Abstract
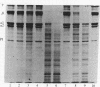
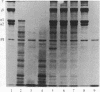
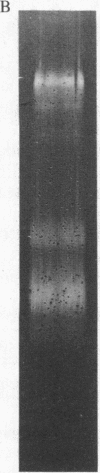
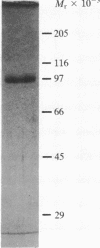
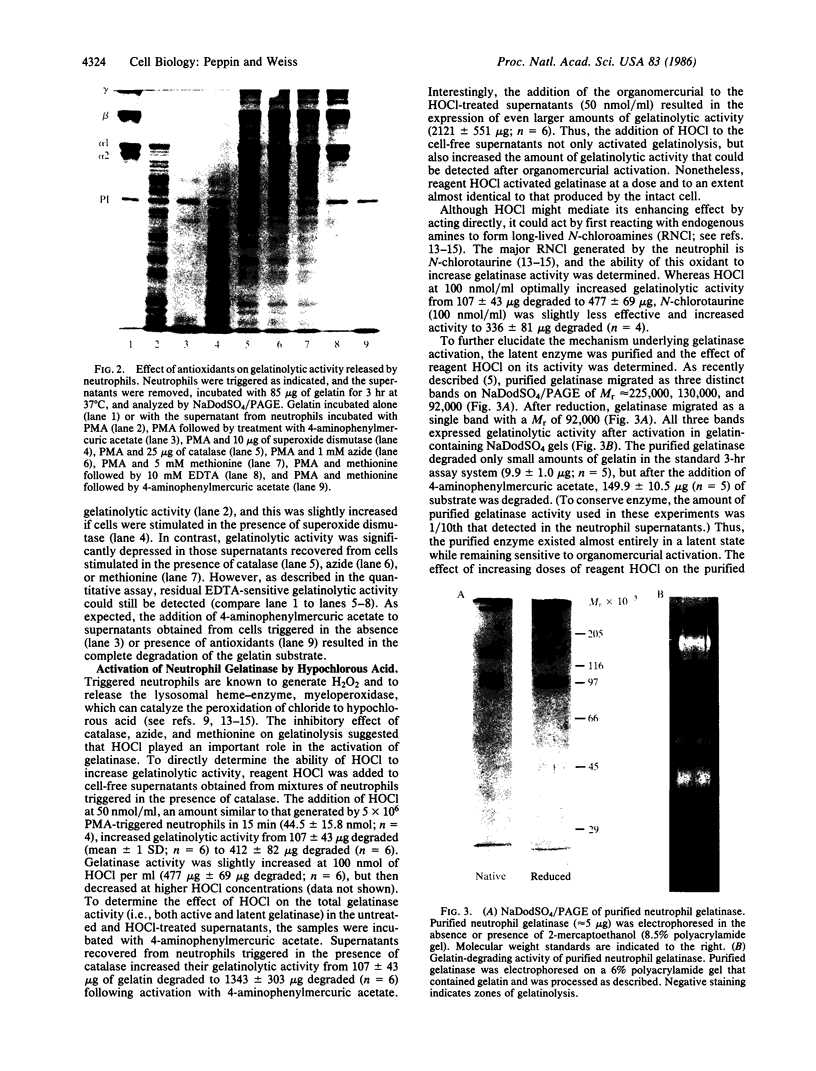
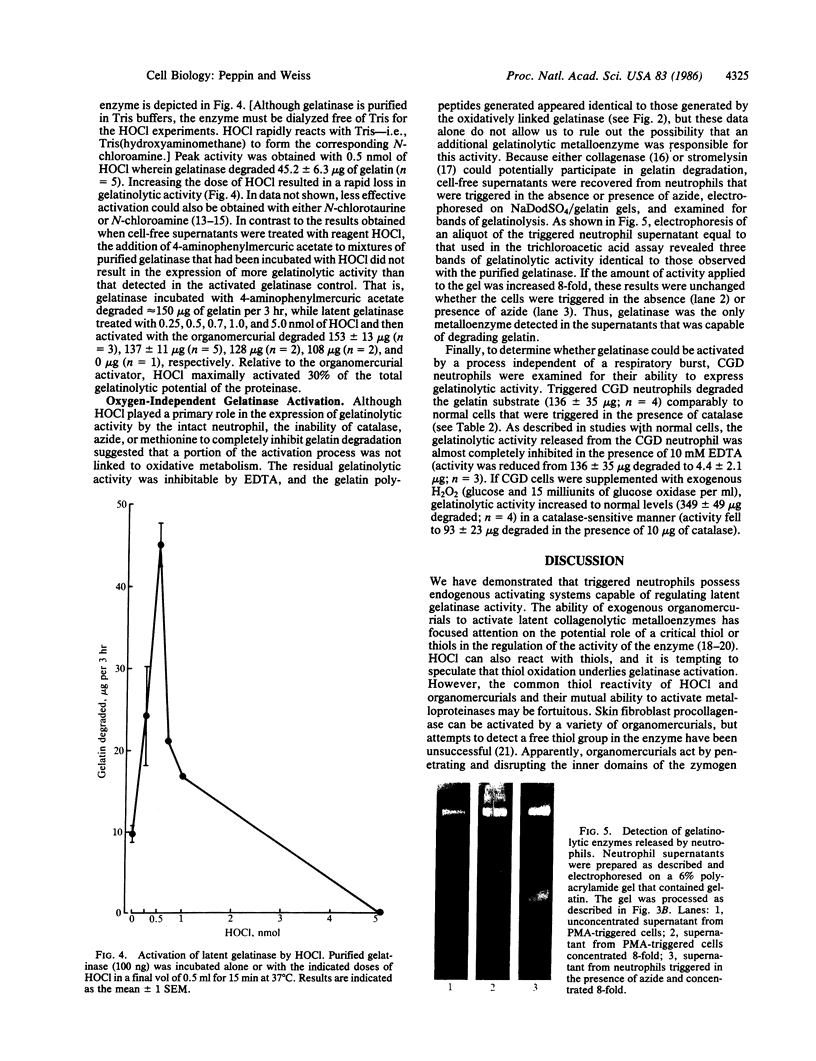
Triggered human neutrophils degraded denatured type I collagen (gelatin) by releasing and activating the latent metalloenzyme, gelatinase. The ability of the neutrophil to activate this enzyme was significantly, but not completely, inhibited by agents known to inhibit or scavenge chlorinated oxidants generated by the H2O2/myeloperoxidase/chloride system. A direct role for chlorinated oxidants in this process was confirmed by the ability of reagent HOCl to activate the latent enzyme in either the cell-free supernatant or in a highly purified state. Gelatinase activity was also expressed by triggered neutrophils isolated from patients with chronic granulomatous disease. The amount of gelatinolytic activity expressed by the patients' cells was similar to that released by normal neutrophils that were triggered in the presence of antioxidants. Thus, human neutrophils have the ability to activate gelatinase by either an HOCl-dependent process or an uncharacterized oxygen-independent process. The ability of the neutrophil to directly regulate this enzyme suggests an important role for the metalloproteinase in physiologic and pathophysiologic connective tissue metabolism.
Full text
PDF


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Chin J. R., Murphy G., Werb Z. Stromelysin, a connective tissue-degrading metalloendopeptidase secreted by stimulated rabbit synovial fibroblasts in parallel with collagenase. Biosynthesis, isolation, characterization, and substrates. J Biol Chem. 1985 Oct 5;260(22):12367–12376. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Cooper T. W., Eisen A. Z., Stricklin G. P., Welgus H. G. Platelet-derived collagenase inhibitor: characterization and subcellular localization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 May;82(9):2779–2783. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.9.2779. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Curnutte J. T. Activation of human neutrophil nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate, reduced (triphosphopyridine nucleotide, reduced) oxidase by arachidonic acid in a cell-free system. J Clin Invest. 1985 May;75(5):1740–1743. doi: 10.1172/JCI111885. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Dewald B., Bretz U., Baggiolini M. Release of gelatinase from a novel secretory compartment of human neutrophils. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):518–525. doi: 10.1172/JCI110643. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gallin J. I., Buescher E. S. Abnormal regulation of inflammatory skin responses in male patients with chronic granulomatous disease. Inflammation. 1983 Sep;7(3):227–232. doi: 10.1007/BF00917259. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grisham M. B., Jefferson M. M., Melton D. F., Thomas E. L. Chlorination of endogenous amines by isolated neutrophils. Ammonia-dependent bactericidal, cytotoxic, and cytolytic activities of the chloramines. J Biol Chem. 1984 Aug 25;259(16):10404–10413. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Harris E. D., Jr, Krane S. M. An endopeptidase from rheumatoid synovial tissue culture. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1972 Feb 28;258(2):566–576. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(72)90249-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. S., Hasty K. A., Kang A. H., Mainardi C. L. Secretion of collagenolytic enzymes by human polymorphonuclear leukocytes. Coll Relat Res. 1984 Dec;4(6):467–477. doi: 10.1016/s0174-173x(84)80013-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hibbs M. S., Hasty K. A., Seyer J. M., Kang A. H., Mainardi C. L. Biochemical and immunological characterization of the secreted forms of human neutrophil gelatinase. J Biol Chem. 1985 Feb 25;260(4):2493–2500. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Laemmli U. K. Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature. 1970 Aug 15;227(5259):680–685. doi: 10.1038/227680a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Macartney H. W., Tschesche H. Latent and active human polymorphonuclear leukocyte collagenases. Isolation, purification and characterisation. Eur J Biochem. 1983 Jan 17;130(1):71–78. doi: 10.1111/j.1432-1033.1983.tb07118.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Bretz U., Baggiolini M., Reynolds J. J. The latent collagenase and gelatinase of human polymorphonuclear neutrophil leucocytes. Biochem J. 1980 Nov 15;192(2):517–525. doi: 10.1042/bj1920517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Murphy G., Reynolds J. J., Bretz U., Baggiolini M. Partial purification of collagenase and gelatinase from human polymorphonuclear leucocytes. Analysis of their actions on soluble and insoluble collagens. Biochem J. 1982 Apr 1;203(1):209–221. doi: 10.1042/bj2030209. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neurath H. Evolution of proteolytic enzymes. Science. 1984 Apr 27;224(4647):350–357. doi: 10.1126/science.6369538. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sopata I., Wize J. A latent gelatin specific proteinase of human leucocytes and its activation. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1979 Dec 7;571(2):305–312. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(79)90100-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stricklin G. P., Jeffrey J. J., Roswit W. T., Eisen A. Z. Human skin fibroblast procollagenase: mechanisms of activation by organomercurials and trypsin. Biochemistry. 1983 Jan 4;22(1):61–68. doi: 10.1021/bi00270a009. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Test S. T., Lampert M. B., Ossanna P. J., Thoene J. G., Weiss S. J. Generation of nitrogen-chlorine oxidants by human phagocytes. J Clin Invest. 1984 Oct;74(4):1341–1349. doi: 10.1172/JCI111544. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Uitto V. J., Turto H., Huttunen A., Lindy S., Uitto J. Activation of human leukocyte collagenase by compounds reacting with sulfhydryl groups. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1980;613(1):168–177. doi: 10.1016/0005-2744(80)90203-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Klein R., Slivka A., Wei M. Chlorination of taurine by human neutrophils. Evidence for hypochlorous acid generation. J Clin Invest. 1982 Sep;70(3):598–607. doi: 10.1172/JCI110652. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Lampert M. B., Test S. T. Long-lived oxidants generated by human neutrophils: characterization and bioactivity. Science. 1983 Nov 11;222(4624):625–628. doi: 10.1126/science.6635660. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Weiss S. J., Peppin G., Ortiz X., Ragsdale C., Test S. T. Oxidative autoactivation of latent collagenase by human neutrophils. Science. 1985 Feb 15;227(4688):747–749. doi: 10.1126/science.2982211. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Welgus H. G., Jeffrey J. J., Stricklin G. P., Eisen A. Z. The gelatinolytic activity of human skin fibroblast collagenase. J Biol Chem. 1982 Oct 10;257(19):11534–11539. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]