Abstract
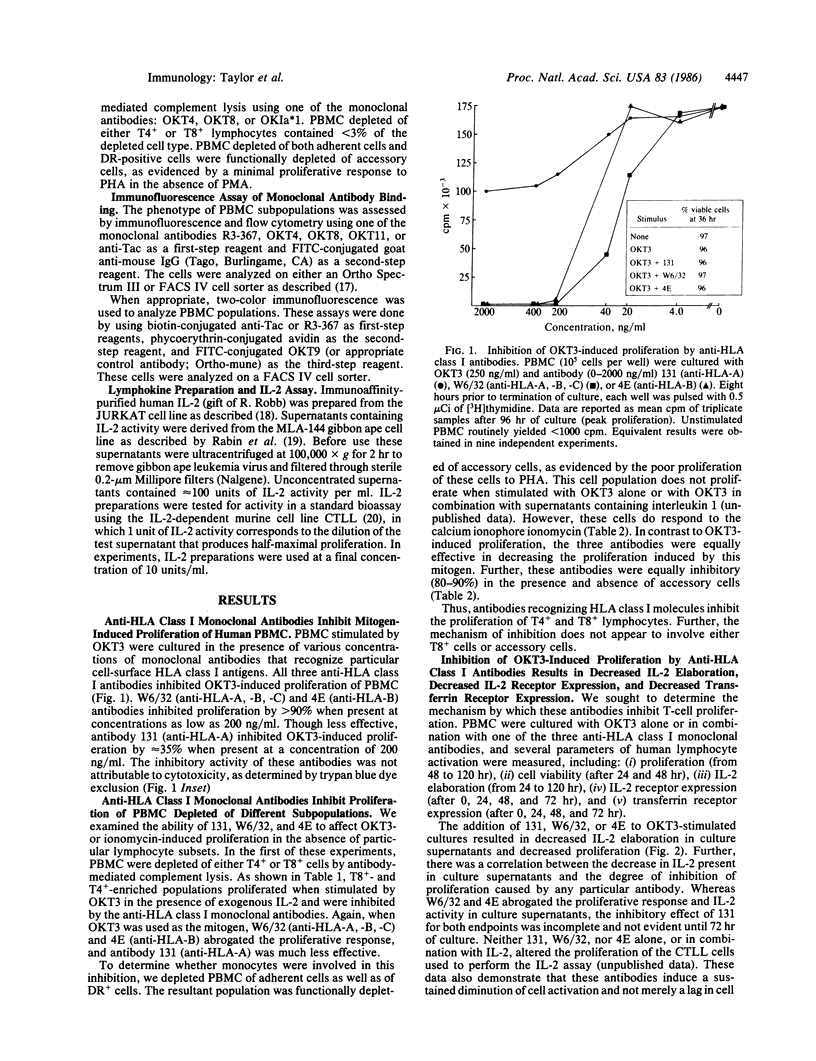
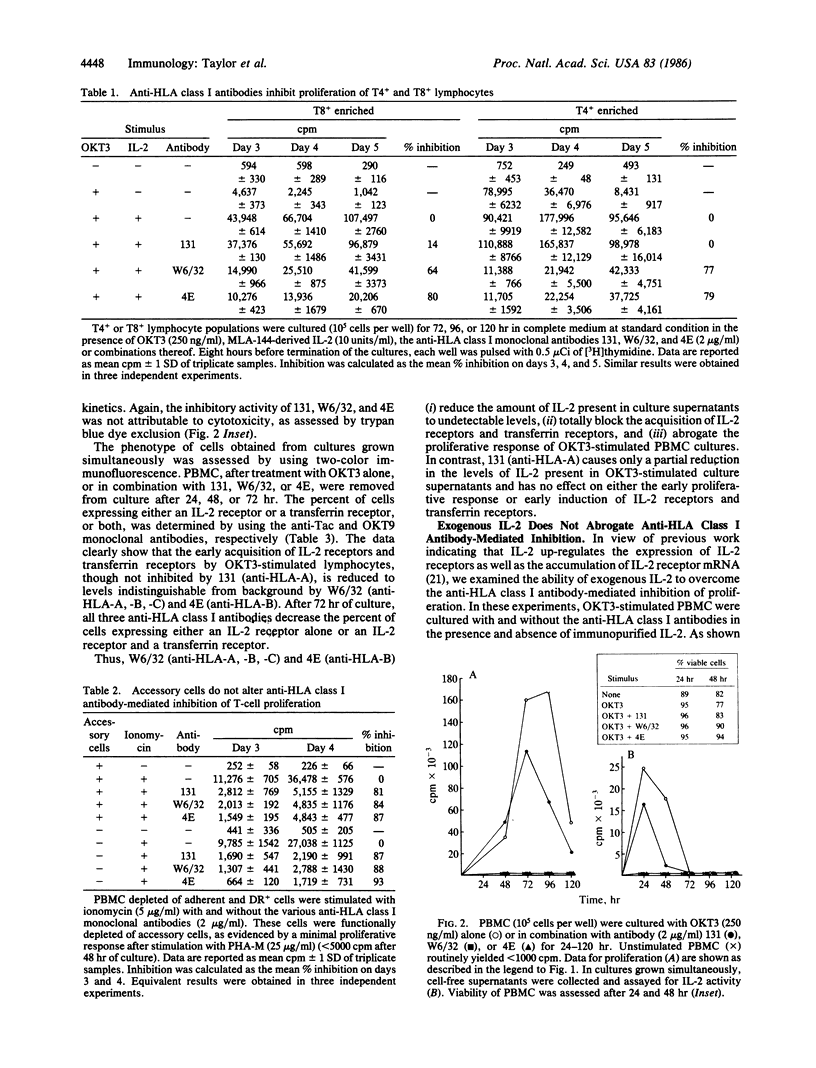
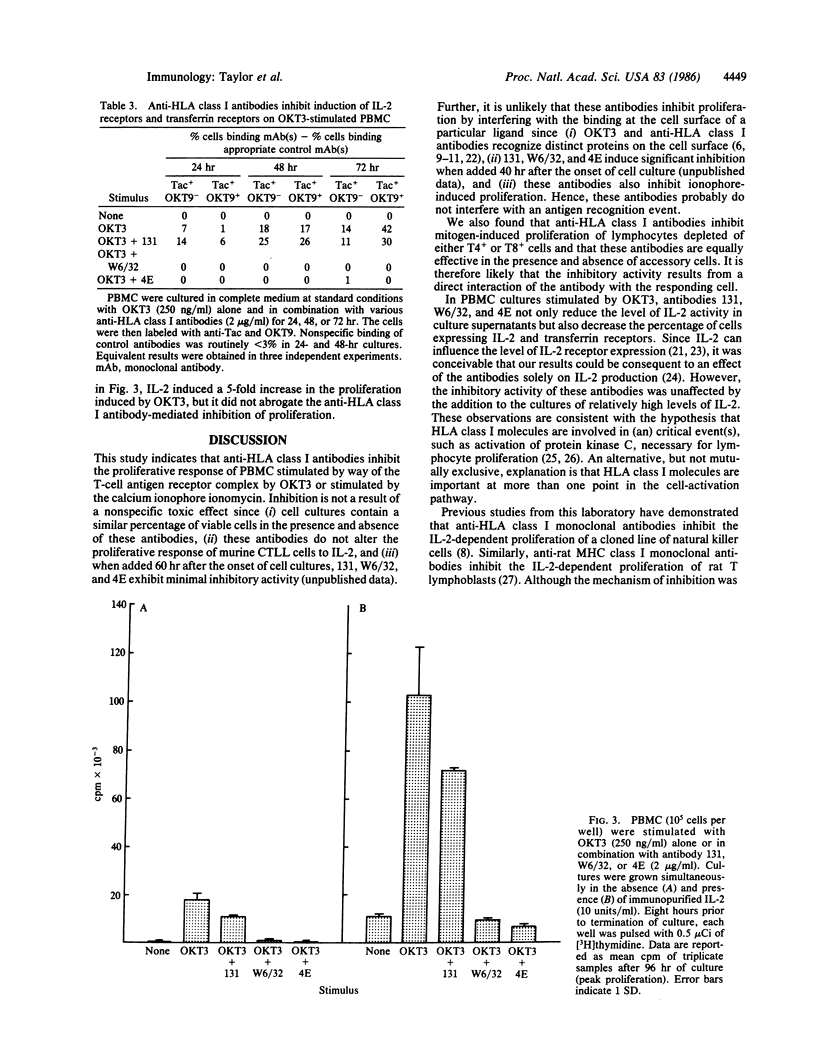
This investigation addressed the role of major histocompatibility complex-encoded class I molecules in the activation and proliferation of human lymphocytes. We studied the effect of antibodies specific for HLA-A and HLA-B locus gene products on mitogen-stimulated peripheral blood mononuclear cell (PBMC) subpopulations. Three individually derived, well-characterized anti-HLA class I monoclonal antibodies were demonstrated to inhibit the proliferation of human PBMC stimulated by either OKT3 or the calcium ionophore ionomycin. The antibody directed against HLA-A, -B, and -C locus gene products (W6/32) and the antibody directed against HLA-B locus gene products (4E) inhibited proliferation induced by either mitogen by 70-90%. The HLA-A locus-specific antibody (131), though inhibiting ionomycin-induced proliferation by 80-90%, was much less effective when OKT3 was the stimulus. The inhibition affected T4+ and T8+ cells and was not mediated by DR+ accessory cells. The inhibitory effect of these antibodies was associated with a decrease in the level of interleukin 2 activity present in culture supernatants, decreased interleukin 2 receptor expression, and decreased transferrin receptor expression and was not overcome by the addition of exogenous interleukin 2. Our results suggest that HLA class I molecules are directly involved in the early critical events of human lymphocyte activation and proliferation.
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Baker P. E., Gillis S., Smith K. A. Monoclonal cytolytic T-cell lines. J Exp Med. 1979 Jan 1;149(1):273–278. doi: 10.1084/jem.149.1.273. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Berridge M. J., Irvine R. F. Inositol trisphosphate, a novel second messenger in cellular signal transduction. Nature. 1984 Nov 22;312(5992):315–321. doi: 10.1038/312315a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickell P. M., Latchman D. S., Murphy D., Willison K., Rigby P. W. Activation of a Qa/Tla class I major histocompatibility antigen gene is a general feature of oncogenesis in the mouse. Nature. 1983 Dec 22;306(5945):756–760. doi: 10.1038/306756a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Brickell P. M., Latchman D. S., Murphy D., Willison K., Rigby P. W. The class I major histocompatibility antigen gene activated in a line of SV40-transformed mouse cells is H-2Dd, not Qa/Tla. Nature. 1985 Jul 11;316(6024):162–163. doi: 10.1038/316162a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Böyum A. Isolation of mononuclear cells and granulocytes from human blood. Isolation of monuclear cells by one centrifugation, and of granulocytes by combining centrifugation and sedimentation at 1 g. Scand J Clin Lab Invest Suppl. 1968;97:77–89. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chouaib S., Welte K., Dupont B. Differential effect of anti-beta 2-microglobulin on IL 2 production and IL 2 receptor expression in the primary mixed lymphocyte culture reaction. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):940–948. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Chvatchko Y., Van Obberghen E., Kiger N., Fehlmann M. Immunoprecipitation of insulin receptors by antibodies against Class 1 antigens of the murine H-2 major histocompatibility complex. FEBS Lett. 1983 Nov 14;163(2):207–211. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(83)80820-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Depper J. M., Leonard W. J., Drogula C., Krönke M., Waldmann T. A., Greene W. C. Interleukin 2 (IL-2) augments transcription of the IL-2 receptor gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(12):4230–4234. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.12.4230. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hara T., Fu S. M., Hansen J. A. Human T cell activation. II. A new activation pathway used by a major T cell population via a disulfide-bonded dimer of a 44 kilodalton polypeptide (9.3 antigen). J Exp Med. 1985 Jun 1;161(6):1513–1524. doi: 10.1084/jem.161.6.1513. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth J., Spear B., Raab S. S., Wilson D. B. Evidence for the role of class I and class II HLA antigens in the lytic function of a cloned line of human natural killer cells. J Immunol. 1985 Feb;134(2):728–735. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kornbluth J., Wilson D. B. Monoclonal antibodies directed against HLA molecules affect the lytic and proliferative behavior of a cloned line of human natural killer cells. Hum Immunol. 1984 Dec;11(4):239–247. doi: 10.1016/0198-8859(84)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Meuer S. C., Hussey R. E., Fabbi M., Fox D., Acuto O., Fitzgerald K. A., Hodgdon J. C., Protentis J. P., Schlossman S. F., Reinherz E. L. An alternative pathway of T-cell activation: a functional role for the 50 kd T11 sheep erythrocyte receptor protein. Cell. 1984 Apr;36(4):897–906. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(84)90039-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Moretta A., Pantaleo G., Lopez-Botet M., Moretta L. Involvement of T44 molecules in an antigen-independent pathway of T cell activation. Analysis of the correlations to the T cell antigen-receptor complex. J Exp Med. 1985 Sep 1;162(3):823–838. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.3.823. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Neckers L. M., Cossman J. Transferrin receptor induction in mitogen-stimulated human T lymphocytes is required for DNA synthesis and cell division and is regulated by interleukin 2. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1983 Jun;80(11):3494–3498. doi: 10.1073/pnas.80.11.3494. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nishizuka Y. The role of protein kinase C in cell surface signal transduction and tumour promotion. Nature. 1984 Apr 19;308(5961):693–698. doi: 10.1038/308693a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Osawa H., Herrmann T., Diamantstein T. Inhibition of IL 2-dependent proliferation of rat T lymphoblasts by the monoclonal antibody ART62 which reacts with MHC class 1 antigens. J Immunol. 1985 Jun;134(6):3901–3906. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Palacios R., Martinez-Maza O. Is the E receptor on human T lymphocytes a "negative signal receptor"? J Immunol. 1982 Dec;129(6):2479–2485. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Parham P., Barnstable C. J., Bodmer W. F. Use of a monoclonal antibody (W6/32) in structural studies of HLA-A,B,C, antigens. J Immunol. 1979 Jul;123(1):342–349. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rabin H., Hopkins R. F., 3rd, Ruscetti F. W., Neubauer R. H., Brown R. L., Kawakami T. G. Spontaneous release of a factor with properties of T cell growth factor from a continuous line of primate tumor T cells. J Immunol. 1981 Nov;127(5):1852–1856. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reed J. C., Tadmori W., Kamoun M., Koretzky G., Nowell P. C. Suppression of interleukin 2 receptor acquisition by monoclonal antibodies recognizing the 50 KD protein associated with the sheep erythrocyte receptor on human T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1631–1639. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Greene W. C. Direct demonstration of the identity of T cell growth factor binding protein and the Tac antigen. J Exp Med. 1983 Oct 1;158(4):1332–1337. doi: 10.1084/jem.158.4.1332. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robb R. J., Munck A., Smith K. A. T cell growth factor receptors. Quantitation, specificity, and biological relevance. J Exp Med. 1981 Nov 1;154(5):1455–1474. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.5.1455. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schreiber A. B., Schlessinger J., Edidin M. Interaction between major histocompatibility complex antigens and epidermal growth factor receptors on human cells. J Cell Biol. 1984 Feb;98(2):725–731. doi: 10.1083/jcb.98.2.725. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Snodgrass H. R., Wilson D. B., Bosma M. J. T lymphocytes specific for immunoglobulin allotype. I. Igh-1b-specific T cells demonstrated by suppression in vivo and cytotoxicity in vitro. J Exp Med. 1981 Aug 1;154(2):480–490. doi: 10.1084/jem.154.2.480. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Spear B. T., Kornbluth J., Strominger J. L., Wilson D. B. Evidence for a shared HLA-A intralocus determinant defined by monoclonal antibody 131. J Exp Med. 1985 Dec 1;162(6):1802–1810. doi: 10.1084/jem.162.6.1802. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sterkers G., Henin Y., Kalil J., Bagot M., Levy J. P. Influence of HLA class I- and class II-specific monoclonal antibodies on DR-restricted lymphoproliferative responses. I. Unseparated populations of effector cells. J Immunol. 1983 Dec;131(6):2735–2740. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Swierkosz J. E., Rock K., Marrack P., Kappler J. W. The role of H-2 linked genes in helper T-cell function. II. Isolation on antigen-pulsed macrophages of two separate populations of F1 helper T cells each specific for antigen and one set of parental H-2 products. J Exp Med. 1978 Feb 1;147(2):554–570. doi: 10.1084/jem.147.2.554. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tadmori W., Reed J. C., Nowell P. C., Kamoun M. Functional properties of the 50 kd protein associated with the E-receptor on human T lymphocytes: suppression of IL 2 production by anti-p50 monoclonal antibodies. J Immunol. 1985 Mar;134(3):1709–1716. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Taylor D. S., Kern J. A., Nowell P. C. IL 2 alone is mitogenic only for Tac-positive lymphocytes in human peripheral blood. J Immunol. 1986 Mar 1;136(5):1620–1624. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yang S. Y., Morishima Y., Collins N. H., Alton T., Pollack M. S., Yunis E. J., Dupont B. Comparison of one-dimensional IEF patterns for serologically detectable HLA-A and B allotypes. Immunogenetics. 1984;19(3):217–231. doi: 10.1007/BF00364765. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. H-2 compatability requirement for T-cell-mediated lysis of target cells infected with lymphocytic choriomeningitis virus. Different cytotoxic T-cell specificities are associated with structures coded for in H-2K or H-2D;. J Exp Med. 1975 Jun 1;141(6):1427–1436. doi: 10.1084/jem.141.6.1427. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Zinkernagel R. M., Doherty P. C. MHC-restricted cytotoxic T cells: studies on the biological role of polymorphic major transplantation antigens determining T-cell restriction-specificity, function, and responsiveness. Adv Immunol. 1979;27:51–177. doi: 10.1016/s0065-2776(08)60262-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- van Agthoven A., Terhorst C., Reinherz E., Schlossman S. Characterization of T cell surface glycoproteins T 1 and T 3 present on all human peripheral T lymphocytes and functionally mature thymocytes. Eur J Immunol. 1981 Jan;11(1):18–21. doi: 10.1002/eji.1830110105. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


