Abstract
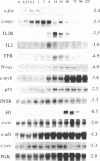
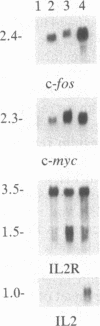
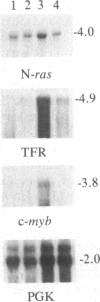
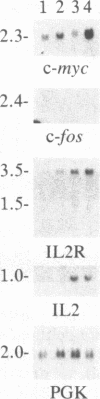
The proliferation of non-neoplastic T lymphocytes is regulated, in part, by the coordinated expression of genes encoding T-cell growth factor (interleukin 2, IL2), IL2 receptors (IL2R), and transferrin receptors (TFR). In addition to growth factors and their receptors, protooncogenes may regulate lymphocyte proliferation. We used cloned cDNAs homologous to 21 different protooncogenes to screen for their expression at the mRNA level in human peripheral blood mononuclear cells (PBMC) stimulated with the mitogenic lectin phytohemagglutinin (PHA), and we compared the time course of accumulation of mRNAs for these protooncogenes to that of mRNAs for the IL2, IL2R, TFR, and histone H3 genes. mRNAs for c-abl, c-ets, c-yes, and N-ras were present in unstimulated PBMC. After stimulation of PBMC by PHA, we detected marked increases within 10 min in the levels of mRNA for c-fos and c-myc; within 6 hr for IL2 and IL2R mRNAs; within 14 hr for c-myb, p53, N-ras, and TFR mRNAs; and within 24-36 hr for H3 mRNA. Expression of c-abl, c-ets, and c-yes increased gradually following stimulation with PHA. None of the other protooncogenes tested was expressed in PBMC. Addition of the protein synthesis inhibitor cycloheximide, before the addition of PHA to cultures, abolished the PHA-induced accumulation of mRNAs for c-myb, N-ras, and TFR, but not of mRNAs for c-fos, c-myc, IL2, and IL2R. These data indicate that c-fos, c-myc, IL2, and IL2R belong to a group of genes expressed early, whereas c-myb, N-ras, and TFR belong to a group of genes expressed later in PHA-activated PBMC, and that the products of the c-fos and c-myc protooncogenes are not required for expression of IL2 or IL2R genes. Addition of purified IL2 augmented the expression of the later-expressed genes c-myb, p53, N-ras, and TFR in PHA-stimulated cultures of PBMC, as well as of the early genes c-myc and IL2R, but not of c-fos and IL2, thus suggesting that PHA and IL2 stimulate the expression of overlapping, but nonidentical, sets of genes in PBMC.
Full text
PDF




Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Bishop J. M. Cellular oncogenes and retroviruses. Annu Rev Biochem. 1983;52:301–354. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.52.070183.001505. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Campisi J., Gray H. E., Pardee A. B., Dean M., Sonenshein G. E. Cell-cycle control of c-myc but not c-ras expression is lost following chemical transformation. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):241–247. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90217-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cantrell D. A., Smith K. A. The interleukin-2 T-cell system: a new cell growth model. Science. 1984 Jun 22;224(4655):1312–1316. doi: 10.1126/science.6427923. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chen J. H. The proto-oncogene c-ets is preferentially expressed in lymphoid cells. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Nov;5(11):2993–3000. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.11.2993. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chirgwin J. M., Przybyla A. E., MacDonald R. J., Rutter W. J. Isolation of biologically active ribonucleic acid from sources enriched in ribonuclease. Biochemistry. 1979 Nov 27;18(24):5294–5299. doi: 10.1021/bi00591a005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford L. The 53,000-dalton cellular protein and its role in transformation. Int Rev Exp Pathol. 1983;25:1–50. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Miller A. D., Zokas L., Verma I. M. Viral and cellular fos proteins: a comparative analysis. Cell. 1984 Feb;36(2):259–268. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90219-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curran T., Peters G., Van Beveren C., Teich N. M., Verma I. M. FBJ murine osteosarcoma virus: identification and molecular cloning of biologically active proviral DNA. J Virol. 1982 Nov;44(2):674–682. doi: 10.1128/jvi.44.2.674-682.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cuypers H. T., Selten G., Quint W., Zijlstra M., Maandag E. R., Boelens W., van Wezenbeek P., Melief C., Berns A. Murine leukemia virus-induced T-cell lymphomagenesis: integration of proviruses in a distinct chromosomal region. Cell. 1984 May;37(1):141–150. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90309-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Darzynkiewicz Z., Traganos F., Sharpless T., Melamed M. R. Lymphocyte stimulation: a rapid multiparameter analysis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1976 Aug;73(8):2881–2884. doi: 10.1073/pnas.73.8.2881. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- DeLorbe W. J., Luciw P. A., Goodman H. M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M. Molecular cloning and characterization of avian sarcoma virus circular DNA molecules. J Virol. 1980 Oct;36(1):50–61. doi: 10.1128/jvi.36.1.50-61.1980. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Drogula C., Krönke M., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Interleukin 2 (IL-2) augments transcription of the IL-2 receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4230–4234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Donner L., Fedele L. A., Garon C. F., Anderson S. J., Sherr C. J. McDonough feline sarcoma virus: characterization of the molecularly cloned provirus and its feline oncogene (v-fms). J Virol. 1982 Feb;41(2):489–500. doi: 10.1128/jvi.41.2.489-500.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eisenman R. N., Tachibana C. Y., Abrams H. D., Hann S. R. V-myc- and c-myc-encoded proteins are associated with the nuclear matrix. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Jan;5(1):114–126. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.1.114. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ellis R. W., Defeo D., Shih T. Y., Gonda M. A., Young H. A., Tsuchida N., Lowy D. R., Scolnick E. M. The p21 src genes of Harvey and Kirsten sarcoma viruses originate from divergent members of a family of normal vertebrate genes. Nature. 1981 Aug 6;292(5823):506–511. doi: 10.1038/292506a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feramisco J. R., Gross M., Kamata T., Rosenberg M., Sweet R. W. Microinjection of the oncogene form of the human H-ras (T-24) protein results in rapid proliferation of quiescent cells. Cell. 1984 Aug;38(1):109–117. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90531-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Franchini G., Even J., Sherr C. J., Wong-Staal F. onc sequences (v-fes) of Snyder-Theilen feline sarcoma virus are derived from noncontiguous regions of a cat cellular gene (c-fes). Nature. 1981 Mar 12;290(5802):154–157. doi: 10.1038/290154a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Glisin V., Crkvenjakov R., Byus C. Ribonucleic acid isolated by cesium chloride centrifugation. Biochemistry. 1974 Jun 4;13(12):2633–2637. doi: 10.1021/bi00709a025. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goff S. P., Gilboa E., Witte O. N., Baltimore D. Structure of the Abelson murine leukemia virus genome and the homologous cellular gene: studies with cloned viral DNA. Cell. 1980 Dec;22(3):777–785. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(80)90554-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goubin G., Goldman D. S., Luce J., Neiman P. E., Cooper G. M. Molecular cloning and nucleotide sequence of a transforming gene detected by transfection of chicken B-cell lymphoma DNA. Nature. 1983 Mar 10;302(5904):114–119. doi: 10.1038/302114a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Robb R. J. Receptors for T-cell growth factor: structure, function and expression on normal and neoplastic cells. Contemp Top Mol Immunol. 1985;10:1–34. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4684-4838-2_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holbrook N. J., Smith K. A., Fornace A. J., Jr, Comeau C. M., Wiskocil R. L., Crabtree G. R. T-cell growth factor: complete nucleotide sequence and organization of the gene in normal and malignant cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1634–1638. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1634. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jones M., Bosselman R. A., van der Hoorn F. A., Berns A., Fan H., Verma I. M. Identification and molecular cloning of Moloney mouse sarcoma virus-specific sequences from uninfected mouse cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1980 May;77(5):2651–2655. doi: 10.1073/pnas.77.5.2651. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Calabretta B., Baserga R. Expression of cell-cycle-dependent genes in phytohemagglutinin-stimulated human lymphocytes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5375–5379. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5375. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Hyland J. K., Watt R., Rosenberg M., Baserga R. Microinjected c-myc as a competence factor. Science. 1985 Jun 14;228(4705):1313–1315. doi: 10.1126/science.4001943. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaczmarek L., Oren M., Baserga R. Co-operation between the p53 protein tumor antigen and platelet-poor plasma in the induction of cellular DNA synthesis. Exp Cell Res. 1986 Jan;162(1):268–272. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(86)90445-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kelly K., Cochran B. H., Stiles C. D., Leder P. Cell-specific regulation of the c-myc gene by lymphocyte mitogens and platelet-derived growth factor. Cell. 1983 Dec;35(3 Pt 2):603–610. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90092-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kitamura N., Kitamura A., Toyoshima K., Hirayama Y., Yoshida M. Avian sarcoma virus Y73 genome sequence and structural similarity of its transforming gene product to that of Rous sarcoma virus. Nature. 1982 May 20;297(5863):205–208. doi: 10.1038/297205a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Klempnauer K. H., Symonds G., Evan G. I., Bishop J. M. Subcellular localization of proteins encoded by oncogenes of avian myeloblastosis virus and avian leukemia virus E26 and by chicken c-myb gene. Cell. 1984 Jun;37(2):537–547. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90384-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lachman H. M., Hatton K. S., Skoultchi A. I., Schildkraut C. L. c-myc mRNA levels in the cell cycle change in mouse erythroleukemia cells following inducer treatment. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Aug;82(16):5323–5327. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.16.5323. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lane M. A., Sainten A., Doherty K. M., Cooper G. M. Isolation and characterization of a stage-specific transforming gene, Tlym-I, from T-cell lymphomas. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Apr;81(7):2227–2231. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.7.2227. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Crabtree G. R., Rudikoff S., Pumphrey J., Robb R. J., Krönke M., Svetlik P. B., Peffer N. J., Waldmann T. A. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs for the human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):626–631. doi: 10.1038/311626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macara I. G. Oncogenes, ions, and phospholipids. Am J Physiol. 1985 Jan;248(1 Pt 1):C3–11. doi: 10.1152/ajpcell.1985.248.1.C3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mally M. I., Vogt M., Swift S. E., Haas M. Oncogene expression in murine splenic T cells and in murine T-cell neoplasms. Virology. 1985 Jul 15;144(1):115–126. doi: 10.1016/0042-6822(85)90310-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- McClelland A., Kühn L. C., Ruddle F. H. The human transferrin receptor gene: genomic organization, and the complete primary structure of the receptor deduced from a cDNA sequence. Cell. 1984 Dec;39(2 Pt 1):267–274. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90004-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Michelson A. M., Markham A. F., Orkin S. H. Isolation and DNA sequence of a full-length cDNA clone for human X chromosome-encoded phosphoglycerate kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):472–476. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.472. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Müller R., Bravo R., Burckhardt J., Curran T. Induction of c-fos gene and protein by growth factors precedes activation of c-myc. Nature. 1984 Dec 20;312(5996):716–720. doi: 10.1038/312716a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckers L. M., Cossman J. Transferrin receptor induction in mitogen-stimulated human T lymphocytes is required for DNA synthesis and cell division and is regulated by interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3494–3498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nowell P. C., Daniele R. P., Winger L. A. Kinetics of human lymphocyte proliferation: proportion of cells responsive to phytohemagglutinin and correlation with E rosette formation. J Reticuloendothel Soc. 1975 Jan;17(1):47–56. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nunn M. F., Seeburg P. H., Moscovici C., Duesberg P. H. Tripartite structure of the avian erythroblastosis virus E26 transforming gene. Nature. 1983 Nov 24;306(5941):391–395. doi: 10.1038/306391a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Persson H., Hennighausen L., Taub R., DeGrado W., Leder P. Antibodies to human c-myc oncogene product: evidence of an evolutionarily conserved protein induced during cell proliferation. Science. 1984 Aug 17;225(4663):687–693. doi: 10.1126/science.6431612. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pledger W. J., Stiles C. D., Antoniades H. N., Scher C. D. An ordered sequence of events is required before BALB/c-3T3 cells become committed to DNA synthesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2839–2843. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2839. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Plumb M., Stein J., Stein G. Coordinate regulation of multiple histone mRNAs during the cell cycle in HeLa cells. Nucleic Acids Res. 1983 Apr 25;11(8):2391–2410. doi: 10.1093/nar/11.8.2391. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rapp U. R., Goldsborough M. D., Mark G. E., Bonner T. I., Groffen J., Reynolds F. H., Jr, Stephenson J. R. Structure and biological activity of v-raf, a unique oncogene transduced by a retrovirus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jul;80(14):4218–4222. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.14.4218. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Greene W. C., Hoover R. G., Nowell P. C. Monoclonal antibody OKT11A inhibits and recombinant interleukin 2 (IL 2) augments expression of IL 2 receptors at a pretranslational level. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2478–2482. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Nowell P. C., Hoover R. G. Regulation of c-myc mRNA levels in normal human lymphocytes by modulators of cell proliferation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4221–4224. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4221. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Sabath D. E., Hoover R. G., Prystowsky M. B. Recombinant interleukin 2 regulates levels of c-myc mRNA in a cloned murine T lymphocyte. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Dec;5(12):3361–3368. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.12.3361. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reich N. C., Levine A. J. Growth regulation of a cellular tumour antigen, p53, in nontransformed cells. Nature. 1984 Mar 8;308(5955):199–201. doi: 10.1038/308199a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robbins K. C., Devare S. G., Reddy E. P., Aaronson S. A. In vivo identification of the transforming gene product of simian sarcoma virus. Science. 1982 Dec 10;218(4577):1131–1133. doi: 10.1126/science.6293053. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Santos E., Tronick S. R., Aaronson S. A., Pulciani S., Barbacid M. T24 human bladder carcinoma oncogene is an activated form of the normal human homologue of BALB- and Harvey-MSV transforming genes. Nature. 1982 Jul 22;298(5872):343–347. doi: 10.1038/298343a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwab M., Varmus H. E., Bishop J. M., Grzeschik K. H., Naylor S. L., Sakaguchi A. Y., Brodeur G., Trent J. Chromosome localization in normal human cells and neuroblastomas of a gene related to c-myc. Nature. 1984 Mar 15;308(5956):288–291. doi: 10.1038/308288a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shibuya M., Wang L. H., Hanafusa H. Molecular cloning of the Fujinami sarcoma virus genome and its comparison with sequences of other related transforming viruses. J Virol. 1982 Jun;42(3):1007–1016. doi: 10.1128/jvi.42.3.1007-1016.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shimizu K., Goldfarb M., Perucho M., Wigler M. Isolation and preliminary characterization of the transforming gene of a human neuroblastoma cell line. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jan;80(2):383–387. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.2.383. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stacey D. W., Kung H. F. Transformation of NIH 3T3 cells by microinjection of Ha-ras p21 protein. Nature. 1984 Aug 9;310(5977):508–511. doi: 10.1038/310508a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thompson C. B., Challoner P. B., Neiman P. E., Groudine M. Levels of c-myc oncogene mRNA are invariant throughout the cell cycle. 1985 Mar 28-Apr 3Nature. 314(6009):363–366. doi: 10.1038/314363a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Torelli G., Selleri L., Donelli A., Ferrari S., Emilia G., Venturelli D., Moretti L., Torelli U. Activation of c-myb expression by phytohemagglutinin stimulation in normal human T lymphocytes. Mol Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;5(10):2874–2877. doi: 10.1128/mcb.5.10.2874. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ullrich A., Bell J. R., Chen E. Y., Herrera R., Petruzzelli L. M., Dull T. J., Gray A., Coussens L., Liao Y. C., Tsubokawa M. Human insulin receptor and its relationship to the tyrosine kinase family of oncogenes. 1985 Feb 28-Mar 6Nature. 313(6005):756–761. doi: 10.1038/313756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Vennström B., Bishop J. M. Isolation and characterization of chicken DNA homologous to the two putative oncogenes of avian erythroblastosis virus. Cell. 1982 Jan;28(1):135–143. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(82)90383-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang A., Lu S. D., Mark D. F. Site-specific mutagenesis of the human interleukin-2 gene: structure-function analysis of the cysteine residues. Science. 1984 Jun 29;224(4656):1431–1433. doi: 10.1126/science.6427925. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wilhelmsen K. C., Temin H. M. Structure and dimorphism of c-rel (turkey), the cellular homolog to the oncogene of reticuloendotheliosis virus strain T. J Virol. 1984 Feb;49(2):521–529. doi: 10.1128/jvi.49.2.521-529.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zakut-Houri R., Bienz-Tadmor B., Givol D., Oren M. Human p53 cellular tumor antigen: cDNA sequence and expression in COS cells. EMBO J. 1985 May;4(5):1251–1255. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1985.tb03768.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ar-Rushdi A., Nishikura K., Erikson J., Watt R., Rovera G., Croce C. M. Differential expression of the translocated and the untranslocated c-myc oncogene in Burkitt lymphoma. Science. 1983 Oct 28;222(4622):390–393. doi: 10.1126/science.6414084. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]