Abstract
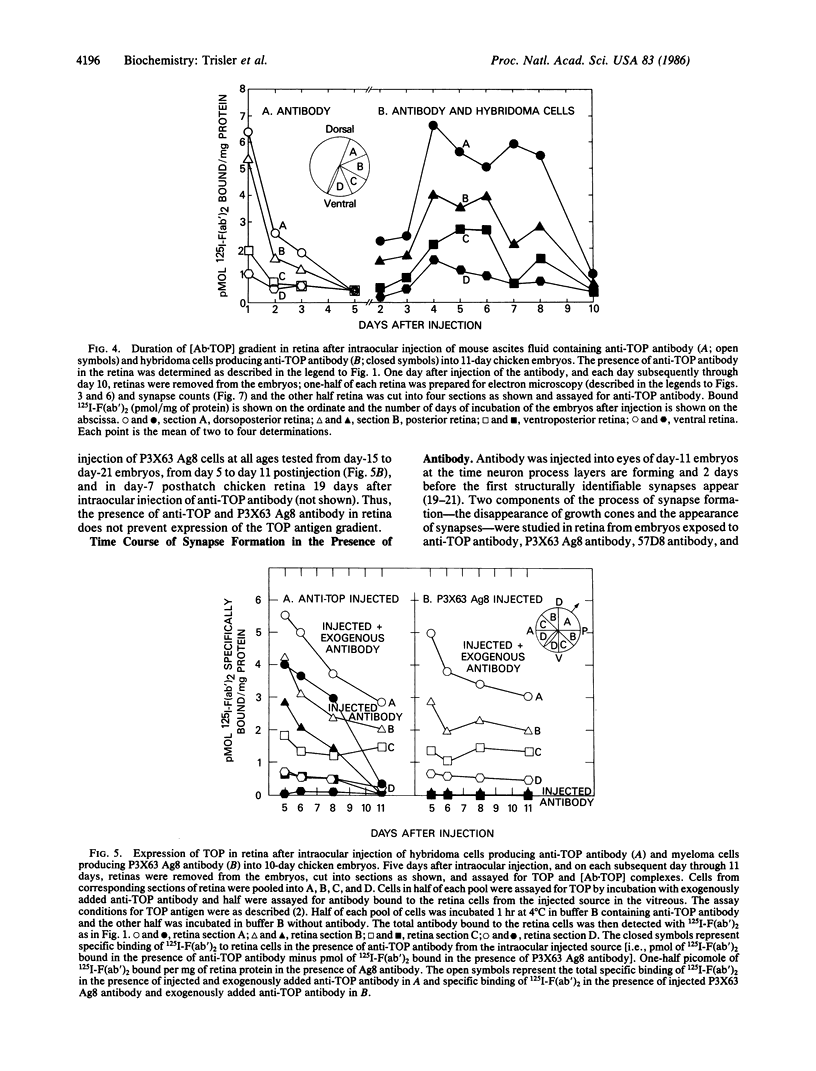
A topographic gradient of TOP molecules in retina can be used to identify neuron position. Antibody to TOP from hybridoma cells that were injected into in vivo embryo eyes diffused into the retina and bound in a topographic gradient of [antibody.TOP] ([Ab.TOP]) complexes. Synapse formation in retina was inhibited in the presence of anti-TOP antibody. This suggests that TOP is involved in synapse formation and that recognition of position by neurons is necessary for normal synapse formation.
Full text
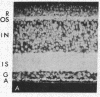
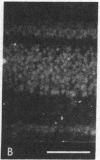
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baskin D. G., Erlandsen S. L., Parsons J. A. Influence of hydrogen peroxide or alcoholic sodium hydroxide on the immunocytochemical detection of growth hormone and prolactin after osmium fixation. J Histochem Cytochem. 1979 Sep;27(9):1290–1292. doi: 10.1177/27.9.383831. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crawford G., Slemmon J. R., Salvaterra P. M. Monoclonal antibodies selective for Drosophila melanogaster choline acetyltransferase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Apr 10;257(7):3853–3856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Daniels M. P., Vogel Z. Localization of alpha-bungarotoxin binding sites in synapses of the developing chick retina. Brain Res. 1980 Nov 10;201(1):45–56. doi: 10.1016/0006-8993(80)90774-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- De Cerro M. P., Snider R. S. Studies on the developing cerebellum. Ultrastructure of the growth cones. J Comp Neurol. 1968 Jul;133(3):341–362. doi: 10.1002/cne.901330305. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fraser S. E., Murray B. A., Chuong C. M., Edelman G. M. Alteration of the retinotectal map in Xenopus by antibodies to neural cell adhesion molecules. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Jul;81(13):4222–4226. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.13.4222. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hausman R. E., Moscona A. A. Immunologic detection of retina cognin on the surface of embryonic cells. Exp Cell Res. 1979 Mar 15;119(2):191–204. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(79)90348-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Henke-Fahle S., Bonhoeffer F. Inhibition of axonal growth by a monoclonal antibody. Nature. 1983 May 5;303(5912):65–67. doi: 10.1038/303065a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hughes W. F., LaVelle A. On the synaptogenic sequence in the chick retina. Anat Rec. 1974 Jul;179(3):297–301. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091790302. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kawana E., Sandri C., Akert K. Ultrastructure of growth cones in the cerebellar cortex of the neonatal rat and cat. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1971;115(2):284–298. doi: 10.1007/BF00391129. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Leifer D., Lipton S. A., Barnstable C. J., Masland R. H. Monoclonal antibody to Thy-1 enhances regeneration of processes by rat retinal ganglion cells in culture. Science. 1984 Apr 20;224(4646):303–306. doi: 10.1126/science.6143400. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Levi-Montalcini R., Booker B. DESTRUCTION OF THE SYMPATHETIC GANGLIA IN MAMMALS BY AN ANTISERUM TO A NERVE-GROWTH PROTEIN. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1960 Mar;46(3):384–391. doi: 10.1073/pnas.46.3.384. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lindner J., Rathjen F. G., Schachner M. L1 mono- and polyclonal antibodies modify cell migration in early postnatal mouse cerebellum. 1983 Sep 29-Oct 5Nature. 305(5933):427–430. doi: 10.1038/305427a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Malkinson M. The transmission of passive immunity to Escherichia coli from mother to young in the domestic fowl (Gallus domesticus). Immunology. 1965 Oct;9(4):311–317. [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- SPERRY R. W. CHEMOAFFINITY IN THE ORDERLY GROWTH OF NERVE FIBER PATTERNS AND CONNECTIONS. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1963 Oct;50:703–710. doi: 10.1073/pnas.50.4.703. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz M., Spirman N. Sprouting from chicken embryo dorsal root ganglia induced by nerve growth factor is specifically inhibited by affinity-purified antiganglioside antibodies. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1982 Oct;79(19):6080–6083. doi: 10.1073/pnas.79.19.6080. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sheffield J. B., Fischman D. A. Intercellular junctions in the developing neural retina of the chick embryo. Z Zellforsch Mikrosk Anat. 1970;104(3):405–418. doi: 10.1007/BF00335691. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strauss W. L., Nirenberg M. Inhibition of choline acetyltransferase by monoclonal antibodies. J Neurosci. 1985 Jan;5(1):175–180. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.05-01-00175.1985. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thanos S., Bonhoeffer F., Rutishauser U. Fiber-fiber interaction and tectal cues influence the development of the chicken retinotectal projection. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1984 Mar;81(6):1906–1910. doi: 10.1073/pnas.81.6.1906. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Thiery J. P., Brackenbury R., Rutishauser U., Edelman G. M. Adhesion among neural cells of the chick embryo. II. Purification and characterization of a cell adhesion molecule from neural retina. J Biol Chem. 1977 Oct 10;252(19):6841–6845. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trapp B. D., Itoyama Y., Sternberger N. H., Quarles R. H., Webster H. Immunocytochemical localization of P0 protein in Golgi complex membranes and myelin of developing rat Schwann cells. J Cell Biol. 1981 Jul;90(1):1–6. doi: 10.1083/jcb.90.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trisler G. D., Schneider M. D., Nirenberg M. A topographic gradient of molecules in retina can be used to identify neuron position. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1981 Apr;78(4):2145–2149. doi: 10.1073/pnas.78.4.2145. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Warner A. E., Guthrie S. C., Gilula N. B. Antibodies to gap-junctional protein selectively disrupt junctional communication in the early amphibian embryo. Nature. 1984 Sep 13;311(5982):127–131. doi: 10.1038/311127a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]