Abstract
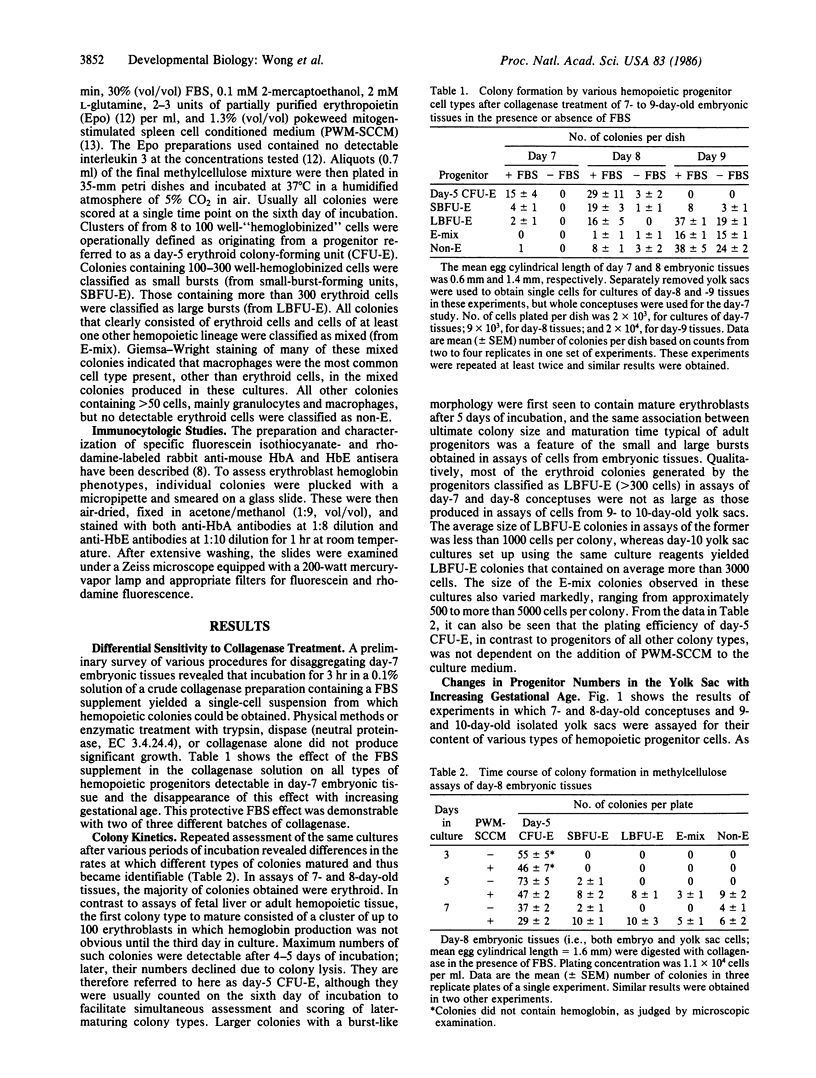
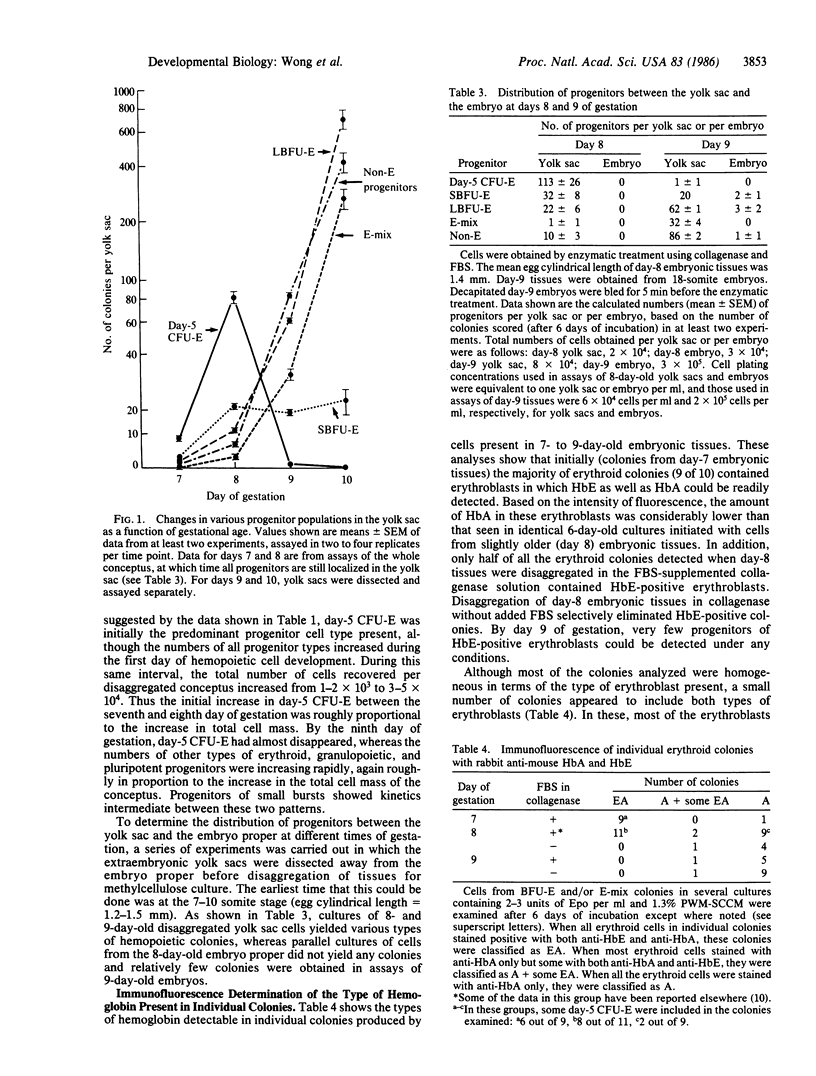
We have found that a variety of clonogenic hemopoietic cells can be obtained in a viable state from mouse conceptuses as early as day 7 of gestation when tissues are disaggregated in a crude collagenase solution containing fetal bovine serum. Examination of the time course of colony formation, and the ultimate size and lineages represented in colonies produced in semisolid medium containing methylcellulose, together with analysis of individual erythroid colonies stained with rabbit antisera specific for adult (HbA) and embryonic (HbE) mouse hemoglobins, revealed the presence on days 7 and 8 of gestation (but not later) of erythropoietic progenitors that give rise to mature erythroid colonies containing up to 100 HbE-containing erythroblasts after 4-6 days of growth in culture. These progenitors are highly sensitive to the disaggregation conditions used. Clonogenic progenitors of exclusively HbA-positive erythroblasts can also be detected in the day-7 conceptus. Assays of progenitors from separately disaggregated yolk sacs and embryos from day-8 conceptuses yielded colonies only from yolk sac suspensions, and again these contained either HbE- and HbA-positive erythroblasts or only HbA-positive erythroblasts. These findings demonstrate the very early appearance in the yolk sac of a population of erythroid progenitors with a number of unique properties. Although most of these yield HbE-positive erythroblasts in vitro, some produce erythroblasts containing HbA only. Such a developmental pattern is consistent with the hypothesis that definitive erythropoiesis in the mammalian fetal liver is derived from stem cells that originate in the yolk sac blood islands.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barker J. E. Development of the mouse hematopoietic system. I. Types of hemoglobin produced in embryonic yolk sac and liver. Dev Biol. 1968 Jul;18(1):14–29. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(68)90020-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Beaupain D., Martin C., Dieterlen-Lièvre F. Are developmental hemoglobin changes related to the origin of stem cells and site of erythropoiesis? Blood. 1979 Feb;53(2):212–225. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brotherton T. W., Chui D. H., Gauldie J., Patterson M. Hemoglobin ontogeny during normal mouse fetal development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Jun;76(6):2853–2857. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.6.2853. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CRAIG M. L., RUSSELL E. S. A DEVELOPMENTAL CHANGE IN HEMOGLOBINS CORRELATED WITH AN EMBRYONIC RED CELL POPULATION IN THE MOUSE. Dev Biol. 1964 Oct;10:191–201. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(64)90040-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Coulombel L., Eaves A. C., Eaves C. J. Enzymatic treatment of long-term human marrow cultures reveals the preferential location of primitive hemopoietic progenitors in the adherent layer. Blood. 1983 Aug;62(2):291–297. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudennec C. A., Thiery J. P., Le Douarin N. M. In vitro induction of adult erythropoiesis in early mouse yolk sac. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2412–2416. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2412. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dieterlen-Lievre F. On the origin of haemopoietic stem cells in the avian embryo: an experimental approach. J Embryol Exp Morphol. 1975 Jun;33(3):607–619. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihle J. N., Keller J., Oroszlan S., Henderson L. E., Copeland T. D., Fitch F., Prystowsky M. B., Goldwasser E., Schrader J. W., Palaszynski E. Biologic properties of homogeneous interleukin 3. I. Demonstration of WEHI-3 growth factor activity, mast cell growth factor activity, p cell-stimulating factor activity, colony-stimulating factor activity, and histamine-producing cell-stimulating factor activity. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):282–287. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Johnson G. R., Barker D. C. Erythroid progenitor cells and stimulating factors during murine embryonic and fetal development. Exp Hematol. 1985 Mar;13(3):200–208. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kovach J. S., Marks P. A., Russell E. S., Epler H. Erythroid cell development in fetal mice: ultrastructural characteristics and hemoglobin synthesis. J Mol Biol. 1967 Apr 14;25(1):131–142. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(67)90284-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Krystal G., Eaves C. J., Eaves A. C. CM Affi-Gel Blue chromatography of human urine: a simple one-step procedure for obtaining erythropoietin suitable for in vitro erythropoietic progenitor assays. Br J Haematol. 1984 Nov;58(3):533–546. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1984.tb04001.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Marks P. A., Kovach J. S. Development of mammalian erythroid cells. Curr Top Dev Biol. 1966;1:213–252. doi: 10.1016/s0070-2153(08)60014-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moore M. A., Metcalf D. Ontogeny of the haemopoietic system: yolk sac origin of in vivo and in vitro colony forming cells in the developing mouse embryo. Br J Haematol. 1970 Mar;18(3):279–296. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2141.1970.tb01443.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rifkind R. A., Chui D., Epler H. An ultrastructural study of early morphogenetic events during the establishment of fetal hepatic erythropoiesis. J Cell Biol. 1969 Feb;40(2):343–365. doi: 10.1083/jcb.40.2.343. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Russell E. S. Hereditary anemias of the mouse: a review for geneticists. Adv Genet. 1979;20:357–459. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. M., Chung S. W., Reicheld S. M., Chui D. H. Hemoglobin switching during murine embryonic development: evidence for two populations of embryonic erythropoietic progenitor cells. Blood. 1986 Mar;67(3):716–721. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. M., Chung S. W., White J. S., Reicheld S. M., Patterson M., Clarke B. J., Chui D. H. Adult hemoglobins are synthesized in murine fetal hepatic erythropoietic cells. Blood. 1983 Dec;62(6):1280–1288. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wong P. M., Clarke B. J., Carr D. H., Chui D. H. Adult hemoglobins are synthesized in erythroid colonies in vitro derived from murine circulating hemopoietic progenitor cells during embryonic development. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 May;79(9):2952–2956. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.9.2952. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



