Abstract
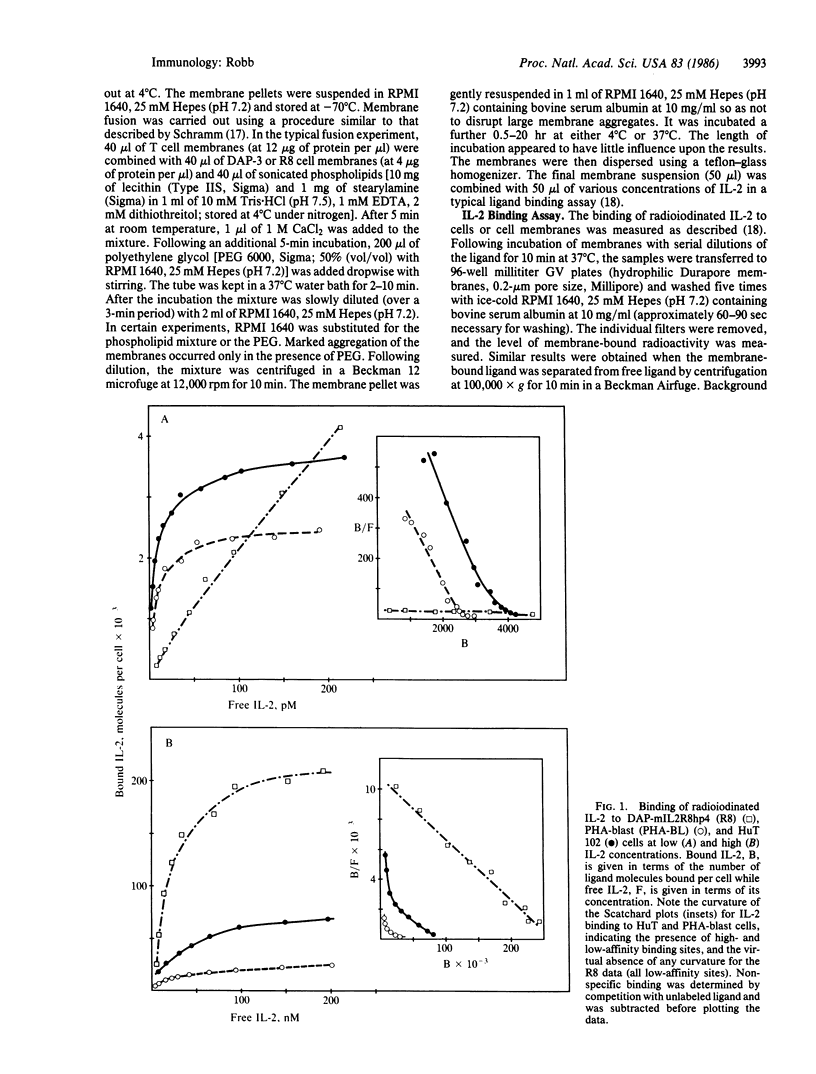
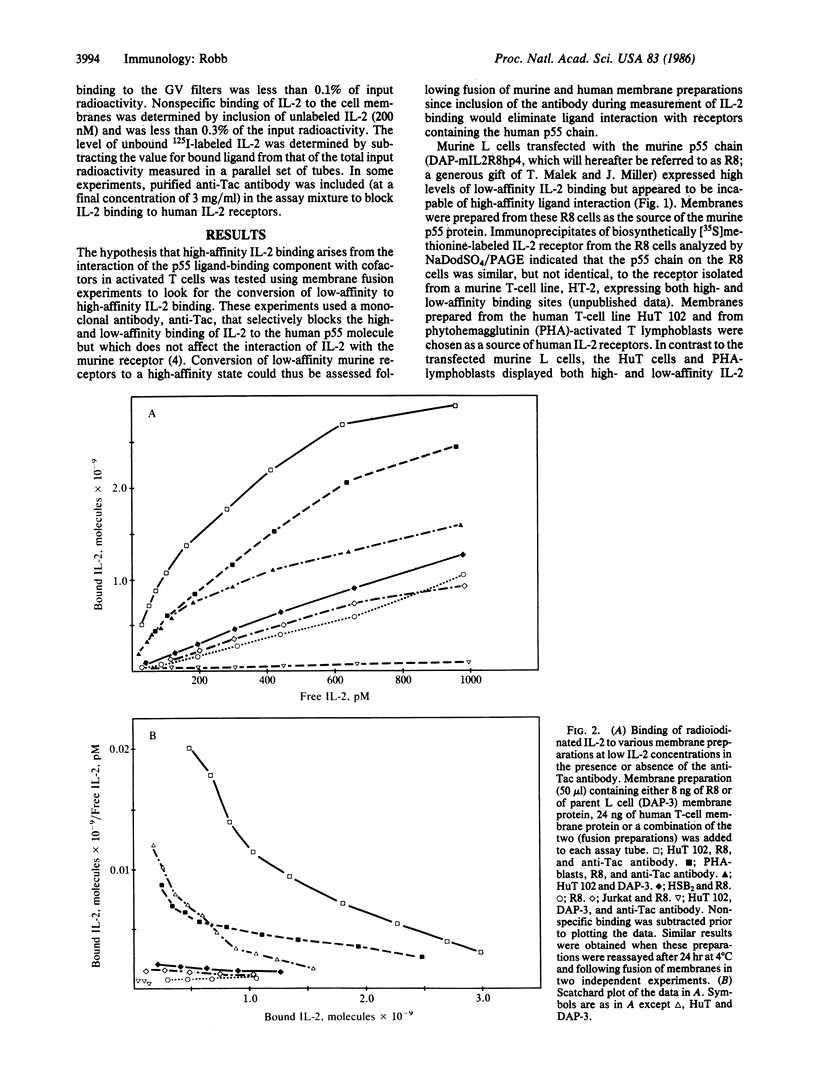
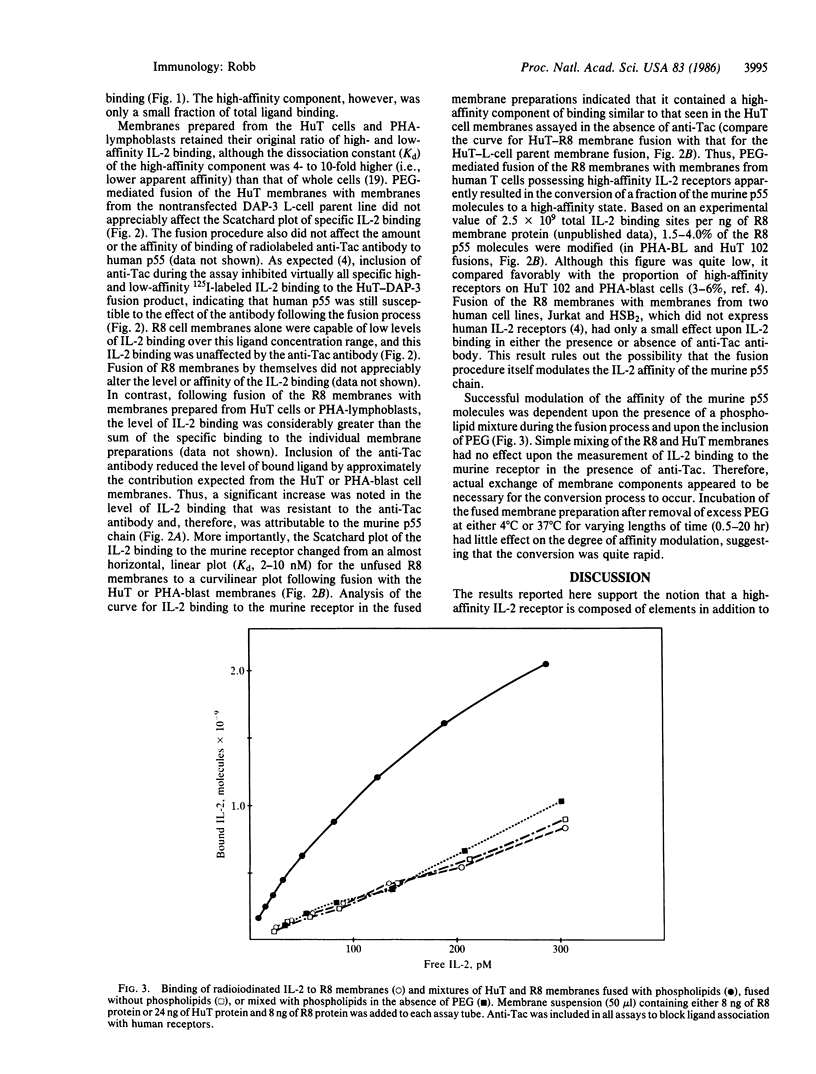
The cellular receptors for interleukin 2 (IL-2) exist in at least two forms, one with a particularly high affinity and a second, more numerous class, with a much lower affinity for IL-2. Indirect evidence suggests that both classes of receptors use the same p55 glycoprotein as their ligand-binding component. L cells transfected with cDNA encoding this protein, however, displayed only low-affinity IL-2 binding. To determine if such receptors could be converted to a high-affinity state, L-cell membranes containing the murine p55 protein were fused with membranes from human T cells displaying high-affinity receptors. The anti-Tac antibody was used to block ligand binding to human p55 on the fusion product. The results showed that a fraction of the murine p55 chains were converted to a dramatically higher affinity following fusion. Fusion of the L-cell membranes with themselves or with membrane preparations from human T-cell lines lacking the IL-2 receptor resulted in little or no affinity modulation. One explanation of the results is that cofactors present in receptor-positive T-cell lines crossed species lines and combined with the murine p55 chain to create "high-affinity" binding sites. Thus, depending upon its environment, the same p55 molecule can apparently form either a low- or high-affinity IL-2 receptor.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Buxser S. E., Kelleher D. J., Watson L., Puma P., Johnson G. L. Change in state of nerve growth factor receptor. Modulation of receptor affinity by wheat germ agglutinin. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 25;258(6):3741–3749. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greene W. C., Robb R. J., Svetlik P. B., Rusk C. M., Depper J. M., Leonard W. J. Stable expression of cDNA encoding the human interleukin 2 receptor in eukaryotic cells. J Exp Med. 1985 Jul 1;162(1):363–368. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.1.363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatakeyama M., Minamoto S., Uchiyama T., Hardy R. R., Yamada G., Taniguchi T. Reconstitution of functional receptor for human interleukin-2 in mouse cells. Nature. 1985 Dec 5;318(6045):467–470. doi: 10.1038/318467a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawamoto T., Sato J. D., Le A., Polikoff J., Sato G. H., Mendelsohn J. Growth stimulation of A431 cells by epidermal growth factor: identification of high-affinity receptors for epidermal growth factor by an anti-receptor monoclonal antibody. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Mar;80(5):1337–1341. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.5.1337. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Crabtree G. R., Rudikoff S., Pumphrey J., Robb R. J., Krönke M., Svetlik P. B., Peffer N. J., Waldmann T. A. Molecular cloning and expression of cDNAs for the human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):626–631. doi: 10.1038/311626a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leonard W. J., Depper J. M., Krönke M., Robb R. J., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. The human receptor for T-cell growth factor. Evidence for variable post-translational processing, phosphorylation, sulfation, and the ability of precursor forms of the receptor to bind T-cell growth factor. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1872–1880. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Miller J., Malek T. R., Leonard W. J., Greene W. C., Shevach E. M., Germain R. N. Nucleotide sequence and expression of a mouse interleukin 2 receptor cDNA. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):4212–4217. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nikaido T., Shimizu A., Ishida N., Sabe H., Teshigawara K., Maeda M., Uchiyama T., Yodoi J., Honjo T. Molecular cloning of cDNA encoding human interleukin-2 receptor. Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):631–635. doi: 10.1038/311631a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C. Direct demonstration of the identity of T cell growth factor binding protein and the Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1332–1337. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C., Rusk C. M. Low and high affinity cellular receptors for interleukin 2. Implications for the level of Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1984 Oct 1;160(4):1126–1146. doi: 10.1084/jem.160.4.1126. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J. Human interleukin 2. Methods Enzymol. 1985;116:493–525. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(85)16040-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Mayer P. C., Garlick R. Retention of biological activity following radioiodination of human interleukin 2: comparison with biosynthetically labeled growth factor in receptor binding assays. J Immunol Methods. 1985 Jul 16;81(1):15–30. doi: 10.1016/0022-1759(85)90118-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M. Transfer of glucagon receptor from liver membranes to a foreign adenylate cyclase by a membrane fusion procedure. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1979 Mar;76(3):1174–1178. doi: 10.1073/pnas.76.3.1174. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A., Cantrell D. A. Interleukin 2 regulates its own receptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Feb;82(3):864–868. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.3.864. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith K. A. T-cell growth factor. Immunol Rev. 1980;51:337–357. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1980.tb00327.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Williams L. T., Tremble P. M., Lavin M. F., Sunday M. E. Platelet-derived growth factor receptors form a high affinity state in membrane preparations. Kinetics and affinity cross-linking studies. J Biol Chem. 1984 Apr 25;259(8):5287–5294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]



