Abstract
The binding site in native DNA for a murine monoclonal anti-DNA autoantibody was investigated by measurements of competitive binding of a series of synthetic helical oligonucleotides. The antibody bound to a (dG-dC)3 or (dG-dC)4 core in the center of a base-paired octadecanucleotide. Reactions of analogues containing modifications or substitutions at specific sites indicated that the antibody bound to portions of cytosine and guanine in the major groove, a limited region of the backbone, and the 2-amino group of one guanine in the minor groove. For these interactions to occur, the antibody combining site would straddle the backbone of one of the helical strands of DNA.
Full text
PDF



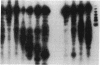
Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ali R., Dersimonian H., Stollar B. D. Binding of monoclonal anti-native DNA autoantibodies to DNA of varying size and conformation. Mol Immunol. 1985 Dec;22(12):1415–1422. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(85)90065-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrews B. S., Eisenberg R. A., Theofilopoulos A. N., Izui S., Wilson C. B., McConahey P. J., Murphy E. D., Roths J. B., Dixon F. J. Spontaneous murine lupus-like syndromes. Clinical and immunopathological manifestations in several strains. J Exp Med. 1978 Nov 1;148(5):1198–1215. doi: 10.1084/jem.148.5.1198. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Andrzejewski C., Jr, Rauch J., Lafer E., Stollar B. D., Schwartz R. S. Antigen-binding diversity and idiotypic cross-reactions among hybridoma autoantibodies to DNA. J Immunol. 1981 Jan;126(1):226–231. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Casperson G. F., Voss E. W., Jr Specificity of anti-DNA antibodies in SLE--II. Relative contribution of backbone, secondary structure and nucleotide sequence to DNA binding. Mol Immunol. 1983 Jun;20(6):581–588. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(83)90002-0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Davies D. R., Metzger H. Structural basis of antibody function. Annu Rev Immunol. 1983;1:87–117. doi: 10.1146/annurev.iy.01.040183.000511. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- ERLANGER B. F., BEISER S. M. ANTIBODIES SPECIFIC FOR RIBONUCLEOSIDES AND RIBONUCLEOTIDES AND THEIR REACTION WITH DNA. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1964 Jul;52:68–74. doi: 10.1073/pnas.52.1.68. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Eilat D. Monoclonal autoantibodies: an approach to studying autoimmune disease. Mol Immunol. 1982 Jul;19(7):943–955. doi: 10.1016/0161-5890(82)90360-1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feldmann R. J., Bing D. H., Furie B. C., Furie B. Interactive computer surface graphics approach to study of the active site of bovine trypsin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1978 Nov;75(11):5409–5412. doi: 10.1073/pnas.75.11.5409. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hahn B. H., Ebling F. M. Suppression of murine lupus nephritis by administration of an anti-idiotypic antibody to anti-DNA. J Immunol. 1984 Jan;132(1):187–190. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Ikuta S., Chattopadhyaya R., Dickerson R. E. Reverse-phase polystyrene column for purification and analysis of DNA oligomers. Anal Chem. 1984 Oct;56(12):2253–2256. doi: 10.1021/ac00276a063. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lacour F., Nahon-Merlin E., Michelson M. Immunological recognition of polynucleotide structure. Curr Top Microbiol Immunol. 1973;62:1–39. doi: 10.1007/978-3-642-65772-6_1. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lafer E. M., Rauch J., Andrzejewski C., Jr, Mudd D., Furie B., Furie B., Schwartz R. S., Stollar B. D. Polyspecific monoclonal lupus autoantibodies reactive with both polynucleotides and phospholipids. J Exp Med. 1981 Apr 1;153(4):897–909. doi: 10.1084/jem.153.4.897. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maxam A. M., Gilbert W. Sequencing end-labeled DNA with base-specific chemical cleavages. Methods Enzymol. 1980;65(1):499–560. doi: 10.1016/s0076-6879(80)65059-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munns T. W., Liszewski M. K. Antibodies specific for modified nucleosides: an immunochemical approach for the isolation and characterization of nucleic acids. Prog Nucleic Acid Res Mol Biol. 1980;24:109–165. doi: 10.1016/s0079-6603(08)60673-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Munns T. W., Liszewski M. K., Hahn B. H. Antibody-nucleic acid complexes. Antigenic domains within nucleosides as defined by solid-phase immunoassay. Biochemistry. 1984 Jun 19;23(13):2958–2964. doi: 10.1021/bi00308a017. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Noble S. A., Fisher E. F., Caruthers M. H. Methylphosphonates as probes of protein-nucleic acid interactions. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Apr 11;12(7):3387–3404. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.7.3387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Pabo C. O., Sauer R. T. Protein-DNA recognition. Annu Rev Biochem. 1984;53:293–321. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.53.070184.001453. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Potter B. V., Eckstein F. Cleavage of phosphorothioate-substituted DNA by restriction endonucleases. J Biol Chem. 1984 Nov 25;259(22):14243–14248. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stec W. J., Zon G., Uznanski B. Reversed-phase high-performance liquid chromatographic separation of diastereomeric phosphorothioate analogues of oligodeoxyribonucleotides and other backbone-modified congeners of DNA. J Chromatogr. 1985 Jun 19;326:263–280. doi: 10.1016/s0021-9673(01)87452-5. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. Antibodies to DNA. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1986;20(1):1–36. doi: 10.3109/10409238609115899. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D., Papalian M. Secondary structure in denatured DNA is responsible for its reaction with antinative DNA antibodies of systemic lupus erythematosus sera. J Clin Invest. 1980 Aug;66(2):210–219. doi: 10.1172/JCI109846. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Stollar B. D. The specificity and applications of antibodies to helical nucleic acids. CRC Crit Rev Biochem. 1975 May;3(1):45–69. doi: 10.3109/10409237509102552. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takeda Y., Ohlendorf D. H., Anderson W. F., Matthews B. W. DNA-binding proteins. Science. 1983 Sep 9;221(4615):1020–1026. doi: 10.1126/science.6308768. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tron F., Charron D., Bach J. F., Talal N. Establishment and characterization of a murine hybridoma secreting monoclonal anti-DNA autoantibody. J Immunol. 1980 Dec;125(6):2805–2809. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]