Abstract
The relationship of the neurofibrillary tangle, found in Alzheimer disease and aged brains, to normal or abnormal cytoskeletal proteins remains elusive. Although immunohistochemical studies have yielded disparate results, most antigenic determinants localized to neurofibrillary tangles are cytoskeletal constituents normally present in neuronal perikarya or dendrites. We report light and electron microscopic immunolabeling of neurofibrillary tangles by a monoclonal antibody to the microtubule-associated protein tau (tau). Dephosphorylation of tissue slices not only increased the number of tau-positive tangles but also produced marked positive immunoreactivity of neuritic plaques. The localization of tau, an axonal protein, to neurofibrillary tangles in the perikaryon in particular suggests that abnormal synthesis, modification, or aggregation of tau may induce aberrant cytoskeletal--cell organelle interactions, subsequent interference with axonal flow, and resultant tangle formation.
Full text
PDF

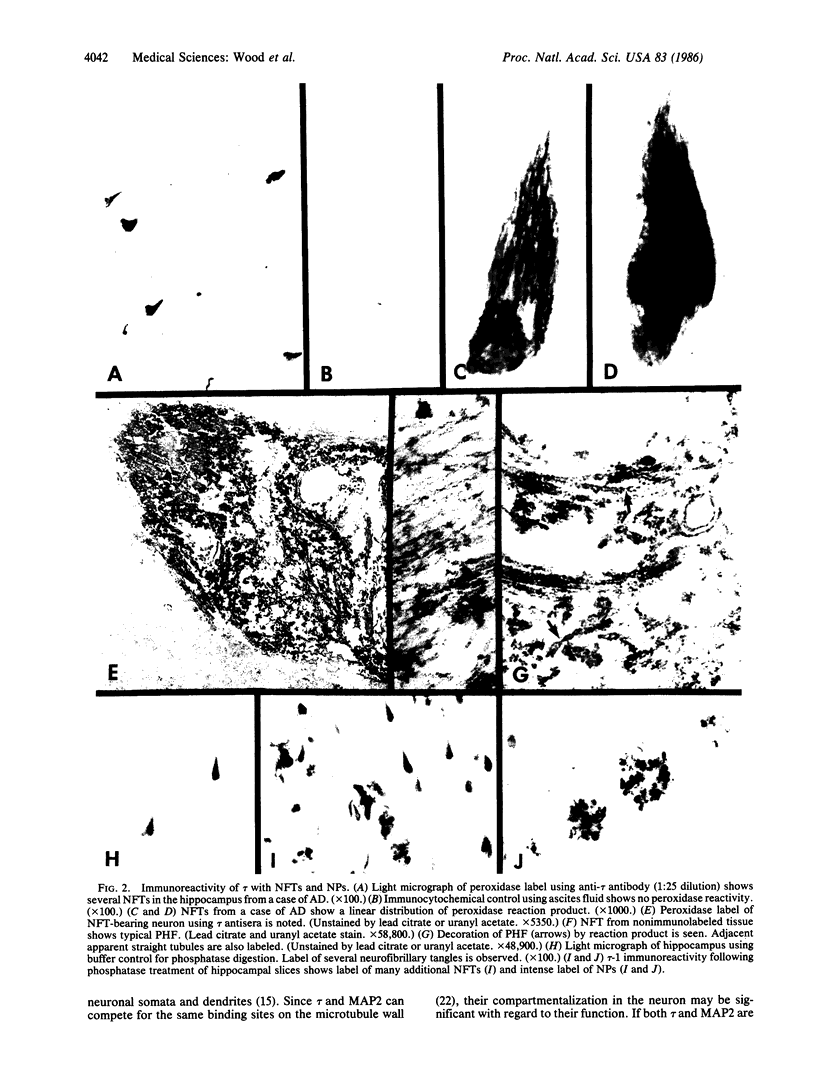

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Balkema G. W., Dräger U. C. Light-dependent antibody labelling of photoreceptors. Nature. 1985 Aug 15;316(6029):630–633. doi: 10.1038/316630a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bernhardt R., Matus A. Light and electron microscopic studies of the distribution of microtubule-associated protein 2 in rat brain: a difference between dendritic and axonal cytoskeletons. J Comp Neurol. 1984 Jun 20;226(2):203–221. doi: 10.1002/cne.902260205. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Binder L. I., Frankfurter A., Rebhun L. I. The distribution of tau in the mammalian central nervous system. J Cell Biol. 1985 Oct;101(4):1371–1378. doi: 10.1083/jcb.101.4.1371. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Caceres A., Binder L. I., Payne M. R., Bender P., Rebhun L., Steward O. Differential subcellular localization of tubulin and the microtubule-associated protein MAP2 in brain tissue as revealed by immunocytochemistry with monoclonal hybridoma antibodies. J Neurosci. 1984 Feb;4(2):394–410. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-02-00394.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cleveland D. W., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. Physical and chemical properties of purified tau factor and the role of tau in microtubule assembly. J Mol Biol. 1977 Oct 25;116(2):227–247. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(77)90214-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dahl D., Selkoe D. J., Pero R. T., Bignami A. Immunostaining of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer's senile dementia with a neurofilament antiserum. J Neurosci. 1982 Jan;2(1):113–119. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.02-01-00113.1982. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dickson D. W., Kress Y., Crowe A., Yen S. H. Monoclonal antibodies to Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. 2. Demonstration of a common antigenic determinant between ANT and neurofibrillary degeneration in progressive supranuclear palsy. Am J Pathol. 1985 Aug;120(2):292–303. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Elovaara I., Paetau A., Lehto V. P., Dahl D., Virtanen I., Palo J. Immunocytochemical studies of Alzheimer neuronal perikarya with intermediate filament antisera. J Neurol Sci. 1983 Dec;62(1-3):315–326. doi: 10.1016/0022-510x(83)90208-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Francon J., Lennon A. M., Fellous A., Mareck A., Pierre M., Nunez J. Heterogeneity of microtubule-associated proteins and brain development. Eur J Biochem. 1982 Dec 15;129(2):465–471. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1982.tb07072.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambetti P., Autilio-Gambetti L., Shecket G. Immunological and silver staining characteristics of neurofibrillary tangles of Alzheimer type. Exp Brain Res. 1982;Suppl 5:15–19. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68507-1_3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gambetti P., Shecket G., Ghetti B., Hirano A., Dahl D. Neurofibrillary changes in human brain. An immunocytochemical study with a neurofilament antiserum. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1983 Jan;42(1):69–79. doi: 10.1097/00005072-198301000-00006. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Tung Y. C., Wisniewski H. M. Alzheimer paired helical filaments: immunochemical identification of polypeptides. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;62(4):259–267. doi: 10.1007/BF00687607. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grundke-Iqbal I., Iqbal K., Wisniewski H. M. Immunocytochemical studies on neurofibrillary changes. Exp Brain Res. 1982;Suppl 5:20–25. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-68507-1_4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ihara Y., Abraham C., Selkoe D. J. Antibodies to paired helical filaments in Alzheimer's disease do not recognize normal brain proteins. Nature. 1983 Aug 25;304(5928):727–730. doi: 10.1038/304727a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Iqbal K., Zaidi T., Thompson C. H., Merz P. A., Wisniewski H. M. Alzheimer paired helical filaments: bulk isolation, solubility, and protein composition. Acta Neuropathol. 1984;62(3):167–177. doi: 10.1007/BF00691849. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIDD M. Paired helical filaments in electron microscopy of Alzheimer's disease. Nature. 1963 Jan 12;197:192–193. doi: 10.1038/197192b0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kosik K. S., Duffy L. K., Dowling M. M., Abraham C., McCluskey A., Selkoe D. J. Microtubule-associated protein 2: monoclonal antibodies demonstrate the selective incorporation of certain epitopes into Alzheimer neurofibrillary tangles. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Dec;81(24):7941–7945. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.24.7941. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Perry G., Rizzuto N., Autilio-Gambetti L., Gambetti P. Paired helical filaments from Alzheimer disease patients contain cytoskeletal components. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3916–3920. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3916. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasool C. G., Abraham C., Anderton B. H., Haugh M., Kahn J., Selkoe D. J. Alzheimer's disease: immunoreactivity of neurofibrillary tangles with anti-neurofilament and anti-paired helical filament antibodies. Brain Res. 1984 Sep 24;310(2):249–260. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(84)90148-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sandoval I. V., Vandekerckhove J. S. A comparative study of the in vitro polymerization of tubulin in the presence of the microtubule-associated proteins MAP2 and tau. J Biol Chem. 1981 Aug 25;256(16):8795–8800. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Selkoe D. J., Ihara Y., Salazar F. J. Alzheimer's disease: insolubility of partially purified paired helical filaments in sodium dodecyl sulfate and urea. Science. 1982 Mar 5;215(4537):1243–1245. doi: 10.1126/science.6120571. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sternberger N. H., Sternberger L. A., Ulrich J. Aberrant neurofilament phosphorylation in Alzheimer disease. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4274–4276. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4274. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- TERRY R. D. THE FINE STRUCTURE OF NEUROFIBRILLARY TANGLES IN ALZHEIMER'S DISEASE. J Neuropathol Exp Neurol. 1963 Oct;22:629–642. doi: 10.1097/00005072-196310000-00005. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weingarten M. D., Lockwood A. H., Hwo S. Y., Kirschner M. W. A protein factor essential for microtubule assembly. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1975 May;72(5):1858–1862. doi: 10.1073/pnas.72.5.1858. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wood J. G., Wallace R. W., Whitaker J. N., Cheung W. Y. Immunocytochemical localization of calmodulin and a heat-labile calmodulin-binding protein (CaM-BP80) in basal ganglia of mouse brain. J Cell Biol. 1980 Jan;84(1):66–76. doi: 10.1083/jcb.84.1.66. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yen S. H., Gaskin F., Fu S. M. Neurofibrillary tangles in senile dementia of the Alzheimer type share an antigenic determinant with intermediate filaments of the vimentin class. Am J Pathol. 1983 Dec;113(3):373–381. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]