Abstract
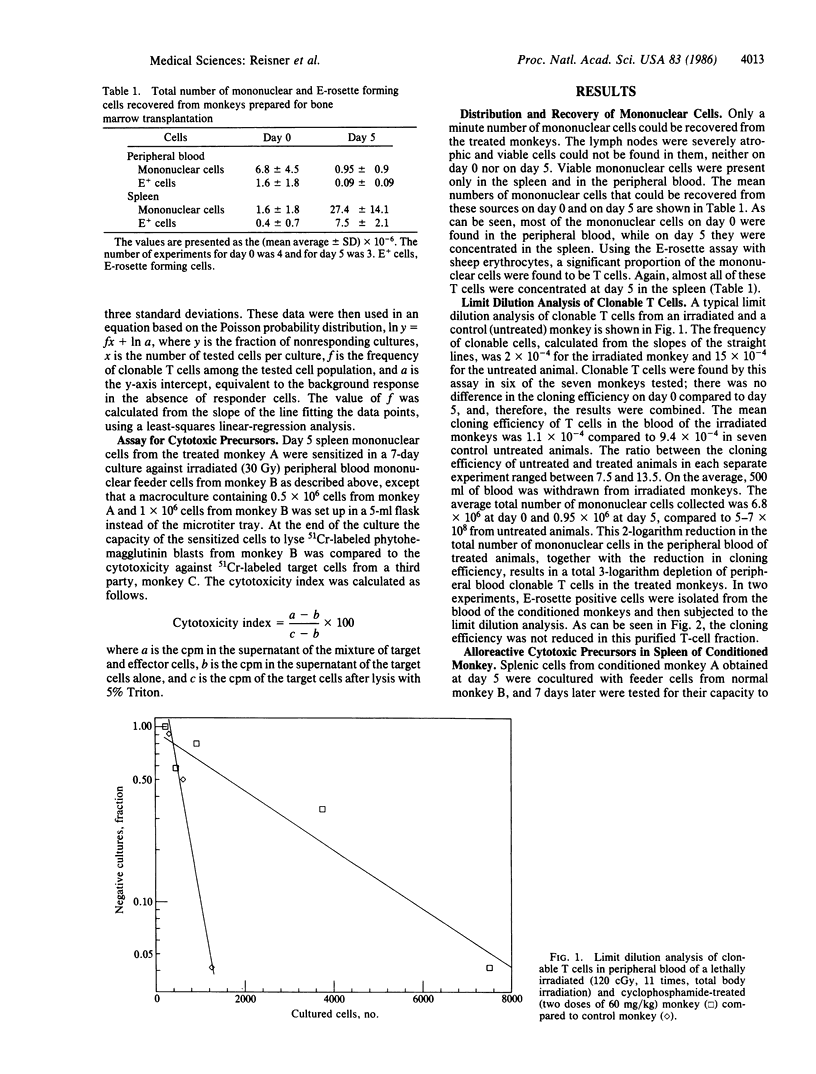
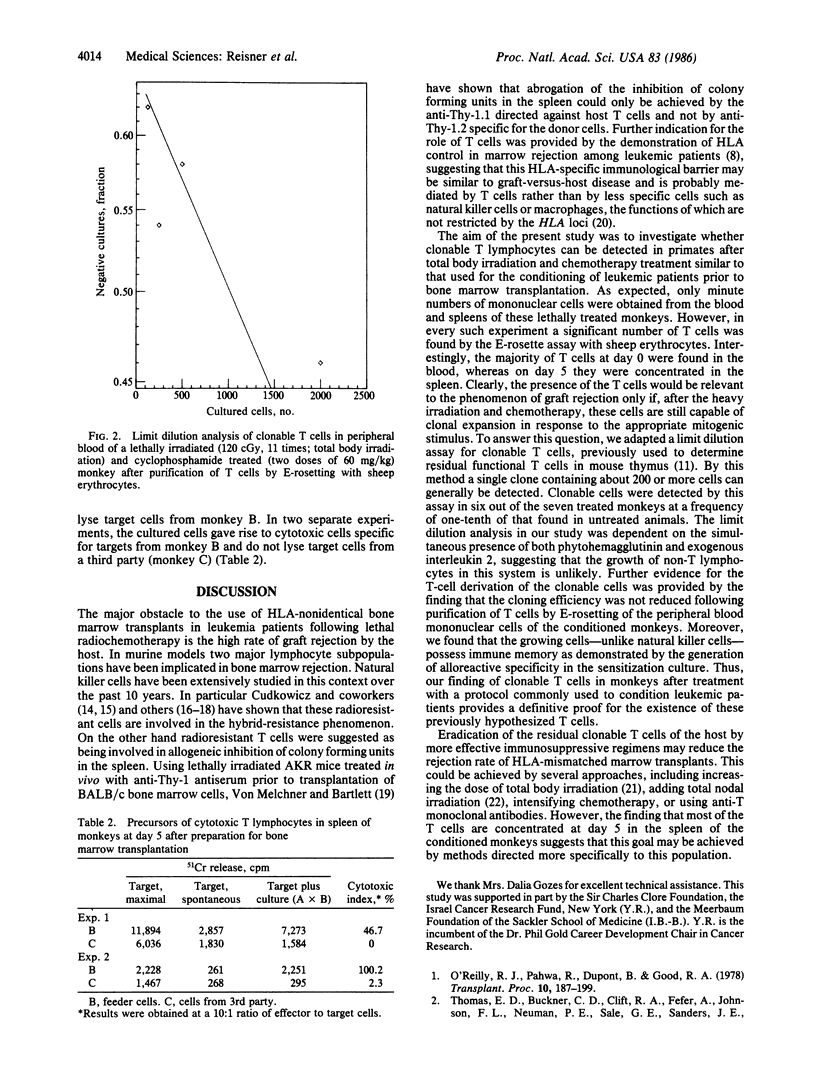
The phenomenon of marrow rejection following supralethal radiochemotherapy was explained in the past mainly by non-T-cell mechanisms known to be resistant to high-dose irradiation. In the present study a low but significant number of radiochemoresistant-clonable T cells was found in the peripheral blood and spleen of Rhesus monkeys following the cytoreductive protocol used for treatment of leukemia patients prior to bone marrow transplantation. More than 95% of the clonable cells are concentrated in the spleen 5 days after transplant. The cells possess immune memory as demonstrated by the generation of alloreactive-specific cytotoxicity. The present findings suggest that host-versus-graft activity may be mediated by alloreactive T cells. It is hoped that elimination of such cells prior to bone marrow transplantation will increase the engraftment rate of HLA-nonidentical marrow in leukemia patients.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Brain P., Gordon J., Willetts W. A. Rosette formation by peripheral lymphocytes. Clin Exp Immunol. 1970 May;6(5):681–688. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cudkowicz G., Bennett M. Peculiar immunobiology of bone marrow allografts. II. Rejection of parental grafts by resistant F 1 hybrid mice. J Exp Med. 1971 Dec 1;134(6):1513–1528. doi: 10.1084/jem.134.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Friedrich W., Goldmann S. F., Vetter U., Fliedner T. M., Heymer B., Peter H. H., Reisner Y., Kleihauer E. Immunoreconstitution in severe combined immunodeficiency after transplantation of HLA-haploidentical, T-cell-depleted bone marrow. Lancet. 1984 Apr 7;1(8380):761–764. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(84)91277-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hansson M., Kiessling R., Andersson B. Human fetal thymus and bone marrow contain target cells for natural killer cells. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Jan;11(1):8–12. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110103. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henderson L. E., Hewetson J. F., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Sowder R. C., Neubauer R. H., Rabin H. A rapid, large scale purification procedure for gibbon interleukin 2. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):810–815. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kiessling R., Hochman P. S., Haller O., Shearer G. M., Wigzell H., Cudkowicz G. Evidence for a similar or common mechanism for natural killer cell activity and resistance to hemopoietic grafts. Eur J Immunol. 1977 Sep;7(9):655–663. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830070915. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- O'Reilly R. J., Pahwa R., Dupont B., Good R. A. Severe combined immunodeficiency: transplantation approaches for patients lacking an HLA genotypically identical sibling. Transplant Proc. 1978 Mar;10(1):187–199. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin H., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Ruscetti F. W., Neubauer R. H., Brown R. L., Kawakami T. G. Spontaneous release of a factor with properties of T cell growth factor from a continuous line of primate tumor T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1852–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reinherz E. L., Geha R., Rappeport J. M., Wilson M., Penta A. C., Hussey R. E., Fitzgerald K. A., Daley J. F., Levine H., Rosen F. S. Reconstitution after transplantation with T-lymphocyte-depleted HLA haplotype-mismatched bone marrow for severe combined immunodeficiency. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6047–6051. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6047. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner Y., Kapoor N., Kirkpatrick D., Pollack M. S., Cunningham-Rundles S., Dupont B., Hodes M. Z., Good R. A., O'Reilly R. J. Transplantation for severe combined immunodeficiency with HLA-A,B,D,DR incompatible parental marrow cells fractionated by soybean agglutinin and sheep red blood cells. Blood. 1983 Feb;61(2):341–348. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reisner Y., Kapoor N., Kirkpatrick D., Pollack M. S., Dupont B., Good R. A., O'Reilly R. J. Transplantation for acute leukaemia with HLA-A and B nonidentical parental marrow cells fractionated with soybean agglutinin and sheep red blood cells. Lancet. 1981 Aug 15;2(8242):327–331. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(81)90647-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shank B., Chu F. C., Dinsmore R., Kapoor N., Kirkpatrick D., Teitelbaum H., Reid A., Bonfiglio P., Simpson L., O'Reilly R. J. Hyperfractionated total body irradiation for bone marrow transplantation. Results in seventy leukemia patients with allogeneic transplants. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys. 1983 Nov;9(11):1607–1611. doi: 10.1016/0360-3016(83)90412-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thomas E. D., Buckner C. D., Clift R. A., Fefer A., Johnson F. L., Neiman P. E., Sale G. E., Sanders J. E., Singer J. W., Shulman H. Marrow transplantation for acute nonlymphoblastic leukemia in first remission. N Engl J Med. 1979 Sep 13;301(11):597–599. doi: 10.1056/NEJM197909133011109. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner J. F., Dennert G. Effects of a cloned cell line with NK activity on bone marrow transplants, tumour development and metastasis in vivo. Nature. 1982 Nov 4;300(5887):31–34. doi: 10.1038/300031a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Waterfall M., Rayfield L. S., Brent L. Abrogation of resistance to bone marrow transplantation by induction of specific tolerance in natural killer cells? Nature. 1984 Oct 18;311(5987):663–665. doi: 10.1038/311663a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wei-Feng C., Scollay R., Shortman K. The functional capacity of thymus subpopulations: limit-dilution analysis of all precursors of cytotoxic lymphocytes and of all T cells capable of proliferation in subpopulations separated by the use of peanut agglutinin. J Immunol. 1982 Jul;129(1):18–24. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- von Melchner H., Bartlett P. F. Mechanisms of early allogeneic marrow graft rejection. Immunol Rev. 1983;71:31–56. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1983.tb01067.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


