criterion Γ > 106, this then implies nm for the upper bound Y/Kb = 10 nm−2 [see Fig. 10(c)]. We also find with this modified expression of the ridge energy that spherical bilayer vesicles have lower bending energy than any polyhedral shape considered, and that the icosahedron does not represent the polyhedral shape with minimal bending energy. Applying the lower bound Y/Kb = 10−3 nm−2 has the effect of shifting the curves for the ridge energy to larger polyhedron radii, and does not modify these conclusions. The corresponding results are shown in Fig. 10(d).
What is the polyhedral shape that minimizes the elastic bending energy among the convex polyhedra with regular faces? As apparent from Fig. 10, the answer to this question will generally depend on the polyhedron size and the particular expression of the polyhedron energy considered. Indeed, in the limit Rp → ∞ the icosahedron only represents the 34th-lowest energy shape for the ridge energy in Eq. (7), but the 3rd-lowest energy shape for in Eq. (31). However, for large enough polyhedron sizes, the snub dodecahedron [see Fig. 9(b)] minimizes polyhedral bending energy for all ridge energies considered in Fig. 10. Moreover, independently of the particular expression of the polyhedral bending energy used, the snub cube [see Fig. 9(c)] also has a lower elastic bending energy than the icosahedron in this limit. For the scenarios considered in panels (a), (b), and (c) of Fig. 10, this asymptotic behavior already manifests itself for the typical polyhedron size Rp ≈ 500 nm observed in experiments [6-10], while the lower bound Y/Kb = 10−3 nm−2 in Fig. 10(d) only applies to polyhedron sizes much larger than the observed size of bilayer polyhedra.
In Fig. 11 we compare the total ridge energies of the 13 Catalan solids to the total ridge energy of the icosahedron as a function of the polyhedron radius. Panel (a) of Fig. 11 is obtained using the ridge energy in Eq. (7), whereas panel (b) corresponds to the ridge energy in Eq. (31) with the upper or, analogously, the lower bound on Y/Kb. Comparison of Fig. 11 with the large-Rp regime in Fig. 10 shows that, as already anticipated on intuitive grounds, the total ridge energies of the Catalan solids are indeed much larger than those of the convex polyhedra with regular polygons as faces.
FIG. 11.
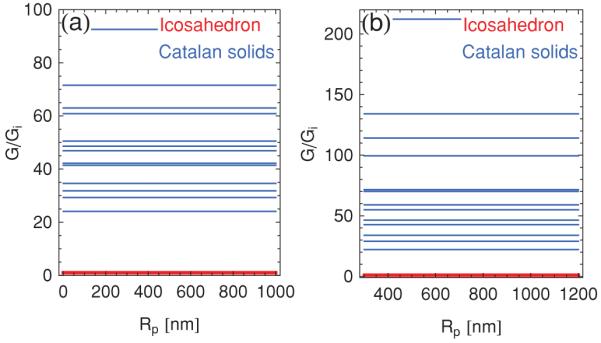
(Color online) Ridge energies of the 13 Catalan solids, normalized by the ridge energy of the icosahedron, Gi, with (a) the ridge energy in Eq. (7), and (b) the upper bound Y/Kb = 10 nm−2 on the ridge energy in Eq. (31).
B. Heterogeneous polyhedra
Perhaps the most basic result of the above analysis of the elastic bending energies of homogeneous bilayer vesicles is that, independently of the particular expression of the polyhedral bending energy considered, spherical bilayer vesicles allow (much) lower bending energies than bilayer polyhedra. However, according to the experimental observations in Refs. [6-8], pores are seeded into bilayers via molecular segregation if there is a slight excess of one amphiphile species over the other. Thus, pores can have a role beyond reducing the elastic bending energy associated with the vertices of bilayer polyhedra. How do the total bending energies of bilayer polyhedra compare to the bending energies of spherical bilayer vesicles having an equal (or greater) number of pores? This question is addressed most conveniently by eliminating the vertex energies altogether and only comparing polyhedral ridge energies to the total elastic energy associated with spherical bilayer vesicles.
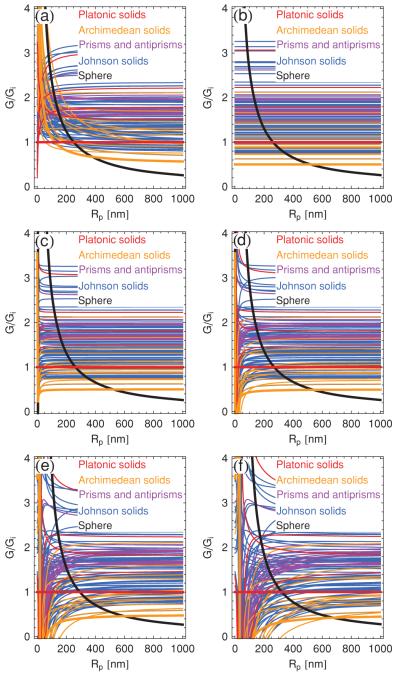
Allowing molecular segregation at pores only, and setting the pore radius equal to zero, we again find that the sphere is energetically favorable over any polyhedral shape for physically relevant values of the polyhedron radius [see Figs. 12(a) and 12(b)]. This conclusion holds for the ridge energy in Eq. (7) [see Fig. 12(a)] as well as for the ridge energy in Eq. (31) [see Fig. 12(b)]. Furthermore, Figs. 12(a) and 12(b) imply that, even if there is no energetic cost associated with the vertices of polyhedral bilayer vesicles, spherical bilayer vesicles are still energetically favorable. The latter point is particularly relevant considering that, in analogy to pores forming in planar membranes [38], the conical and polygonal pore geometries we have considered here may not represent general minima of polyhedral pore energies.
FIG. 12.
(Color online) Total bending energies of the convex polyhedra with regular faces, normalized by the bending energy of the icosahedron, Gi, with segregation of excess amphiphiles at vertices but not at ridges. The energy curves are obtained with the ridge energy in Eq. (7) [panels (a), (c), and (e)] and the upper bound Y/Kb = 10 nm−2 on the ridge energy in Eq. (31) [panels (b), (d), and (f)] with pores of radius (a), (b) r = 0, (c), (d) r = 20 nm, and (e), (f) r = 40 nm at each vertex. The bold black curve=denotes the bending energy of the sphere, and the colored (gray) curves denote the bending energies of bilayer polyhedra, where the bold curve minimizing polyhedral bending energy in the large-Rp regime corresponds to the snub dodecahedron.
Figures 12(c) and 12(d) and Figs. 12(e) and 12(f) show the bending energies of bilayer polyhedra with molecular segregation at pores of radius r = 20 nm and r = 40 nm, respectively, using the ridge energies in Eq. (7) and in Eq. (31). The plots in Figs. 12(c) and 12(d) thereby correspond to the typical polyhedra (Rp ≈ 500 nm) and pore (r ≈ 20 nm) sizes reported in Refs. [6-10]. We note that the polyhedral ridge length decreases with increasing r, leading to a reduction in the polyhedral ridge energy. Hence, we expect that the total polyhedral ridge energy decreases with increasing r and, indeed, approaches zero as 2r approaches the ridge length. This is borne out by the results in Fig. 12. However, the results in Fig. 12 also suggest that, for bilayer polyhedra which only exhibit molecular segregation at vertices, the regime for which polyhedral bending energies are smaller than the bending energy of the sphere is, at best, very narrow. Thus, molecular segregation of excess amphiphiles at polyhedral vertices is not expected to be sufficient to stabilize polyhedral bilayer vesicles over spherical bilayer vesicles, even in the somewhat artificial limit of molecular segregation at pores which are very large in relation to the total polyhedron size.
Figure 13 shows the elastic bending energies of the convex polyhedra with regular faces obtained with the ridge energy in Eq. (22) for perfect molecular segregation along ridges. First, consider the case in which there is molecular segregation at ridges, but not at pores [see Fig. 13(a)]. Using the pore energy in Eq. (21) with r = 0, we find a pronounced regime for which polyhedral bilayer vesicles are energetically favorable over spherical bilayer vesicles (). For small Rp there is a narrow regime for which the icosahedron is the polyhedral shape with minimal bending energy, while there are more prominent regimes at larger polyhedron sizes for which the snub cube and the snub dodecahedron are the polyhedral shapes minimizing bending energy. Thus, molecular segregation along ridges is found to be crucial for the stabilization of polyhedral bilayer vesicles over spherical bilayer vesicles.
FIG. 13.
(Color online) Total bending energies of the convex polyhedra with regular faces, normalized by the bending energy of the icosahedron, Gi, with segregation of excess amphiphiles at ridges but not pores [panel (a)], and at ridges and pores [panels (b)–(f)]. For panel (a) we use the pore energy in Eq. (21) with r 0 and the ridge energy in Eq. (22) with the parameter values [6,7,30] m = 2 nm, h = 0.5 nm, , and . The remaining panels are obtained using only the ridge=energy in Eq. (22) with pores of radius (b) r = 0, (c) r = 1 nm, (d) r = 5 nm, (e) r = 20 nm, and (f) r = 40 nm. The bold black curve =denotes the bending energy of the sphere, and the colored (gray) curves denote the bending energies of bilayer polyhedra, where the bold curve minimizing polyhedral bending energy in the large-Rp regime corresponds to the snub dodecahedron.
Allowing molecular segregation at pores as well as ridges, one obtains [48] the total polyhedral bending energies shown in Figs. 13(b)–13(f). We find a pronounced regime nm for which polyhedral bilayer vesicles are energetically favorable compared to spherical bilayer vesicles if the same number of pores is seeded into all vesicles. The polyhedral shape which generally minimizes elastic bending energy for the typical polyhedron size Rp ≈ 500 nm and pore size r ≈ 20 nm observed in experiments [6-10] is the snub dodecahedron. Moreover, for large pore radii a sequence of polyhedral shapes with minimal bending energy is obtained as a function of pore radius. The most notable of these polyhedral shapes is the great rhombicosidodecahedron [see Fig. 9(d)], which surpasses the snub dodecahedron in bending energy at Rp ≈ 300 nm [Fig. 13(e)] or at Rp ≈ 600 nm [Fig. 13(f)].
As discussed in Sec. III D, the model ≈ of perfect molecular segregation used for Figs. 12 and 13 allows us to obtain a phenomenological estimate of the optimal amount of excess amphiphiles for a given polyhedral shape and size. Figure 14 shows plots of the ratio of the amphiphile species in excess to the total amphiphile content as a function of the polyhedron radius Rp for the convex polyhedra with regular polygons as faces. For the typical polyhedron radius Rp ≈ 500 nm and pore radius r ≈ 20 nm observed in experiments [6-10] we find rI ≈ 0.51 as the optimal imbalance in the concentrations of the two amphiphile species. The corresponding experimental estimate is rI ≈ 0.57 [6,7]. We expect that in experiments not all excess amphiphiles are segregated along the ridges and vertices of polyhedra as a result of, for instance, entropic mixing within bilayer polyhedra or the formation of micelles [7]. Thus, our theoretical estimate of rI is in reasonable accord with the experimental results given the level of approximation involved in making such estimates.
FIG. 14.
(Color online) Theoretical estimates of the optimal amphiphile imbalance rI, defined in Eq. (24), for the convex polyhedra with regular faces as a function of the polyhedron radius Rp with [7] m = 2 nm for (a) r = 0 nm and (b) r = 20 nm.
C. Generalized ridge energy
In Secs. VI A and VI B we found that, for large enough polyhedron sizes, the snub dodecahedron minimizes bending energy among the convex polyhedra with regular polygons as faces. This result was obtained with the heuristic expressions of the ridge energy in Eqs. (7) and (22), and also with the limiting expression of the ridge energy in Eq. (31). Does this conclusion regarding the polyhedral shape with minimal bending energy also hold for more general expressions of the ridge energy? To address this question, consider ridge energies of the form
| (35) |
with p = 2 and q = 1 corresponding to Eqs. (7) and (22), and p = 7/3 and q = 1/3 corresponding to Eq. (31). As before, we seek the minimum energy shape among the convex polyhedra with regular faces, but now as a function of p and q. Numerically one finds that, if q is chosen small () or large () enough, one can have with the snub dodecahedron no longer being the minimum energy shape.
What physical scenarios could lead to a ridge energy with values of p and q so that the snub dodecahedron does not correspond to the most favorable polyhedral shape? As discussed in Secs. III and IV, the available expressions of the ridge energy obtained from elasticity theory firmly lie within the regime for which the snub dodecahedron minimizes elastic bending energy for large polyhedron sizes. However, segregation of excess amphiphiles implies that bilayer polyhedra are locally charged. Hence, electrostatic interactions could, in principle, affect the symmetry of bilayer polyhedra [6,7] and modify the ridge energy [49-51]. In Appendix B we provide a simple example of how electrostatic interactions could lead to an expression of the ridge energy which is qualitatively different from the elastic ridge energies considered in Secs. III and IV, resulting in a polyhedron other than the snub dodecahedron as the energetically most favorable polyhedral shape for large vesicle sizes.
VII. DISCUSSION
In agreement with expectations based on the classic framework for describing and predicting vesicle shape [1-4], our calculations imply that vesicles with smooth curvature are favorable over polyhedral vesicles for bilayers of uniform composition. However, allowing for molecular segregation of excess amphiphiles with high spontaneous curvature we find, consistent with the experimental phenomenology of bilayer polyhedra [6-10], that polyhedral bilayer vesicles can have lower elastic bending energies than spherical bilayer vesicles. Furthermore, on the basis of our calculations we expect bilayer vertices to be unstable to the formation of (closed) pores. Again, this result is in agreement with experimental observations [6-8] and suggests that bilayer polyhedra are permeable.
According to our theoretical analysis, the mechanism lowering the bending energies of certain polyhedral bilayer vesicles below the bending energy of spherical bilayer vesicles is segregation of excess amphiphiles along the ridges of bilayer polyhedra as observed in Ref. [7]. Segregation at pores, which was originally suggested in Ref. [6] as a potential mechanism stabilizing polyhedral vesicle shapes, is not sufficient to produce polyhedra with bending energies which are favorable compared to the sphere for the typical size of bilayer polyhedra observed in experiments [6-10]. Moreover, independent of the particular expressions of ridge, vertex, and pore energies used, we find that the icosahedron does not minimize bending energy among arbitrary polyhedral shapes and sizes. In fact, for large enough polyhedron sizes, the snub dodecahedron is the polyhedral shape minimizing bending energy among the convex polyhedra with regular faces, and the snub cube also has a lower bending energy than the icosahedron in this limit. This result can be understood on a qualitative level as arising from a trade-off between reduction of the total ridge energy via a decrease in the total ridge length, and an accompanying decrease in the dihedral angles associated with ridges, which in turn leads to an increase in the density of the ridge energy.
What sets the characteristic range of polyhedron sizes observed in experiments [6-10]? As noted above, molecular segregation along ridges is crucial for the stabilization of bilayer polyhedra. For molecular segregation to significantly lower the elastic bending energy of bilayer polyhedra, there must be a sufficient number of excess amphiphiles to line polyhedral ridges [52]. However, while the polyhedral ridge length increases linearly with the polyhedron radius Rp, the number of excess amphiphiles increases quadratically with Rp. In contrast, the bending energy of spherical bilayer vesicles is, to a first approximation, independent of Rp. Thus, we speculate that the characteristic range of polyhedron sizes observed in experiments roughly corresponds to the maximum polyhedron size which still gives a lower total bending energy than the sphere. Following this simple heuristic argument, one obtains from Fig. 13 the characteristic polyhedron size Rp ≈ 400–600 nm, which lies at the lower end of the range of polyhedron sizes reported in Refs. [6-10].
Our comparisons between the total elastic bending energies of polyhedral and spherical bilayer vesicles relied crucially on the ridge energies in Eqs. (7), (22), and (31), respectively. The first two of these expressions involve the parameter d corresponding to the arc length suspended by a ridge. We fixed this parameter, and an analogous parameter appearing in the vertex energy in Eq. (10), by assuming that ridges bend over a spatial scale corresponding to only two interamphiphile spacings. Such molecularly sharp ridges are consistent with a polyhedral vesicle shape. Also, with this choice of d, Eqs. (7) and (22) are in broad agreement with the ridge energy in Eq. (31) obtained [21-24] for a diverging Föppl-von Kármán number. However, one might question the validity of the Helfrich-Canham-Evans free energy of bending for ridge and vertex geometries exhibiting large local curvature. Atomistic simulations [30,43,53] would potentially allow the systematic investigation of the limitations of the simple continuum models of polyhedral ridges and vertices used here.
A more gradual bending of the amphiphile bilayer along ridges than assumed in Eqs. (7), (22), and (31) would reduce the density of ridge energies. This, in turn, could potentially stabilize faceted vesicles for polyhedron sizes larger than the maximum polyhedron radii implied by our analysis. Experimental results obtained on the basis of electron and light microscopy indeed suggest [6-10] that larger sizes of faceted vesicles may be stable and that these vesicles exhibit ridges and vertices which bend more gradually than in the case of truly polyhedral vesicles. However, the quantitative description of such faceted vesicles calls for interacting ridge and vertex geometries, which we did not consider in our simple elastic models of polyhedral ridges and vertices. Moreover, a more comprehensive understanding of the characteristic range of polyhedron sizes will, among other things, necessitate a quantitative description of the formation of bilayer polyhedra from spherical bilayer vesicles [6-10] during the cooling down process. Such a description of kinetic effects [30,53] will also be necessary to predict the distribution of the symmetries and sizes of polyhedral bilayer vesicles and may shed light on the mechanism leading to the segregation of excess amphiphiles.
Our investigation of the elastic energy of polyhedral bilayer vesicles was motivated by the proposal [7] that the shape of bilayer polyhedra is governed by minimization of elastic bending energy. The resulting expressions of the total polyhedral bending energy are obtained from simple models based on continuum elasticity theory and do not consider the details of molecular interactions between amphiphiles. An approach complementary to the one developed here would therefore account for specific molecular structures [54] of amphiphile bilayers. In particular, as far as the symmetry of polyhedral bilayer vesicles is concerned, an intriguing possibility is that optimal tilt angles between amphiphiles, which have been reported for a variety of lipid species [55], might influence the packing of amphiphiles along polyhedral vertices and ridges and, hence, affect the preferred vertex and ridge geometries. While such a detailed study of the molecular structure of bilayer polyhedra is beyond the scope of the present article, we note that a molecular-level approach is expected to suggest descriptions of amphiphile segregation superior to the simple models of perfect segregation of excess amphiphiles employed here (see, for instance, Fig. 4), and permit a more realistic representation of the amphiphile species used in experimental investigations of bilayer polyhedra [6-10].
It is instructive to compare the results presented here to recent theoretical studies carried out in the contexts of two-dimensional superconductors with vortices [12], viral capsids [13,14], and the buckling of ionic shells [15], which all employed approaches complementary to ours. In agreement with our analysis, these studies suggest that the elastic energies of chiral shapes such as the snub dodecahedron and the snub cube can be favorable compared to the icosahedron [12-14] and that, even if the icosahedral shape is imposed, the minimum energy structure may still be chiral [15]. In our analysis we followed the experimental phenomenology of bilayer polyhedra [6-10] and focused on contributions to the elastic bending energy captured by the mean curvature. Thus, we neglected other contributions to the free energy of bilayer polyhedra stemming, for instance, from the Gaussian curvature, electrostatic interactions, or entropy loss due to molecular segregation. These other contributions to the free energy, as well as kinetic effects [30,53] and the detailed molecular structure of amphiphile bilayers [54,55] at polyhedral vertices and ridges, could potentially modify the preferred vesicle shape and polyhedral symmetry.
VIII. SUMMARY AND CONCLUSIONS
In this article we explored the total elastic bending energy of polyhedral bilayer vesicles [6-10]. Due to current experimental uncertainties regarding the physical properties of bilayer polyhedra, we did not attempt to make accurate estimates of the absolute values of polyhedral bending energies. Instead, we made general predictions pertaining to the most favorable polyhedral symmetries, and to the competition between polyhedral and spherical bilayer vesicles. Our results only rely on broad assumptions concerning the mechanical properties of bilayer polyhedra and the applicability of the Helfrich-Canham-Evans free energy of bending [17-19] at the ridges and vertices of bilayer polyhedra. We assessed the validity of these phenomenological expressions of ridge and vertex energies by making comparisons to solutions of the two-dimensional equations of elasticity obtained previously [20-25] for polyhedral ridges and vertices in certain limiting cases.
In agreement with experiments on polyhedral bilayer vesicles [6-10], we find that bilayer polyhedra can indeed be energetically favorable compared to spherical bilayer vesicles if one allows for molecular segregation of excess amphiphiles along the ridges of bilayer polyhedra. Furthermore, our calculations suggest that closed bilayer vertices may break up to form pores, which is also consistent with experimental observations [6-8]. However, our analysis implies that, contrary to what has been suggested on the basis of experiments [6,7], the icosahedron does not represent the polyhedral shape with minimal bending energy among arbitrary polyhedral shapes and sizes. Using a variety of different expressions of polyhedral bending energy we find that, for large polyhedron sizes, the snub dodecahedron and the snub cube have lower total bending energies than the icosahedron. Our results suggest revisiting the symmetry of polyhedral bilayer vesicles, and the possible mechanisms governing their formation, in greater experimental detail.
ACKNOWLEDGMENTS
This work was supported by a Collaborative Innovation Award of the Howard Hughes Medical Institute, and the National Institutes of Health through NIH Award No. R01 GM084211 and the Director’s Pioneer Award. We thank A. Agrawal, M. D. Betterton, M. B. Jackson, W. S. Klug, R. W. Pastor, T. R. Powers, D. C. Rees, M. H. B. Stowell, D. P. Tieleman, T. S. Ursell, D. Van Valen, and H. Yin for helpful comments.
APPENDIX A: EVALUATION OF CONICAL PORE ENERGY
Substituting Eqs. (11)–(13) into the Helfrich-Canham-Evans free energy of bending in Eq. (1) one obtains an integral over ω with the integrand composed of a sum of terms proportional to cos(|ω| ± θ)/R2, cos(|ω| ± θ), and cos(|ω| ± θ)R2. The integrals corresponding to the latter two terms can be evaluated by elementary methods. To evaluate the terms with integrands of the form cos(|ω| ± θ)/R2 we note that
| (A1) |
and complete the square in the numerator on the right-hand side of the above equation. We then use the results [56]
| (A2) |
valid for ξ2 > 1, and
| (A3) |
valid for ξ − cos x ≠ 0, to arrive at Eq. (14).
APPENDIX B: ELECTROSTATIC RIDGE ENERGY
Betterton and Brenner [49] analyzed the effect of electrostatics on the stability of planar membranes of fixed area. Assuming that the surface charge density is constant, the total charge contained in the screening cloud surrounding the membrane in solution is also constant. However, the volume of the screening cloud depends on the membrane geometry. In particular, formation of pores increases the volume accessible to counterions, thus leading to an increase in entropy compared to planar membranes. The gain in free energy due to pore formation can be quantified [49] by noting that, for r ⪡ λD, where r is the pore radius and λD is the Debye length, the screening cloud gains a volume 2πλDr2 through pore formation. Similarly, for r ⪢ λD, the volume change is . Approximating the strength of the electrostatic field in the screening cloud by E = σ/∊0D, where σ is the surface charge density, ∊0 is the electric constant, and D is the dielectric constant, one therefore expects an energy decrease of
| (B1) |
in which we have set the energy density of the electrostatic field equal to .
The heuristic estimates in Eq. (B1) are confirmed [49] by solving the Debye-Hückel equation for a pore in a charged membrane. The electrostatic contributions to the free energy in Eq. (B1) are in competition with the energy penalty imposed by line tension along the pore edge. As shown in Sec. V, the elastic pore energy is approximately linear in the pore radius beyond r ≈ 2 nm. Thus, in principle there could be a regime for which pores of a finite radius are stable due to the competition between elastic and electrostatic contributions to the free energy, although attaining such a regime would require [49] delicate adjustment of the various elastic and electrostatic parameters.
Based on the picture [49] outline above, we can obtain a heuristic expression of the electrostatic ridge energy. Describing a ridge as a bilayer bending by an angle π − αi around a cylinder of radius R1 with charged amphiphiles in the outer membrane leaflet only (see Fig. 4), the volume of the screening cloud associated with a ridge of length li is approximately given by
| (B2) |
where, based on the experimental observations in Refs. [6,7], we have assumed that λD ⪢ m. Thus, one finds that the electrostatic energy is decreased by
| (B3) |
through the formation of a ridge. In contrast to elastic ridge energies, the polyhedral shape with the most favorable electrostatic ridge energy maximizes, for R1 ⪡ λD, within this heuristic picture. Among the convex polyhedra with regular polygons as faces, this is achieved by the gyroelongated square dipyramid shown in Fig. 15, while the snub dodecahedron produces a somewhat smaller value of than the icosahedron. However, based on the experimental phenomenology of bilayer polyhedra, electrostatic contributions to the free energy are expected [7] to be negligible compared to elastic contributions. Furthermore, it is questionable whether the assumption of a constant overall charge holds for bilayer polyhedra, and whether the mean-field picture invoked here represents a good approximation of the energetics governing the narrow counterion clouds surrounding polyhedral ridges.
FIG. 15.
(Color online) Image and net representations of the gyroelongated square dipyramid.
References
- [1].Safran SA. Statistical Thermodynamics of Surfaces, Interfaces, and Membranes. Westview Press; Boulder: 2003. [Google Scholar]
- [2].Boal D. Mechanics of the Cell. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 2002. [Google Scholar]
- [3].Phillips RB, Kondev J, Theriot J. Physical Biology of the Cell. Garland Science; New York: 2009. [Google Scholar]
- [4].Seifert U. Adv. Phys. 1997;46:13. [Google Scholar]
- [5].Lim G, Wortis HWM, Mukhopadhyay R. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2002;99:16766. doi: 10.1073/pnas.202617299. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [6].Dubois M, Demé B, Gulik-Krzywicki T, Dedieu J-C, Vautrin C, Désert S, Perez E, Zemb T. Nature (London) 2001;411:672. doi: 10.1038/35079541. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [7].Dubois M, Lizunov V, Meister A, Gulik-Krzywicki T, Verbavatz JM, Perez E, Zimmerberg J, Zemb T. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:15082. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0400837101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [8].Glinel K, Dubois M, Verbavatz J-M, Sukhorukov GB, Zemb T. Langmuir. 2004;20:8546. doi: 10.1021/la049328m. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [9].Meister A, Dubois M, Belloni L, Zemb T. Langmuir. 2003;19:7259. [Google Scholar]
- [10].Vautrin C, Zemb T, Schneider M, Tanaka M. J. Phys. Chem. B. 2004;108:7986. [Google Scholar]
- [11].Haselwandter CA, Phillips R. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2010;105:228101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.105.228101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [12].Dodgson MJW. J. Phys. A. 1996;29:2499. [Google Scholar]
- [13].Bruinsma RF, Gelbart WM, Reguera D, Rudnick J, Zandi R. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2003;90:248101. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.90.248101. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [14].Zandi R, Reguera D, Bruinsma RF, Gelbart WM, Rudnick J. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2004;101:15556. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0405844101. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [15].Vernizzi G, Olvera de la Cruz M. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2007;104:18382. doi: 10.1073/pnas.0703431104. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [16].Levandovsky A, Zandi R. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2009;102:198102. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.102.198102. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [17].Canham PB. J. Theor. Biol. 1970;26:61. doi: 10.1016/s0022-5193(70)80032-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [18].Helfrich W, Naturforsch Z. 1973;28:693. doi: 10.1515/znc-1973-11-1209. C. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [19].Evans E. Biophys. J. 1980;14:923. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(74)85959-X. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [20].Seung HS, Nelson DR. Phys. Rev. A. 1988;38:1005. doi: 10.1103/physreva.38.1005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [21].Lidmar J, Mirny L, Nelson DR. Phys. Rev. E. 2003;68:051910. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.68.051910. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [22].Nguyen TT, Bruinsma RF, Gelbart WM. Phys. Rev. E. 2005;72:051923. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.72.051923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [23].Lobkovsky AE. Phys. Rev. E. 1996;53:3750. doi: 10.1103/physreve.53.3750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [24].Lobkovsky AE, Witten TA. Phys. Rev. E. 1997;55:1577. [Google Scholar]
- [25].DiDonna BA. Phys. Rev. E. 2002;66:016601. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.66.016601. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [26].Coxeter HSM. Introduction to Geometry. 2nd ed. Wiley & Sons; New York: 1980. [Google Scholar]
- [27].Cromwell PR. Polyhedra. Cambridge University Press; Cambridge: 1997. [Google Scholar]
- [28].Weisstein ER. 2009 http://mathworld.wolfram.com.
- [29].Zemb T, Dubois M, Demé B, Gulik-Krzywicki T. Science. 1999;283:816. doi: 10.1126/science.283.5403.816. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [30].Hartmann MA, Weinkamer R, Zemb T, Fischer FD, Fratzl P. Phys. Rev. Lett. 2006;97:018106. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.97.018106. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [31].Winterhalter M, Helfrich W. J. Phys. Chem. 1988;92:6865. [Google Scholar]
- [32].Pincus P, Joanny J-F, Andelman D. Europhys. Lett. 1990;11:763. [Google Scholar]
- [33].Winterhalter M, Helfrich W. J. Phys. Chem. 1992;96:327. [Google Scholar]
- [34].Brotons G, Dubois M, Belloni L, Grillo I, Narayanan T, Zemb T. J. Chem. Phys. 2005;123:024704. doi: 10.1063/1.1950667. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [35].Kawakatsu T. Statistical Physics of Polymers: An Introduction. Springer-Verlag; Berlin: 2004. [Google Scholar]
- [36].The ridge energies in Eqs. (2) and (3) of Ref. [7] appear to contain typos: In the notation of Ref. [7], α should be replaced with π − α, and kc must be the bending modulus per unit length.
- [37].Chizmadzhev YA, Cohen FS, Shcherbakov A, Zimmerberg J. Biophys. J. 1995;69:2485. doi: 10.1016/S0006-3495(95)80119-0. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [38].Jackson MB. J. Membr. Biol. 2009;231:101. doi: 10.1007/s00232-009-9209-x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [39].Landau LD, Lifshitz EM. Theory of Elasticity. 2nd English ed. Pergamon Press; New York: 1970. [Google Scholar]
- [40].Bowick MJ, Nelson DR, Travesset A. Phys. Rev. B. 2000;62:8738. [Google Scholar]
- [41].Bowick MJ, Cacciuto A, Nelson DR, Travesset A. Phys. Rev. B. 2006;73:024115. [Google Scholar]
- [42].These broad ranges are estimated on the basis of Refs. [7,30], which give the values Kb ≈ 103kBT and Y ≈ 0.4 J/m2 = 102kBT/nm2 for 1kBT = 4 × 10−21 J at T = 300 K.
- [43].Wohlert J, de Otter WK, Edholm O, Briels WJ. J. Chem. Phys. 2006;124:154905. doi: 10.1063/1.2171965. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [44].The corresponding plots of the pore energy for θ = 0 and resulting estimates of the optimal pore radius in Refs. [7,8] do not seem to be correct.
- [45].Berman M. J. Franklin Inst. 1971;291:329. [Google Scholar]
- [46].Johnson NW. Can. J. Math. 1966;18:169. [Google Scholar]; Zalgaller VA. Sem. in Math. Vol. 2, Steklov Math. Institute, Leningrad (1967) Consultants Bureau; New York: 1969. English translation. [Google Scholar]
- [47].mathematica 7.0. Wolfram Research, Inc.; Urbana-Champaign, IL: [Google Scholar]
- [48].Figure 13(b) corresponds to Fig. 2(a) of Ref. [11], and Fig. 13(e) corresponds to Fig. 2(b) of Ref. [11].
- [49].Betterton MD, Brenner MP. Phys. Rev. Lett. 1999;82:1598. [Google Scholar]
- [50].Mbamala EC, Fahr A, May S. Langmuir. 2006;22:5129. doi: 10.1021/la060180b. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [51].Mengistu DH, May S. Eur. Phys. J. E. 2008;26:251. doi: 10.1140/epje/i2007-10319-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [52].For a large excess of one amphiphile species over the other, no closed vesicles are obtained [7].
- [53].Noguchi H. Phys. Rev. E. 2003;67:041901. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevE.67.041901. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [54].Nagle JF, Tristram-Nagle S. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2000;1469:159. doi: 10.1016/s0304-4157(00)00016-2. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- [55].Small DM. The Physical Chemistry of Lipids. Plenum Press; New York: 1986. [Google Scholar]
- [56].Gradshteyn IS, Ryzhik IM. Table of Integrals, Series, and Products. 4th ed. Academic Press; 1980. [Google Scholar]