Abstract
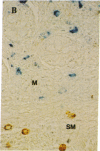
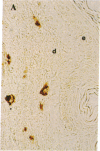
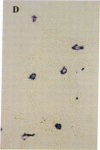
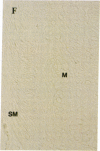
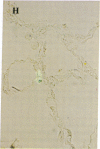
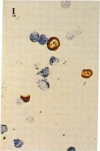
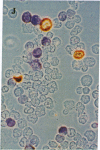
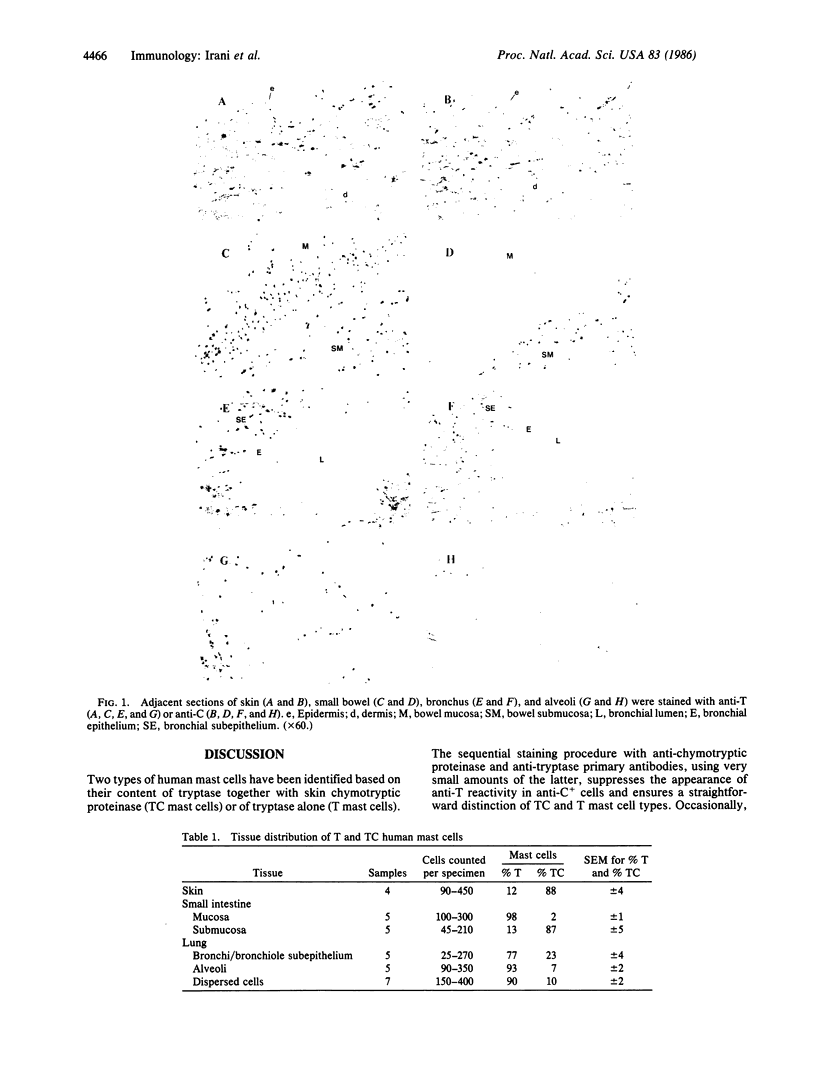
Two human mast cell types were identified by immunohistochemical techniques in skin, lung, and small intestine. One type contains the neutral proteases, tryptase and chymotryptic proteinase, and is termed the TC mast cell. The second type contains only tryptase and is termed the T mast cell. Both types are fixed better by Carnoy's fluid than by formalin. The percentage of mast cells accounted for by the T type was 12 in skin; 98 in mucosa and 13 in submucosa of small intestine; and 77 in bronchial/bronchiolar subepithelium, about 97 in bronchial/bronchiolar epithelium, and 93 in alveoli of lung. Dispersed lung cells contained 90% T mast cells. The mean area of TC mast cells (76 micron2) was slightly larger than that of T mast cells (66 micron2); however, there was such extensive overlap that individual mast cells belonging to different types could not be distinguished on the basis of size. The recognition of human mast cell types with distinct protease compositions suggests a higher level of complexity of human mast cell-mediated reactions than heretofore appreciated.
Full text
PDF



Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Barrett K. E., Metcalfe D. D. Mast cell heterogeneity: evidence and implications. J Clin Immunol. 1984 Jul;4(4):253–261. doi: 10.1007/BF00915292. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Befus A. D., Pearce F. L., Gauldie J., Horsewood P., Bienenstock J. Mucosal mast cells. I. Isolation and functional characteristics of rat intestinal mast cells. J Immunol. 1982 Jun;128(6):2475–2480. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Befus D., Goodacre R., Dyck N., Bienenstock J. Mast cell heterogeneity in man. I. Histologic studies of the intestine. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;76(3):232–236. doi: 10.1159/000233697. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bienenstock J., Befus A. D., Denburg J., Goodacre R., Pearce F., Shanahan F. Mast cell heterogeneity. Monogr Allergy. 1983;18:124–128. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Church M. K., Pao G. J., Holgate S. T. Characterization of histamine secretion from mechanically dispersed human lung mast cells: effects of anti-IgE, calcium ionophore A23187, compound 48/80, and basic polypeptides. J Immunol. 1982 Nov;129(5):2116–2121. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L. Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa. 2. Dye-binding and metachromatic properties. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(3):303–312. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.3.303. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Enerbäck L. Mast cells in rat gastrointestinal mucosa. I. Effects of fixation. Acta Pathol Microbiol Scand. 1966;66(3):289–302. doi: 10.1111/apm.1966.66.3.289. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox B., Bull T. B., Guz A. Mast cells in the human alveolar wall: an electronmicroscopic study. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Dec;34(12):1333–1342. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.12.1333. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fox C. C., Dvorak A. M., Peters S. P., Kagey-Sobotka A., Lichtenstein L. M. Isolation and characterization of human intestinal mucosal mast cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jul;135(1):483–491. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Haig D. M., McKee T. A., Jarrett E. E., Woodbury R., Miller H. R. Generation of mucosal mast cells is stimulated in vitro by factors derived from T cells of helminth-infected rats. Nature. 1982 Nov 11;300(5888):188–190. doi: 10.1038/300188a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Holgate S. T., Benyon R. C., Howarth P. H., Agius R., Hardy C., Robinson C., Durham S. R., Kay A. B., Church M. K. Relationship between mediator release from human lung mast cells in vitro and in vivo. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1985;77(1-2):47–56. doi: 10.1159/000233752. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Katz H. R., Stevens R. L., Austen K. F. Heterogeneity of mammalian mast cells differentiated in vivo and in vitro. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985 Aug;76(2 Pt 2):250–259. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(85)90638-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kido H., Fukusen N., Katunuma N. Chymotrypsin- and trypsin-type serine proteases in rat mast cells: properties and functions. Arch Biochem Biophys. 1985 Jun;239(2):436–443. doi: 10.1016/0003-9861(85)90709-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maier M., Spragg J., Schwartz L. B. Inactivation of human high molecular weight kininogen by human mast cell tryptase. J Immunol. 1983 May;130(5):2352–2356. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Metcalfe D. D., Lewis R. A., Silbert J. E., Rosenberg R. D., Wasserman S. I., Austen K. F. Isolation and characterization of heparin from human lung. J Clin Invest. 1979 Dec;64(6):1537–1543. doi: 10.1172/JCI109613. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Peters S. P., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Schulman E. S., Schleimer R. P., Hayes E. C., Rokach J., Adkinson N. F., Jr, Lichtenstein L. M. Arachidonic acid metabolism in purified human lung mast cells. J Immunol. 1984 Apr;132(4):1972–1979. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Reilly C. F., Tewksbury D. A., Schechter N. M., Travis J. Rapid conversion of angiotensin I to angiotensin II by neutrophil and mast cell proteinases. J Biol Chem. 1982 Aug 10;257(15):8619–8622. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ruitenberg E. J., Gustowska L., Elgersma A., Ruitenberg H. M. Effect of fixation on the light microscopical visualization of mast cells in the mucosa and connective tissue of the human duodenum. Int Arch Allergy Appl Immunol. 1982;67(3):233–238. doi: 10.1159/000233024. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schechter N. M., Fräki J. E., Geesin J. C., Lazarus G. S. Human skin chymotryptic proteinase. Isolation and relation to cathepsin g and rat mast cell proteinase I. J Biol Chem. 1983 Mar 10;258(5):2973–2978. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schulman E. S., Kagey-Sobotka A., MacGlashan D. W., Jr, Adkinson N. F., Jr, Peters S. P., Schleimer R. P., Lichtenstein L. M. Heterogeneity of human mast cells. J Immunol. 1983 Oct;131(4):1936–1941. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Bradford T. R., Littman B. H., Wintroub B. U. The fibrinogenolytic activity of purified tryptase from human lung mast cells. J Immunol. 1985 Oct;135(4):2762–2767. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Bradford T., Griffin J. H. The effect of tryptase from human mast cells on human prekallikrein. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1985 May 31;129(1):76–81. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(85)91405-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Foley J. V., Austen K. F., Soter N. A., Shepard R., Murphy G. F. Localization of tryptase to human cutaneous mast cells and keratinocytes by immunofluorescence and immunoperoxidase cytochemistry with monoclonal antitryptase antibody. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 1985 Aug;76(2 Pt 1):182–188. doi: 10.1016/0091-6749(85)90699-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Kawahara M. S., Hugli T. E., Vik D., Fearon D. T., Austen K. F. Generation of C3a anaphylatoxin from human C3 by human mast cell tryptase. J Immunol. 1983 Apr;130(4):1891–1895. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Lewis R. A., Austen K. F. Tryptase from human pulmonary mast cells. Purification and characterization. J Biol Chem. 1981 Nov 25;256(22):11939–11943. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B., Lewis R. A., Seldin D., Austen K. F. Acid hydrolases and tryptase from secretory granules of dispersed human lung mast cells. J Immunol. 1981 Apr;126(4):1290–1294. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schwartz L. B. Monoclonal antibodies against human mast cell tryptase demonstrate shared antigenic sites on subunits of tryptase and selective localization of the enzyme to mast cells. J Immunol. 1985 Jan;134(1):526–531. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Seldin D. C., Adelman S., Austen K. F., Stevens R. L., Hein A., Caulfield J. P., Woodbury R. G. Homology of the rat basophilic leukemia cell and the rat mucosal mast cell. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1985 Jun;82(11):3871–3875. doi: 10.1073/pnas.82.11.3871. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sredni B., Friedman M. M., Bland C. E., Metcalfe D. D. Ultrastructural, biochemical, and functional characteristics of histamine-containing cells cloned from mouse bone marrow: tentative identification as mucosal mast cells. J Immunol. 1983 Aug;131(2):915–922. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Strobel S., Miller H. R., Ferguson A. Human intestinal mucosal mast cells: evaluation of fixation and staining techniques. J Clin Pathol. 1981 Aug;34(8):851–858. doi: 10.1136/jcp.34.8.851. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintroub B. U., Kaempfer C. E., Schechter N. M., Proud D. A human lung mast cell chymotrypsin-like enzyme. Identification and partial characterization. J Clin Invest. 1986 Jan;77(1):196–201. doi: 10.1172/JCI112276. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wintroub B. U., Schechter N. B., Lazarus G. S., Kaempfer C. E., Schwartz L. B. Angiotensin I conversion by human and rat chymotryptic proteinases. J Invest Dermatol. 1984 Nov;83(5):336–339. doi: 10.1111/1523-1747.ep12264144. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Woodbury R. G., Gruzenski G. M., Lagunoff D. Immunofluorescent localization of a serine protease in rat small intestine. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Jun;75(6):2785–2789. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.6.2785. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yurt R. W., Leid R. W., Jr, Austen K. F. Native heparin from rat peritoneal mast cells. J Biol Chem. 1977 Jan 25;252(2):518–521. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]