Abstract
Mutations at the fused (Fu) locus on chromosome 17 of the mouse disrupt embryonic development by altering the organization of the neurectoderm. We have examined the interactions among several independent fused mutations, including a deletion of the locus, to define the nature of the mutant defects. Closely linked restriction fragment length polymorphisms made possible the unambiguous identification of genotype in all progeny. Tests with the deletion, as well as interactions among alleles, indicate that all three spontaneous mutations are "gain of function" defects. Comparisons of relative viabilities of the various mutant combinations rank them into a series of increasing severity and place constraints on possible modes of gene action.
Full text
PDF

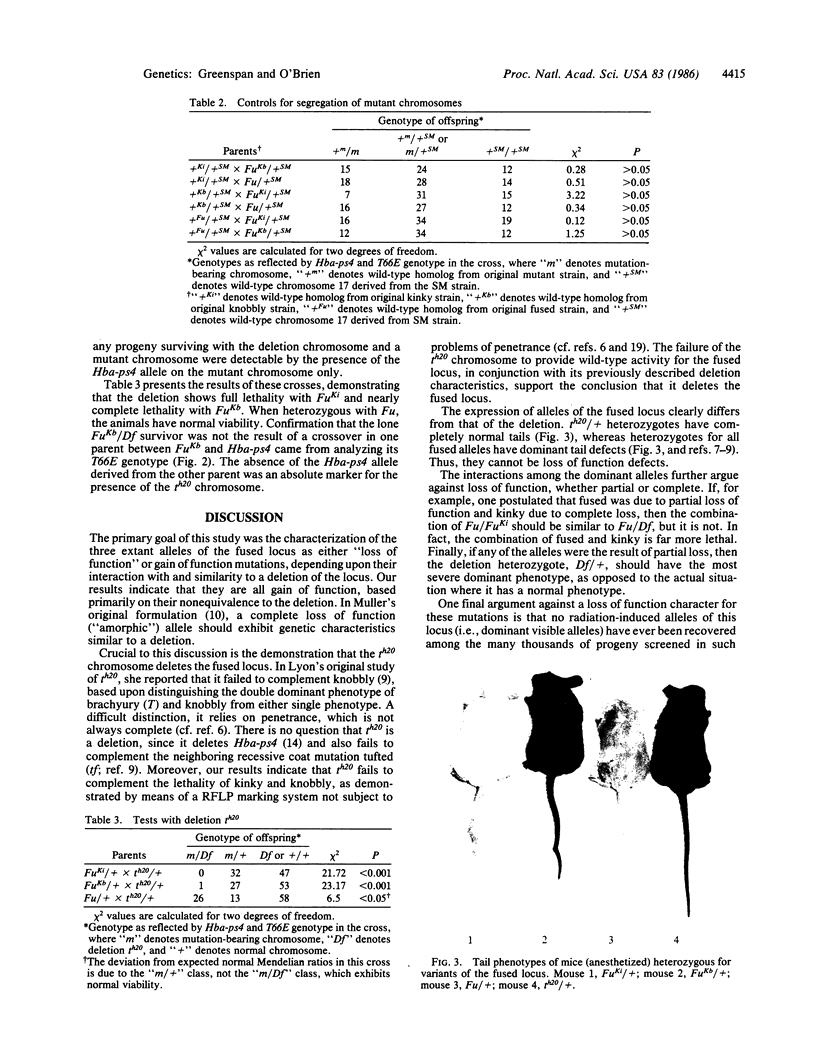


Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- D'Eustachio P., Fein B., Michaelson J., Taylor B. A. The alpha-globin pseudogene on mouse chromosome 17 is closely linked to H-2. J Exp Med. 1984 Mar 1;159(3):958–963. doi: 10.1084/jem.159.3.958. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox H. S., Martin G. R., Lyon M. F., Herrmann B., Frischauf A. M., Lehrach H., Silver L. M. Molecular probes define different regions of the mouse t complex. Cell. 1985 Jan;40(1):63–69. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(85)90309-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox H. S., Silver L. M., Martin G. R. An alpha globin pseudogene is located within the mouse t complex. Immunogenetics. 1984;19(2):125–130. doi: 10.1007/BF00387855. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Gimlich R. L., Cooke J. Cell lineage and the induction of second nervous systems in amphibian development. Nature. 1983 Dec 1;306(5942):471–473. doi: 10.1038/306471a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Greenwald I. S., Sternberg P. W., Horvitz H. R. The lin-12 locus specifies cell fates in Caenorhabditis elegans. Cell. 1983 Sep;34(2):435–444. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(83)90377-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Grosschedl R., Weaver D., Baltimore D., Costantini F. Introduction of a mu immunoglobulin gene into the mouse germ line: specific expression in lymphoid cells and synthesis of functional antibody. Cell. 1984 Oct;38(3):647–658. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90259-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Herrmann B., Bućan M., Mains P. E., Frischauf A. M., Silver L. M., Lehrach H. Genetic analysis of the proximal portion of the mouse t complex: evidence for a second inversion within t haplotypes. Cell. 1986 Feb 14;44(3):469–476. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(86)90468-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Jacobs-Cohen R. J., Spiegelman M., Cookingham J. C., Bennett D. Knobbly, a new dominant mutation in the mouse that affects embryonic ectoderm organization. Genet Res. 1984 Feb;43(1):43–50. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300025702. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., Bechtol K. B. Derivation of mutant t-haplotypes of the mouse by presumed duplication or deletion. Genet Res. 1977 Aug;30(1):63–76. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300017468. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., Glenister P. H., Loutit J. F., Evans E. P., Peters J. A presumed deletion covering the W and Ph loci of the mouse. Genet Res. 1984 Oct;44(2):161–168. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300026367. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lyon M. F., Jarvis S. E., Sayers I., Johnson D. R. Complementation reactions of a lethal mouse t-haplotype believed to include a deletion. Genet Res. 1979 Apr;33(2):153–161. doi: 10.1017/s0016672300018280. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Poulson D. F. Chromosomal Deficiencies and the Embryonic Development of Drosophila Melanogaster. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1937 Mar;23(3):133–137. doi: 10.1073/pnas.23.3.133. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed S C. The Inheritance and Expression of Fused, a New Mutation in the House Mouse. Genetics. 1937 Jan;22(1):1–13. doi: 10.1093/genetics/22.1.1. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-Herrero E., Vernós I., Marco R., Morata G. Genetic organization of Drosophila bithorax complex. Nature. 1985 Jan 10;313(5998):108–113. doi: 10.1038/313108a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- THEILER K., GLUECKSOHN-WAELSCH S. The morphological effects and the development of the fused mutation in the mouse. Anat Rec. 1956 May;125(1):83–103. doi: 10.1002/ar.1091250107. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]