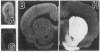
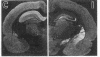
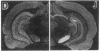
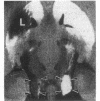
Abstract
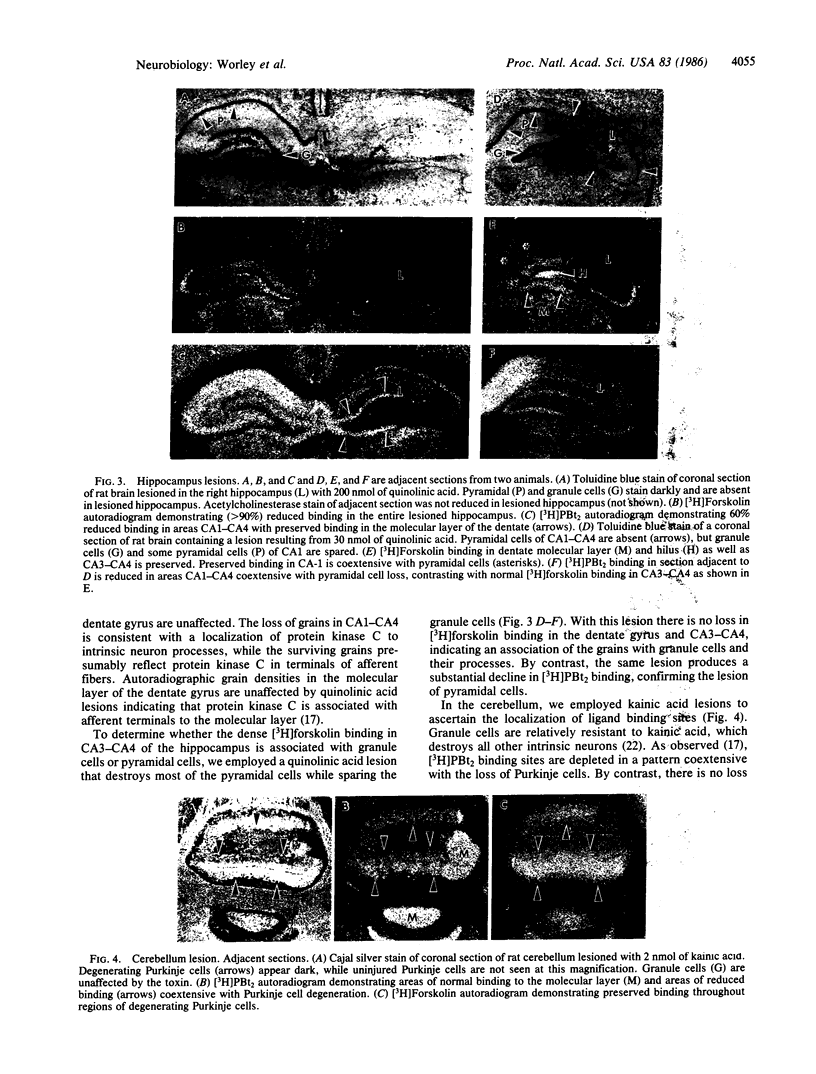
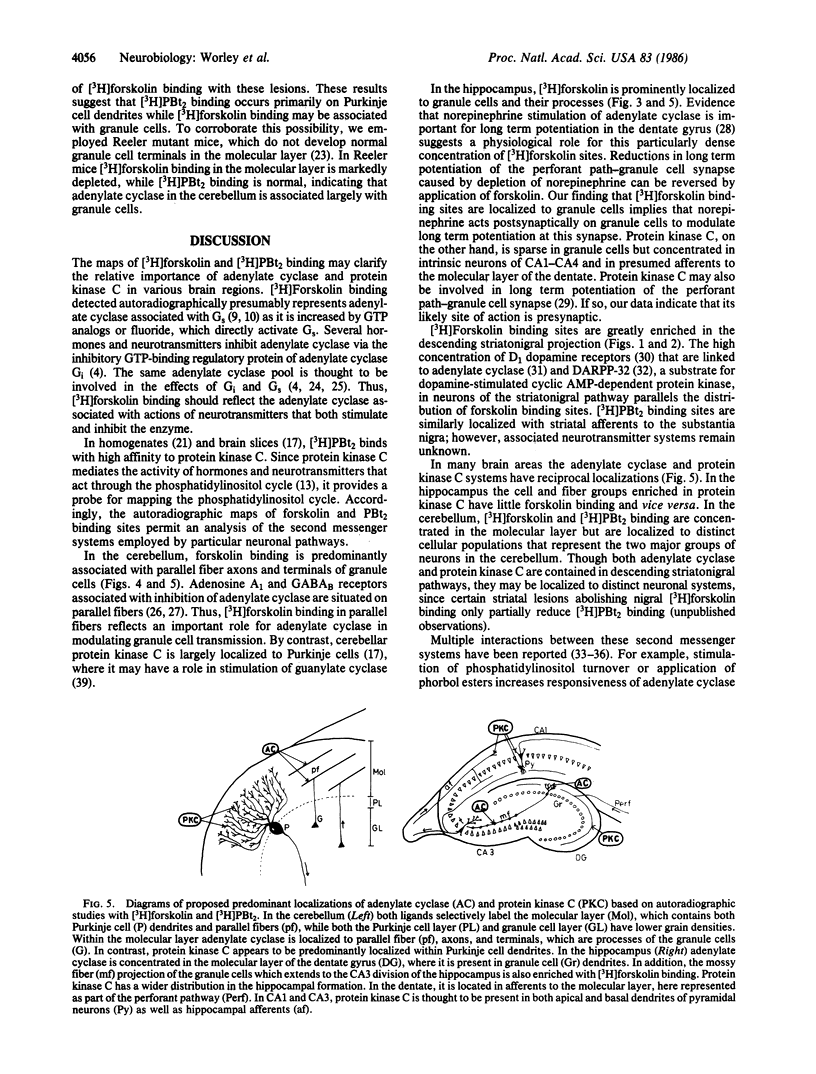
[3H]Forskolin and [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate have been used to map the adenylate cyclase and phosphatidylinositol systems respectively in brain slices by light-microscopic autoradiography. [3H]Forskolin binding to brain sections is displaced potently by forskolin (KD approximately equal to 15 nM) and is enhanced by fluoride and GTP analogs, agents which activate the stimulatory GTP-binding regulatory protein of adenylate cyclase, Gs. Highest [3H]forskolin binding occurs in the corpus striatum, substantia nigra, hippocampus, and molecular layer of the cerebellum. Lesion studies demonstrate that binding sites in the substantia nigra are associated with striatal afferents, while hippocampal sites are localized to granule cell dendrites and mossy fiber terminals, and the intense binding in the cerebellar molecular layer is largely associated with granule cell axons and terminals. Protein kinase C mediates the activity of hormones and neurotransmitters, which act through the phosphatidylinositol cycle, and is labeled with high affinity by [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate. At many synapses, maps of adenylate cyclase and protein kinase C reveal reciprocal distributions, which may have implications for second messenger regulation of synaptic transmission.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baraban J. M., Gould R. J., Peroutka S. J., Snyder S. H. Phorbol ester effects on neurotransmission: interaction with neurotransmitters and calcium in smooth muscle. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(2):604–607. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.2.604. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H., Alger B. E. Protein kinase C regulates ionic conductance in hippocampal pyramidal neurons: electrophysiological effects of phorbol esters. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Apr;82(8):2538–2542. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.8.2538. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barovsky K., Pedone C., Brooker G. Distinct mechanisms of forskolin-stimulated cyclic AMP accumulation and forskolin-potentiated hormone responses in C6-2B cells. Mol Pharmacol. 1984 Mar;25(2):256–260. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bell J. D., Buxton I. L., Brunton L. L. Enhancement of adenylate cyclase activity in S49 lymphoma cells by phorbol esters. Putative effect of C kinase on alpha s-GTP-catalytic subunit interaction. J Biol Chem. 1985 Mar 10;260(5):2625–2628. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Blumberg P. M., Jaken S., König B., Sharkey N. A., Leach K. L., Jeng A. Y., Yeh E. Mechanism of action of the phorbol ester tumor promoters: specific receptors for lipophilic ligands. Biochem Pharmacol. 1984 Mar 15;33(6):933–940. doi: 10.1016/0006-2952(84)90448-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dawson T. M., Gehlert D. R., Yamamura H. I., Barnett A., Wamsley J. K. D-1 dopamine receptors in the rat brain: autoradiographic localization using [3H]SCH 23390. Eur J Pharmacol. 1985 Feb 5;108(3):323–325. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(85)90458-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dunphy W. G., Delclos K. B., Blumberg P. M. Characterization of specific binding of [3H]phorbol 12,13-dibutyrate and [3H]phorbol 12-myristate 13-acetate to mouse brain. Cancer Res. 1980 Oct;40(10):3635–3641. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gehlert D. R., Dawson T. M., Yamamura H. I., Wamsley J. K. Localization of [3H]forskolin binding sites in the rat brain using quantitative autoradiography. Eur J Pharmacol. 1984 Oct 30;106(1):223–225. doi: 10.1016/0014-2999(84)90707-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goodman R. R., Kuhar M. J., Hester L., Snyder S. H. Adenosine receptors: autoradiographic evidence for their location on axon terminals of excitatory neurons. Science. 1983 May 27;220(4600):967–969. doi: 10.1126/science.6302841. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Green D. A., Clark R. B. Direct evidence for the role of the coupling proteins in forskolin activation of adenylate cyclase. J Cyclic Nucleotide Res. 1982;8(5):337–346. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herndon R. M., Coyle J. T., Addicks E. Ultrastructural analysis of kainic acid lesion to cerebellar cortex. Neuroscience. 1980;5(6):1015–1026. doi: 10.1016/0306-4522(80)90182-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hildebrandt J. D., Birnbaumer L. Inhibitory regulation of adenylyl cyclase in the absence of stimulatory regulation. Requirements and kinetics of guanine nucleotide-induced inhibition of the cyc- S49 adenylyl cyclase. J Biol Chem. 1983 Nov 10;258(21):13141–13147. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hollingsworth E. B., Sears E. B., Daly J. W. An activator of protein kinase C (phorbol-12-myristate-13-acetate) augments 2-chloroadenosine-elicited accumulation of cyclic AMP in guinea pig cerebral cortical particulate preparations. FEBS Lett. 1985 May 20;184(2):339–342. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80634-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kassis S., Zaremba T., Patel J., Fishman P. H. Phorbol esters and beta-adrenergic agonists mediate desensitization of adenylate cyclase in rat glioma C6 cells by distinct mechanisms. J Biol Chem. 1985 Jul 25;260(15):8911–8917. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katada T., Northup J. K., Bokoch G. M., Ui M., Gilman A. G. The inhibitory guanine nucleotide-binding regulatory component of adenylate cyclase. Subunit dissociation and guanine nucleotide-dependent hormonal inhibition. J Biol Chem. 1984 Mar 25;259(6):3578–3585. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kebabian J. W., Calne D. B. Multiple receptors for dopamine. Nature. 1979 Jan 11;277(5692):93–96. doi: 10.1038/277093a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kupfermann I. Modulatory actions of neurotransmitters. Annu Rev Neurosci. 1979;2:447–465. doi: 10.1146/annurev.ne.02.030179.002311. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Merrifield R. E., Simmons H. E. Topology of bonding in pi-electron systems. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jan;82(1):1–3. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nabika T., Nara Y., Yamori Y., Lovenberg W., Endo J. Angiotensin II and phorbol ester enhance isoproterenol- and vasoactive intestinal peptide (VIP)-induced cyclic AMP accumulation in vascular smooth muscle cells. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 Aug 30;131(1):30–36. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91765-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson C. A., Seamon K. B. Regulation of [3H]forskolin binding to human platelet membranes by GppNHp, NaF, and prostaglandin E1. FEBS Lett. 1985 Apr 22;183(2):349–352. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(85)80808-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nelson R. B., Routtenberg A. Characterization of protein F1 (47 kDa, 4.5 pI): a kinase C substrate directly related to neural plasticity. Exp Neurol. 1985 Jul;89(1):213–224. doi: 10.1016/0014-4886(85)90277-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. Turnover of inositol phospholipids and signal transduction. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1365–1370. doi: 10.1126/science.6147898. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ouimet C. C., Miller P. E., Hemmings H. C., Jr, Walaas S. I., Greengard P. DARPP-32, a dopamine- and adenosine 3':5'-monophosphate-regulated phosphoprotein enriched in dopamine-innervated brain regions. III. Immunocytochemical localization. J Neurosci. 1984 Jan;4(1):111–124. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.04-01-00111.1984. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Phelps M. E., Mazziotta J. C. Positron emission tomography: human brain function and biochemistry. Science. 1985 May 17;228(4701):799–809. doi: 10.1126/science.2860723. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schramm M., Selinger Z. Message transmission: receptor controlled adenylate cyclase system. Science. 1984 Sep 21;225(4668):1350–1356. doi: 10.1126/science.6147897. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Padgett W., Daly J. W. Forskolin: unique diterpene activator of adenylate cyclase in membranes and in intact cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Jun;78(6):3363–3367. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.6.3363. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K. B., Vaillancourt R., Edwards M., Daly J. W. Binding of [3H]forskolin to rat brain membranes. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Aug;81(16):5081–5085. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.16.5081. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seamon K., Daly J. W. Activation of adenylate cyclase by the diterpene forskolin does not require the guanine nucleotide regulatory protein. J Biol Chem. 1981 Oct 10;256(19):9799–9801. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snyder S. H. Drug and neurotransmitter receptors in the brain. Science. 1984 Apr 6;224(4644):22–31. doi: 10.1126/science.6322304. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stanton P. K., Sarvey J. M. Depletion of norepinephrine, but not serotonin, reduces long-term potentiation in the dentate gyrus of rat hippocampal slices. J Neurosci. 1985 Aug;5(8):2169–2176. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-08-02169.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Unnerstall J. R., Niehoff D. L., Kuhar M. J., Palacios J. M. Quantitative receptor autoradiography using [3H]ultrofilm: application to multiple benzodiazepine receptors. J Neurosci Methods. 1982 Jul;6(1-2):59–73. doi: 10.1016/0165-0270(82)90016-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Watson S. P., McConnell R. T., Lapetina E. G. The rapid formation of inositol phosphates in human platelets by thrombin is inhibited by prostacyclin. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 10;259(21):13199–13203. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wojcik W. J., Cavalla D., Neff N. H. Co-localized adenosine A1 and gamma-aminobutyric acid B (GABAB) receptors of cerebellum may share a common adenylate cyclase catalytic unit. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 1985 Jan;232(1):62–66. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Worley P. F., Baraban J. M., Snyder S. H. Heterogeneous localization of protein kinase C in rat brain: autoradiographic analysis of phorbol ester receptor binding. J Neurosci. 1986 Jan;6(1):199–207. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.06-01-00199.1986. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Young W. S., 3rd, Kuhar M. J. A new method for receptor autoradiography: [3H]opioid receptors in rat brain. Brain Res. 1979 Dec 28;179(2):255–270. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(79)90442-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zwiller J., Revel M. O., Malviya A. N. Protein kinase C catalyzes phosphorylation of guanylate cyclase in vitro. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 10;260(3):1350–1353. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]