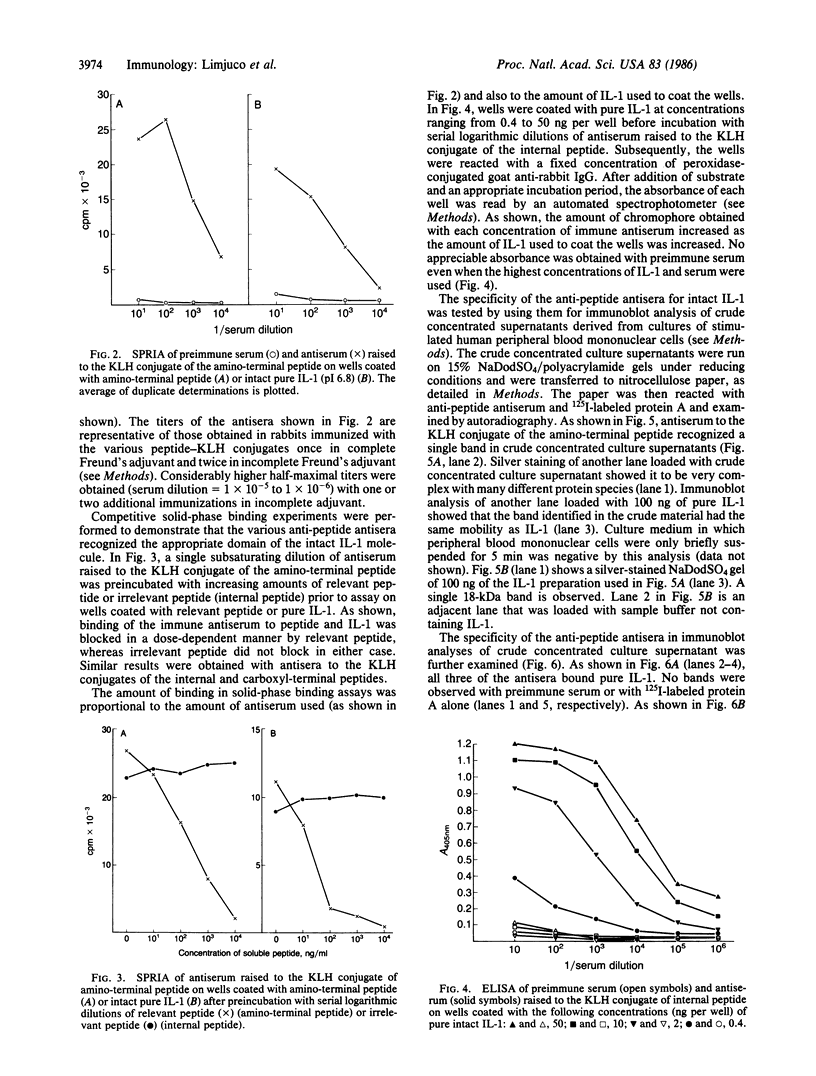
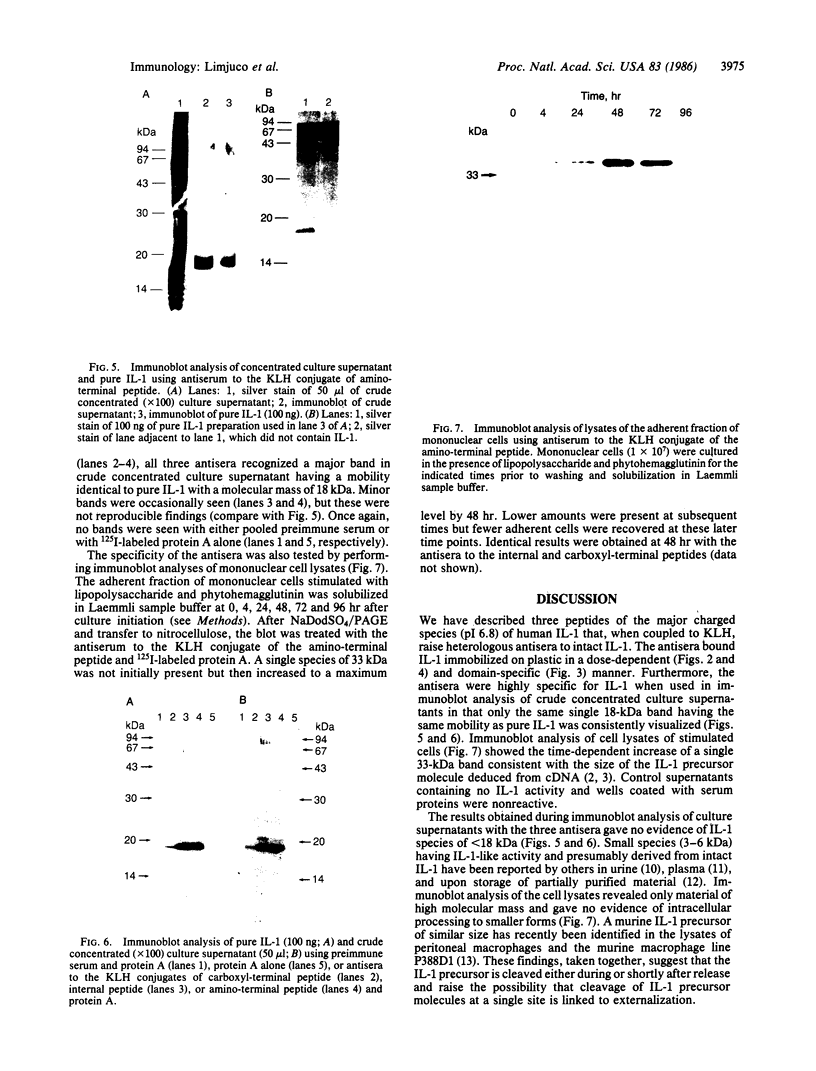
Abstract
The development of highly specific antisera to human interleukin 1 (IL-1) has been an elusive goal hampered mainly by the availability of only limited amounts of pure immunogen. To surmount this difficulty, three peptides of the major charged species of IL-1 (pI 6.8) were synthesized and covalently coupled to keyhole limpet hemocyanin (KLH). All three peptide-KLH conjugates raised rabbit heterologous antisera that bound intact pure IL-1 in a dose-dependent and domain-specific manner. Immunoblot analysis of crude concentrated culture supernatants with these antisera showed each of them to be highly specific for mature 18-kDa IL-1. Immunoblot analysis of monocyte lysates revealed a single 33-kDa band consistent with the size of the IL-1 precursor molecule deduced from cloned cDNA. These reagents should prove to be valuable tools in the localization and measurement of IL-1 in cells and fluids and may permit the separate study of individual IL-1 species as well as discrete domains of intact IL-1 molecules.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Auron P. E., Webb A. C., Rosenwasser L. J., Mucci S. F., Rich A., Wolff S. M., Dinarello C. A. Nucleotide sequence of human monocyte interleukin 1 precursor cDNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7907–7911. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7907. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cameron P., Limjuco G., Rodkey J., Bennett C., Schmidt J. A. Amino acid sequence analysis of human interleukin 1 (IL-1). Evidence for biochemically distinct forms of IL-1. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):790–801. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.790. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Clowes G. H., Jr, George B. C., Villee C. A., Jr, Saravis C. A. Muscle proteolysis induced by a circulating peptide in patients with sepsis or trauma. N Engl J Med. 1983 Mar 10;308(10):545–552. doi: 10.1056/NEJM198303103081001. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Clowes G. H., Jr, Gordon A. H., Saravis C. A., Wolff S. M. Cleavage of human interleukin 1: isolation of a peptide fragment from plasma of febrile humans and activated monocytes. J Immunol. 1984 Sep;133(3):1332–1338. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dinarello C. A., Renfer L., Wolff S. M. Human leukocytic pyrogen: purification and development of a radioimmunoassay. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Oct;74(10):4624–4627. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.10.4624. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Durum S. K., Schmidt J. A., Oppenheim J. J. Interleukin 1: an immunological perspective. Annu Rev Immunol. 1985;3:263–287. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.03.040185.001403. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Emini E. A., Hughes J. V., Perlow D. S., Boger J. Induction of hepatitis A virus-neutralizing antibody by a virus-specific synthetic peptide. J Virol. 1985 Sep;55(3):836–839. doi: 10.1128/jvi.55.3.836-839.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Giri J. G., Lomedico P. T., Mizel S. B. Studies on the synthesis and secretion of interleukin 1. I. A 33,000 molecular weight precursor for interleukin 1. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):343–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hayes E. C., Lombardo D. L., Girard Y., Maycock A. L., Rokach J., Rosenthal A. S., Young R. N., Egan R. W., Zweerink H. J. Measuring leukotrienes of slow reacting substance of anaphylaxis: development of a specific radioimmunoassay. J Immunol. 1983 Jul;131(1):429–433. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kimball E. S., Pickeral S. F., Oppenheim J. J., Rossio J. L. Interleukin 1 activity in normal human urine. J Immunol. 1984 Jul;133(1):256–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitagawa T., Aikawa T. Enzyme coupled immunoassay of insulin using a novel coupling reagent. J Biochem. 1976 Jan;79(1):233–236. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a131053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lomedico P. T., Gubler U., Hellmann C. P., Dukovich M., Giri J. G., Pan Y. C., Collier K., Semionow R., Chua A. O., Mizel S. B. Cloning and expression of murine interleukin-1 cDNA in Escherichia coli. 1984 Nov 29-Dec 5Nature. 312(5993):458–462. doi: 10.1038/312458a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- March C. J., Mosley B., Larsen A., Cerretti D. P., Braedt G., Price V., Gillis S., Henney C. S., Kronheim S. R., Grabstein K. Cloning, sequence and expression of two distinct human interleukin-1 complementary DNAs. Nature. 1985 Jun 20;315(6021):641–647. doi: 10.1038/315641a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. A., Mizel S. B., Cohen D., Green I. Interleukin 1, a potential regulator of fibroblast proliferation. J Immunol. 1982 May;128(5):2177–2182. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. A., Oliver C. N., Lepe-Zuniga J. L., Green I., Gery I. Silica-stimulated monocytes release fibroblast proliferation factors identical to interleukin 1. A potential role for interleukin 1 in the pathogenesis of silicosis. J Clin Invest. 1984 May;73(5):1462–1472. doi: 10.1172/JCI111350. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schmidt J. A. Purification and partial biochemical characterization of normal human interleukin 1. J Exp Med. 1984 Sep 1;160(3):772–787. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.3.772. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]








