Abstract
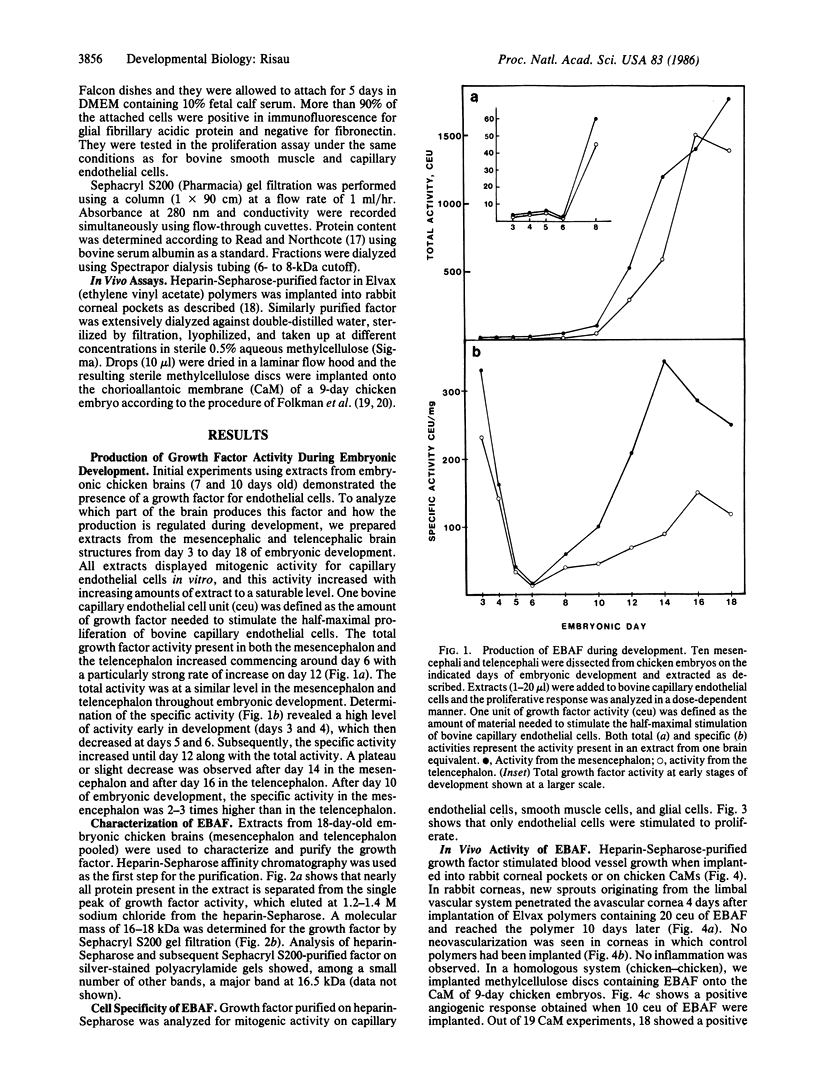
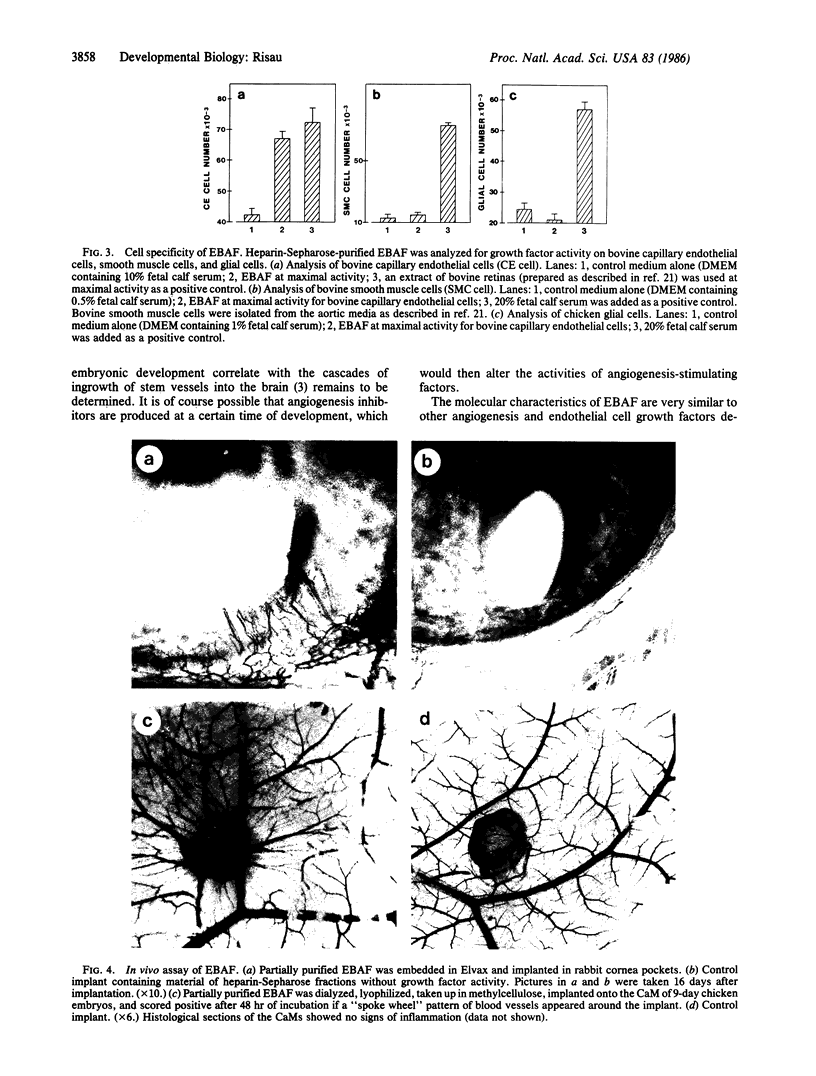
Embryonic chicken brain was analyzed for the presence of growth factors for capillary endothelial cells. A growth factor was found whose total and specific activities began to increase around the 12th day of development and reached a plateau around the 14th-16th day. A high specific activity was observed early in embryonic development at days 3 and 4. The growth factor was partially purified from extracts of 18-day-old embryonic chicken brain by heparin-Sepharose affinity chromatography where it eluted as a single peak of activity at 1.2-1.4 M sodium chloride. In chromatography on Sephacryl S200 gels, the activity eluted at a molecular size of 16- to 18-kDa. The growth factor is mitogenic for endothelial cells but not for smooth muscle or glial cells. In vivo assays using rabbit cornea and chicken chorioallantoic membrane demonstrated the angiogenic capacity of the chromatographed growth factor. The relationship between this early factor, the subsequent invasion of blood vessels into neural tissue, and the formation of the blood-brain barrier is discussed.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baird A., Mormède P., Ying S. Y., Wehrenberg W. B., Ueno N., Ling N., Guillemin R. A nonmitogenic pituitary function of fibroblast growth factor: regulation of thyrotropin and prolactin secretion. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5545–5549. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bradbury M. W. The structure and function of the blood-brain barrier. Fed Proc. 1984 Feb;43(2):186–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bär T. The vascular system of the cerebral cortex. Adv Anat Embryol Cell Biol. 1980;59:I-VI,1-62. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-67432-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bär T., Wolff J. R. The formation of capillary basement membranes during internal vascularization of the rat's cerebral cortex. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1972;133(2):231–248. doi: 10.1007/BF00307145. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Conn G., Hatcher V. B. The isolation and purification of two anionic endothelial cell growth factors from human brain. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1984 Oct 15;124(1):262–268. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(84)90946-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- D'Amore P. A., Klagsbrun M. Endothelial cell mitogens derived from retina and hypothalamus: biochemical and biological similarities. J Cell Biol. 1984 Oct;99(4 Pt 1):1545–1549. doi: 10.1083/jcb.99.4.1545. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeBault L. E., Cancilla P. A. gamma-Glutamyl transpeptidase in isolated brain endothelial cells: induction by glial cells in vitro. Science. 1980 Feb 8;207(4431):653–655. doi: 10.1126/science.6101511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Duckett S. The establishment of internal vascularization in the human telencephalon. Acta Anat (Basel) 1971;80(1):107–113. doi: 10.1159/000143680. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ekblom P., Sariola H., Karkinen-Jäskeläinen M., Saxén L. The origin of the glomerular endothelium. Cell Differ. 1982 Jan;11(1):35–39. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(82)90014-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Esch F., Baird A., Ling N., Ueno N., Hill F., Denoroy L., Klepper R., Gospodarowicz D., Böhlen P., Guillemin R. Primary structure of bovine pituitary basic fibroblast growth factor (FGF) and comparison with the amino-terminal sequence of bovine brain acidic FGF. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6507–6511. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6507. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J., Langer R., Linhardt R. J., Haudenschild C., Taylor S. Angiogenesis inhibition and tumor regression caused by heparin or a heparin fragment in the presence of cortisone. Science. 1983 Aug 19;221(4612):719–725. doi: 10.1126/science.6192498. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Folkman J. Proceedings: Tumor angiogenesis factor. Cancer Res. 1974 Aug;34(8):2109–2113. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimbrone M. A., Jr, Cotran R. S., Leapman S. B., Folkman J. Tumor growth and neovascularization: an experimental model using the rabbit cornea. J Natl Cancer Inst. 1974 Feb;52(2):413–427. doi: 10.1093/jnci/52.2.413. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gospodarowicz D., Cheng J., Lui G. M., Baird A., Böhlent P. Isolation of brain fibroblast growth factor by heparin-Sepharose affinity chromatography: identity with pituitary fibroblast growth factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Nov;81(22):6963–6967. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.22.6963. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jotereau F. V., Le Douarin N. M. The development relationship between osteocytes and osteoclasts: a study using the quail-chick nuclear marker in endochondral ossification. Dev Biol. 1978 Apr;63(2):253–265. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(78)90132-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klagsbrun M., Shing Y. Heparin affinity of anionic and cationic capillary endothelial cell growth factors: analysis of hypothalamus-derived growth factors and fibroblast growth factors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):805–809. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.805. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Le Douarin N. A biological cell labeling technique and its use in expermental embryology. Dev Biol. 1973 Jan;30(1):217–222. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(73)90061-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lobb R. R., Fett J. W. Purification of two distinct growth factors from bovine neural tissue by heparin affinity chromatography. Biochemistry. 1984 Dec 18;23(26):6295–6299. doi: 10.1021/bi00321a001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maciag T., Mehlman T., Friesel R., Schreiber A. B. Heparin binds endothelial cell growth factor, the principal endothelial cell mitogen in bovine brain. Science. 1984 Aug 31;225(4665):932–935. doi: 10.1126/science.6382607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peterson R. G. Vascularization and basement membranes of the chick brain in light microscopy. Anat Rec. 1968 May;161(1):37–43. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091610104. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Read S. M., Northcote D. H. Minimization of variation in the response to different proteins of the Coomassie blue G dye-binding assay for protein. Anal Biochem. 1981 Sep 1;116(1):53–64. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(81)90321-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ross R. The smooth muscle cell. II. Growth of smooth muscle in culture and formation of elastic fibers. J Cell Biol. 1971 Jul;50(1):172–186. doi: 10.1083/jcb.50.1.172. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shing Y., Folkman J., Sullivan R., Butterfield C., Murray J., Klagsbrun M. Heparin affinity: purification of a tumor-derived capillary endothelial cell growth factor. Science. 1984 Mar 23;223(4642):1296–1299. doi: 10.1126/science.6199844. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. A., Wiley M. J. Developing nervous tissue induces formation of blood-brain barrier characteristics in invading endothelial cells: a study using quail--chick transplantation chimeras. Dev Biol. 1981 May;84(1):183–192. doi: 10.1016/0012-1606(81)90382-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stewart P. A., Wiley M. J. Structural and histochemical features of the avian blood-brain barrier. J Comp Neurol. 1981 Oct 20;202(2):157–167. doi: 10.1002/cne.902020203. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strydom D. J., Fett J. W., Lobb R. R., Alderman E. M., Bethune J. L., Riordan J. F., Vallee B. L. Amino acid sequence of human tumor derived angiogenin. Biochemistry. 1985 Sep 24;24(20):5486–5494. doi: 10.1021/bi00341a031. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas K. A., Rios-Candelore M., Giménez-Gallego G., DiSalvo J., Bennett C., Rodkey J., Fitzpatrick S. Pure brain-derived acidic fibroblast growth factor is a potent angiogenic vascular endothelial cell mitogen with sequence homology to interleukin 1. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Oct;82(19):6409–6413. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.19.6409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wakai S., Hirokawa N. Development of the blood-brain barrier to horseradish peroxidase in the chick embryo. Cell Tissue Res. 1978 Dec 28;195(2):195–203. doi: 10.1007/BF00236719. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilson D. The origin of the endothelium in the developing marginal vein of the chick wing-bud. Cell Differ. 1983 Sep;13(1):63–67. doi: 10.1016/0045-6039(83)90078-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]