Abstract
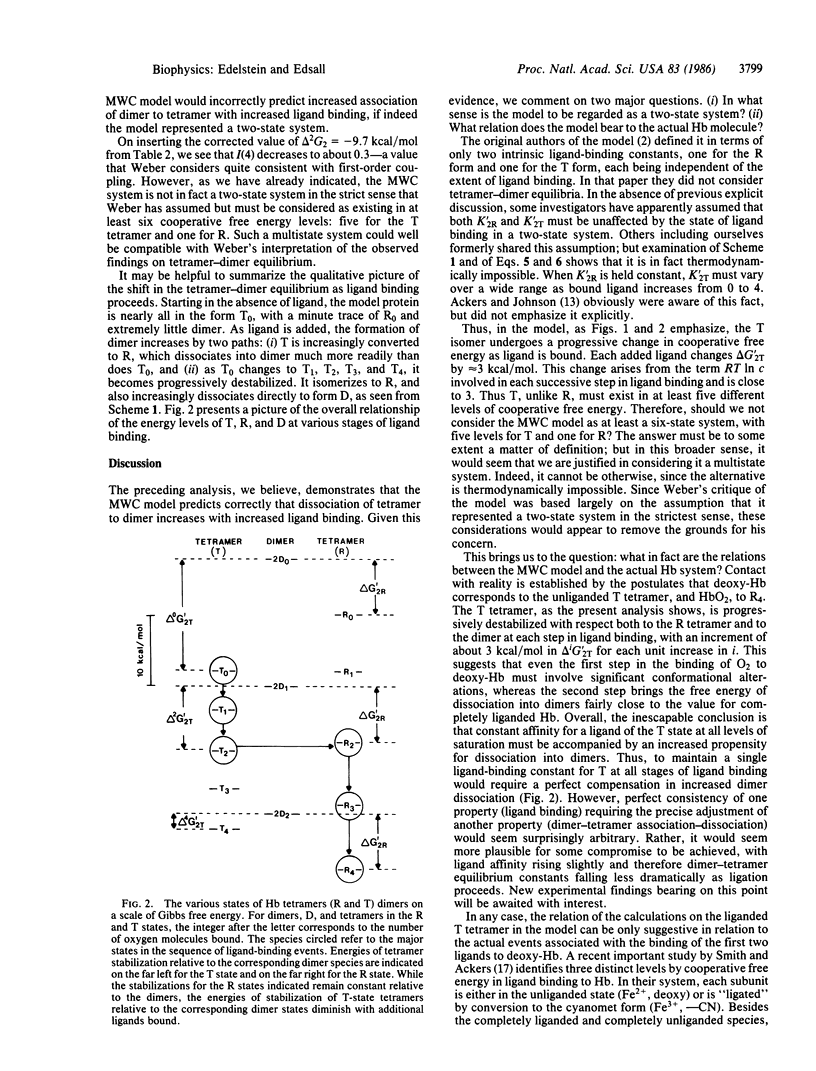
G. Weber [(1984) Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 81, 7098-7102] has inferred that the Monod-Wyman-Changeux (MWC) model for ligand binding by hemoglobin would require (contrary to experimental evidence) that increased ligand binding must promote stabilization of alpha 2 beta 2 tetramers with respect to dissociation into alpha beta dimers. Reexamination of the MWC model, however, in the light of general linkage principles and the specific analysis by G. K. Ackers and M. L. Johnson [(1981) J. Mol. Biol. 147, 559-582] shows that the opposite relation must hold, in agreement with experiment. The T form of the tetramer, with low ligand affinity, must be destabilized and progressively dissociates into the high-affinity dimers, designated D, as ligand binding increases. Each ligand molecule bound shifts the standard Gibbs free energy delta G2T for the D-T equilibrium by approximately 3 kcal/mol in favor of the dimer. Thus, T must exist in (at least) five delta G levels of cooperative free energy as it becomes progressively destabilized by successive binding of ligand molecules. Dissociation of the R tetramer to dimers, in contrast, is independent of the amount of ligand bound, so long as dimers and R-state tetramers possess the same (high) affinity for ligand. While the intrinsic ligand-binding constants of the T and R states (KT and KR) remain unchanged throughout by the postulates of the model, the model should not be regarded as a strictly two-state system in view of the multiple free-energy levels indicated above. The present analysis gives approximate, though not precise, agreement with experimental findings on the dimer-tetramer equilibrium considered by Weber and provides a rationale for interpreting other recent experiments concerning this equilibrium.
Full text
PDF



Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ackers G. K., Johnson M. L. Linked functions in allosteric proteins. Extension of the concerted (MWC) model for ligand-linked subunit assembly and its application to human hemoglobins. J Mol Biol. 1981 Apr 25;147(4):559–582. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(81)90400-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Anderson L. Intermediate structure of normal human haemoglobin: methaemoglobin in the deoxy quaternary conformation. J Mol Biol. 1973 Sep 25;79(3):495–506. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(73)90401-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Antonini E., Ascoli F., Brunori M., Chiancone E., Verzili D., Morris R. J., Gibson Q. H. Kinetics of ligand binding and quaternary conformational change in the homodimeric hemoglobin from Scapharca inaequivalvis. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jun 10;259(11):6730–6738. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J. M. Structure and function of haemoglobin. Prog Biophys Mol Biol. 1975;29(3):225–320. doi: 10.1016/0079-6107(76)90024-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baldwin J., Chothia C. Haemoglobin: the structural changes related to ligand binding and its allosteric mechanism. J Mol Biol. 1979 Apr 5;129(2):175–220. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(79)90277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brzozowski A., Derewenda Z., Dodson E., Dodson G., Grabowski M., Liddington R., Skarzyński T., Vallely D. Bonding of molecular oxygen to T state human haemoglobin. Nature. 1984 Jan 5;307(5946):74–76. doi: 10.1038/307074a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein S. J. Cooperative interactions of hemoglobin. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:209–232. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001233. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelstein S. J. Extensions of the allosteric model for haemoglobin. Nature. 1971 Mar 26;230(5291):224–227. doi: 10.1038/230224a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gelin B. R., Lee A. W., Karplus M. Hemoglobin tertiary structural change on ligand binding. Its role in the co-operative mechanism. J Mol Biol. 1983 Dec 25;171(4):489–559. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(83)90042-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hofrichter J., Sommer J. H., Henry E. R., Eaton W. A. Nanosecond absorption spectroscopy of hemoglobin: elementary processes in kinetic cooperativity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Apr;80(8):2235–2239. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.8.2235. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hopfield J. J., Shulman R. G., Ogawa S. An allosteric model of hemoglobin. I. Kinetics. J Mol Biol. 1971 Oct 28;61(2):425–443. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(71)90391-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- MONOD J., WYMAN J., CHANGEUX J. P. ON THE NATURE OF ALLOSTERIC TRANSITIONS: A PLAUSIBLE MODEL. J Mol Biol. 1965 May;12:88–118. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(65)80285-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Ackers G. K. Thermodynamic studies on the oxygenation and subunit association of human hemoglobin. Temperature dependence of the linkage between dimer-tetramer association and oxygenation state. J Biol Chem. 1979 Apr 25;254(8):2881–2887. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mills F. C., Johnson M. L., Ackers G. K. Oxygenation-linked subunit interactions in human hemoglobin: experimental studies on the concentration dependence of oxygenation curves. Biochemistry. 1976 Nov 30;15(24):5350–5362. doi: 10.1021/bi00669a023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Morris R. J., Gibson Q. H. The apparent quantum yield of T-state human hemoglobin. Contribution of protein and heme to rates of oxygen reactions. J Biol Chem. 1984 Jan 10;259(1):365–371. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perutz M. F. Structure and mechanism of haemoglobin. Br Med Bull. 1976 Sep;32(3):195–208. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.bmb.a071363. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rubin M. M., Changeux J. P. On the nature of allosteric transitions: implications of non-exclusive ligand binding. J Mol Biol. 1966 Nov 14;21(2):265–274. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(66)90097-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shulman R. G., Hopfield J. J., Ogawa S. Allosteric interpretation of haemoglobin properties. Q Rev Biophys. 1975 Jul;8(3):325–420. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500001840. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith F. R., Ackers G. K. Experimental resolution of cooperative free energies for the ten ligation states of human hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5347–5351. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5347. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Szabo A., Karplus M. A mathematical model for structure-function relations in hemoglobin. J Mol Biol. 1972 Dec 14;72(1):163–197. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(72)90077-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas J. O., Edelstein S. J. Observation of the dissociation of unliganded hemoglobin. II. Effect of pH, salt, and dioxane. J Biol Chem. 1973 Apr 25;248(8):2901–2905. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weber G. Order of free energy couplings between ligand binding and protein subunit association in hemoglobin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):7098–7102. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.7098. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wyman J. Regulation in macromolecules as illustrated by haemoglobin. Q Rev Biophys. 1968 May;1(1):35–80. doi: 10.1017/s0033583500000457. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



